+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7jqc | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
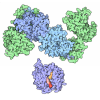
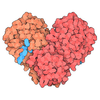
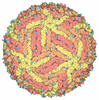
| Title | SARS-CoV-2 Nsp1, CrPV IRES and rabbit 40S ribosome complex | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | RIBOSOME/VIRAL PROTEIN / cryo-EM / single particle / protein expression inhibition / RIBOSOME-VIRAL PROTEIN complex | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of RNA splicing / positive regulation of ubiquitin-protein transferase activity / rRNA modification in the nucleus and cytosol / Formation of the ternary complex, and subsequently, the 43S complex / laminin receptor activity / Ribosomal scanning and start codon recognition / Translation initiation complex formation / fibroblast growth factor binding / SARS-CoV-1 modulates host translation machinery / Peptide chain elongation ...negative regulation of RNA splicing / positive regulation of ubiquitin-protein transferase activity / rRNA modification in the nucleus and cytosol / Formation of the ternary complex, and subsequently, the 43S complex / laminin receptor activity / Ribosomal scanning and start codon recognition / Translation initiation complex formation / fibroblast growth factor binding / SARS-CoV-1 modulates host translation machinery / Peptide chain elongation / Selenocysteine synthesis / Formation of a pool of free 40S subunits / endonucleolytic cleavage to generate mature 3'-end of SSU-rRNA from (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / Eukaryotic Translation Termination / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / Response of EIF2AK4 (GCN2) to amino acid deficiency / ubiquitin ligase inhibitor activity / Viral mRNA Translation / 90S preribosome / positive regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) independent of the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / GTP hydrolysis and joining of the 60S ribosomal subunit / L13a-mediated translational silencing of Ceruloplasmin expression / Major pathway of rRNA processing in the nucleolus and cytosol / phagocytic cup / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) enhanced by the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / Protein methylation / endonucleolytic cleavage in ITS1 to separate SSU-rRNA from 5.8S rRNA and LSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / laminin binding / rough endoplasmic reticulum / ribosomal small subunit export from nucleus / translation regulator activity / Maturation of protein E / gastrulation / Maturation of protein E / ER Quality Control Compartment (ERQC) / Myoclonic epilepsy of Lafora / MDM2/MDM4 family protein binding / FLT3 signaling by CBL mutants / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD Domain Mutants / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex / Prevention of phagosomal-lysosomal fusion / Alpha-protein kinase 1 signaling pathway / Glycogen synthesis / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / Endosomal Sorting Complex Required For Transport (ESCRT) / Membrane binding and targetting of GAG proteins / Negative regulation of FLT3 / Regulation of TBK1, IKKε (IKBKE)-mediated activation of IRF3, IRF7 / PTK6 Regulates RTKs and Their Effectors AKT1 and DOK1 / Regulation of TBK1, IKKε-mediated activation of IRF3, IRF7 upon TLR3 ligation / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / NOTCH2 Activation and Transmission of Signal to the Nucleus / TICAM1,TRAF6-dependent induction of TAK1 complex / TICAM1-dependent activation of IRF3/IRF7 / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Cyclin B / Regulation of FZD by ubiquitination / Downregulation of ERBB4 signaling / APC-Cdc20 mediated degradation of Nek2A / p75NTR recruits signalling complexes / cytosolic ribosome / class I DNA-(apurinic or apyrimidinic site) endonuclease activity / InlA-mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cells / TRAF6 mediated IRF7 activation in TLR7/8 or 9 signaling / Regulation of pyruvate metabolism / NF-kB is activated and signals survival / TRAF6-mediated induction of TAK1 complex within TLR4 complex / Downregulation of ERBB2:ERBB3 signaling / Regulation of innate immune responses to cytosolic DNA / Pexophagy / NRIF signals cell death from the nucleus / Activated NOTCH1 Transmits Signal to the Nucleus / Regulation of PTEN localization / VLDLR internalisation and degradation / Synthesis of active ubiquitin: roles of E1 and E2 enzymes / DNA-(apurinic or apyrimidinic site) lyase / TICAM1, RIP1-mediated IKK complex recruitment / Regulation of BACH1 activity / Translesion synthesis by REV1 / MAP3K8 (TPL2)-dependent MAPK1/3 activation / Degradation of CDH1 / Translesion synthesis by POLK / InlB-mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cell / JNK (c-Jun kinases) phosphorylation and activation mediated by activated human TAK1 / Activation of IRF3, IRF7 mediated by TBK1, IKKε (IKBKE) / Josephin domain DUBs / Downregulation of TGF-beta receptor signaling / Translesion synthesis by POLI / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in GG-NER / IKK complex recruitment mediated by RIP1 / Degradation of CRY and PER proteins / Regulation of activated PAK-2p34 by proteasome mediated degradation / PINK1-PRKN Mediated Mitophagy / TGF-beta receptor signaling in EMT (epithelial to mesenchymal transition) / positive regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway / TNFR1-induced NF-kappa-B signaling pathway / maturation of SSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / Autodegradation of Cdh1 by Cdh1:APC/C / TCF dependent signaling in response to WNT Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |    Cricket paralysis virus Cricket paralysis virus | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Yuan, S. / Xiong, Y. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2020 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2020Title: Nonstructural Protein 1 of SARS-CoV-2 Is a Potent Pathogenicity Factor Redirecting Host Protein Synthesis Machinery toward Viral RNA. Authors: Shuai Yuan / Lei Peng / Jonathan J Park / Yingxia Hu / Swapnil C Devarkar / Matthew B Dong / Qi Shen / Shenping Wu / Sidi Chen / Ivan B Lomakin / Yong Xiong /  Abstract: The causative virus of the COVID-19 pandemic, SARS-CoV-2, uses its nonstructural protein 1 (Nsp1) to suppress cellular, but not viral, protein synthesis through yet unknown mechanisms. We show here ...The causative virus of the COVID-19 pandemic, SARS-CoV-2, uses its nonstructural protein 1 (Nsp1) to suppress cellular, but not viral, protein synthesis through yet unknown mechanisms. We show here that among all viral proteins, Nsp1 has the largest impact on host viability in the cells of human lung origin. Differential expression analysis of mRNA-seq data revealed that Nsp1 broadly alters the cellular transcriptome. Our cryo-EM structure of the Nsp1-40S ribosome complex shows that Nsp1 inhibits translation by plugging the mRNA entry channel of the 40S. We also determined the structure of the 48S preinitiation complex formed by Nsp1, 40S, and the cricket paralysis virus internal ribosome entry site (IRES) RNA, which shows that it is nonfunctional because of the incorrect position of the mRNA 3' region. Our results elucidate the mechanism of host translation inhibition by SARS-CoV-2 and advance understanding of the impacts from a major pathogenicity factor of SARS-CoV-2. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7jqc.cif.gz 7jqc.cif.gz | 1.8 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7jqc.ent.gz pdb7jqc.ent.gz | 1.4 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7jqc.json.gz 7jqc.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jq/7jqc https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jq/7jqc ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jq/7jqc ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jq/7jqc | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  22433MC  7jqbC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-RNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules Ai
| #1: RNA chain | Mass: 602777.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #28: RNA chain | Mass: 61462.207 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Cricket paralysis virus / References: GenBank: 8895506 Cricket paralysis virus / References: GenBank: 8895506 |
+Protein , 23 types, 23 molecules aCDdEfGgHhIJKLNQSTVOPYe
-40S ribosomal protein ... , 5 types, 5 molecules BbWZM
| #3: Protein | Mass: 32958.016 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #4: Protein | Mass: 13047.532 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #25: Protein | Mass: 9124.389 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #26: Protein | Mass: 15107.924 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #29: Protein | Mass: 29658.920 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-Uncharacterized ... , 4 types, 4 molecules RUXc
| #20: Protein | Mass: 16477.377 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #23: Protein | Mass: 16106.640 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #32: Protein | Mass: 18133.984 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #34: Protein | Mass: 15844.666 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-Protein/peptide , 1 types, 1 molecules F
| #27: Protein/peptide | Mass: 4100.354 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: UNP residues 145-180 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: rep, 1a-1b Production host:  References: UniProt: P0DTD1 |
|---|
-Details
| Has protein modification | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: unspecified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: dev_3339: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 48689 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj