[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7c97: Cryo-EM structure of an Escherichia coli RNAP-promoter open compl... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7c97 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
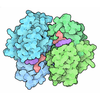
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of an Escherichia coli RNAP-promoter open complex (RPo) with SspA | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSFERASE/DNA / Stringent starvation protein A / RNA polymerase / promoter escape / zinc binding domain / GENE REGULATION / TRANSFERASE-DNA complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationsigma factor antagonist complex / response to starvation / RNA polymerase complex / submerged biofilm formation / cellular response to cell envelope stress / regulation of DNA-templated transcription initiation / response to stress / glutathione transferase / sigma factor activity / bacterial-type flagellum assembly ...sigma factor antagonist complex / response to starvation / RNA polymerase complex / submerged biofilm formation / cellular response to cell envelope stress / regulation of DNA-templated transcription initiation / response to stress / glutathione transferase / sigma factor activity / bacterial-type flagellum assembly / bacterial-type RNA polymerase core enzyme binding / cytosolic DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / glutathione transferase activity / bacterial-type flagellum-dependent cell motility / nitrate assimilation / glutathione metabolic process / regulation of DNA-templated transcription elongation / transcription elongation factor complex / transcription antitermination / DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / cell motility / DNA-templated transcription initiation / ribonucleoside binding / DNA-directed RNA polymerase / DNA-directed RNA polymerase activity / response to heat / protein-containing complex assembly / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / protein dimerization activity / transcription cis-regulatory region binding / response to antibiotic / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / regulation of DNA-templated transcription / DNA-templated transcription / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription / magnesium ion binding / DNA binding / zinc ion binding / metal ion binding / membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.68 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Lin, W. / Feng, Y. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2020 Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2020Title: Structural basis for transcription inhibition by E. coli SspA. Authors: Fulin Wang / Jing Shi / Dingwei He / Bei Tong / Chao Zhang / Aijia Wen / Yu Zhang / Yu Feng / Wei Lin /  Abstract: Stringent starvation protein A (SspA) is an RNA polymerase (RNAP)-associated protein involved in nucleotide metabolism, acid tolerance and virulence of bacteria. Despite extensive biochemical and ...Stringent starvation protein A (SspA) is an RNA polymerase (RNAP)-associated protein involved in nucleotide metabolism, acid tolerance and virulence of bacteria. Despite extensive biochemical and genetic analyses, the precise regulatory role of SspA in transcription is still unknown, in part, because of a lack of structural information for bacterial RNAP in complex with SspA. Here, we report a 3.68 Å cryo-EM structure of an Escherichia coli RNAP-promoter open complex (RPo) with SspA. Unexpectedly, the structure reveals that SspA binds to the E. coli σ70-RNAP holoenzyme as a homodimer, interacting with σ70 region 4 and the zinc binding domain of EcoRNAP β' subunit simultaneously. Results from fluorescent polarization assays indicate the specific interactions between SspA and σ70 region 4 confer its σ selectivity, thereby avoiding its interactions with σs or other alternative σ factors. In addition, results from in vitro transcription assays verify that SspA inhibits transcription probably through suppressing promoter escape. Together, the results here provide a foundation for understanding the unique physiological function of SspA in transcription regulation in bacteria. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7c97.cif.gz 7c97.cif.gz | 801.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7c97.ent.gz pdb7c97.ent.gz | 636.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7c97.json.gz 7c97.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/c9/7c97 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/c9/7c97 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/c9/7c97 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/c9/7c97 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  30307MC  7chwC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 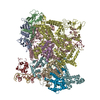
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules HG
| #1: DNA chain | Mass: 19671.666 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically Details: Nontemplate strand DNA of transcription initiation scaffold(RPo) Source: (synth.)  |
|---|---|
| #8: DNA chain | Mass: 19159.285 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically Details: Template strand DNA of transcription initiation scaffold(RPo) Source: (synth.)  |
-Protein , 2 types, 3 molecules IJF
| #2: Protein | Mass: 24332.885 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   References: UniProt: H4IXP2, UniProt: P0ACA3*PLUS, glutathione transferase #7: Protein | | Mass: 70352.242 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|
-DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit ... , 4 types, 6 molecules KABCDE
| #3: Protein | Mass: 36558.680 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   References: UniProt: F4VJT6, UniProt: P0A7Z4*PLUS, DNA-directed RNA polymerase #4: Protein | | Mass: 150804.922 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: D516V Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: K12 Gene: rpoB, groN, nitB, rif, ron, stl, stv, tabD, b3987, JW3950 Production host:  #5: Protein | | Mass: 155366.781 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   References: UniProt: M9GTE2, UniProt: P0A8T7*PLUS, DNA-directed RNA polymerase #6: Protein | | Mass: 10249.547 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   References: UniProt: T9C803, UniProt: P0A800*PLUS, DNA-directed RNA polymerase |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 3 molecules 


| #9: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / |
|---|---|
| #10: Chemical |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Escherichia coli RNAP-promoter open complex (RPo) with stringent starvation protein A(SspA) Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#8 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.55 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.9 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 59 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.68 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 60145 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj