+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-7939 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Integrin alpha-v beta-8 in complex with the Fabs 8B8 and 68 | |||||||||||||||||||||
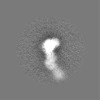
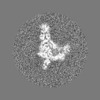
 Map data Map data | Headpiece map, 4.8 A resolution, sharpened with a B-factor of -144 | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | GLYCOPROTEIN / MEMBRANE PROTEIN / ADHESION / FAB | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationganglioside metabolic process / Langerhans cell differentiation / integrin alphav-beta8 complex / integrin alphav-beta6 complex / transforming growth factor beta production / negative regulation of entry of bacterium into host cell / integrin alphav-beta5 complex / opsonin binding / integrin alphav-beta1 complex / Cross-presentation of particulate exogenous antigens (phagosomes) ...ganglioside metabolic process / Langerhans cell differentiation / integrin alphav-beta8 complex / integrin alphav-beta6 complex / transforming growth factor beta production / negative regulation of entry of bacterium into host cell / integrin alphav-beta5 complex / opsonin binding / integrin alphav-beta1 complex / Cross-presentation of particulate exogenous antigens (phagosomes) / extracellular matrix protein binding / Laminin interactions / placenta blood vessel development / integrin alphav-beta3 complex / negative regulation of lipoprotein metabolic process / alphav-beta3 integrin-PKCalpha complex / entry into host cell by a symbiont-containing vacuole / alphav-beta3 integrin-HMGB1 complex / negative regulation of lipid transport / hard palate development / regulation of phagocytosis / Elastic fibre formation / alphav-beta3 integrin-IGF-1-IGF1R complex / transforming growth factor beta binding / positive regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction / filopodium membrane / extracellular matrix binding / cartilage development / apolipoprotein A-I-mediated signaling pathway / negative regulation of low-density lipoprotein particle clearance / wound healing, spreading of epidermal cells / apoptotic cell clearance / integrin complex / heterotypic cell-cell adhesion / Molecules associated with elastic fibres / negative chemotaxis / cell adhesion mediated by integrin / Mechanical load activates signaling by PIEZO1 and integrins in osteocytes / Syndecan interactions / positive regulation of osteoblast proliferation / microvillus membrane / cell-substrate adhesion / endodermal cell differentiation / PECAM1 interactions / TGF-beta receptor signaling activates SMADs / fibronectin binding / lamellipodium membrane / positive regulation of intracellular signal transduction / negative regulation of macrophage derived foam cell differentiation / negative regulation of lipid storage / ECM proteoglycans / Integrin cell surface interactions / vasculogenesis / specific granule membrane / voltage-gated calcium channel activity / coreceptor activity / phagocytic vesicle / ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand / substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading / positive regulation of cell adhesion / transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway / Turbulent (oscillatory, disturbed) flow shear stress activates signaling by PIEZO1 and integrins in endothelial cells / protein kinase C binding / cell-matrix adhesion / integrin-mediated signaling pathway / Signal transduction by L1 / negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / cell-cell adhesion / VEGFA-VEGFR2 Pathway / calcium ion transmembrane transport / integrin binding / response to virus / ruffle membrane / positive regulation of angiogenesis / cell migration / positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / virus receptor activity / protease binding / angiogenesis / cell adhesion / positive regulation of cell migration / immune response / negative regulation of gene expression / external side of plasma membrane / focal adhesion / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / Neutrophil degranulation / symbiont entry into host cell / positive regulation of gene expression / cell surface / extracellular exosome / metal ion binding / membrane / plasma membrane / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.8 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Cormier A / Campbell MG | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 6 items United States, 6 items
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2018 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2018Title: Cryo-EM structure of the αvβ8 integrin reveals a mechanism for stabilizing integrin extension. Authors: Anthony Cormier / Melody G Campbell / Saburo Ito / Shenping Wu / Jianlong Lou / James Marks / Jody L Baron / Stephen L Nishimura / Yifan Cheng /  Abstract: Integrins are conformationally flexible cell surface receptors that survey the extracellular environment for their cognate ligands. Interactions with ligands are thought to be linked to global ...Integrins are conformationally flexible cell surface receptors that survey the extracellular environment for their cognate ligands. Interactions with ligands are thought to be linked to global structural rearrangements involving transitions between bent, extended-closed and extended-open forms. Thus far, structural details are lacking for integrins in the extended conformations due to extensive flexibility between the headpiece and legs in this conformation. Here we present single-particle electron cryomicroscopy structures of human αvβ8 integrin in the extended-closed conformation, which has been considered to be a low-affinity intermediate. Our structures show the headpiece rotating about a flexible αv knee, suggesting a ligand surveillance mechanism for integrins in their extended-closed form. Our model predicts that the extended conformation is mainly stabilized by an interface formed between flexible loops in the upper and lower domains of the αv leg. Confirming these findings with the αvβ3 integrin suggests that our model of stabilizing the extended-closed conformation is generalizable to other integrins. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_7939.map.gz emd_7939.map.gz | 2.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-7939-v30.xml emd-7939-v30.xml emd-7939.xml emd-7939.xml | 53.6 KB 53.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_7939.png emd_7939.png | 104.3 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-7939.cif.gz emd-7939.cif.gz | 10.3 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_7939_additional_1.map.gz emd_7939_additional_1.map.gz emd_7939_additional_10.map.gz emd_7939_additional_10.map.gz emd_7939_additional_11.map.gz emd_7939_additional_11.map.gz emd_7939_additional_2.map.gz emd_7939_additional_2.map.gz emd_7939_additional_3.map.gz emd_7939_additional_3.map.gz emd_7939_additional_4.map.gz emd_7939_additional_4.map.gz emd_7939_additional_5.map.gz emd_7939_additional_5.map.gz emd_7939_additional_6.map.gz emd_7939_additional_6.map.gz emd_7939_additional_7.map.gz emd_7939_additional_7.map.gz emd_7939_additional_8.map.gz emd_7939_additional_8.map.gz emd_7939_additional_9.map.gz emd_7939_additional_9.map.gz | 59.2 MB 12.1 MB 12.1 MB 59.4 MB 59.3 MB 59.2 MB 2.7 MB 56.6 MB 2.4 MB 14.6 MB 14.6 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7939 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7939 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7939 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7939 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6djpMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_7939.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_7939.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Headpiece map, 4.8 A resolution, sharpened with a B-factor of -144 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
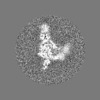
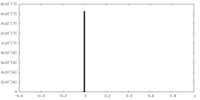
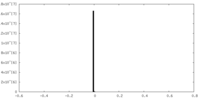
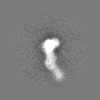
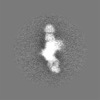
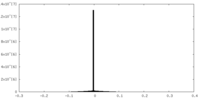
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.67 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
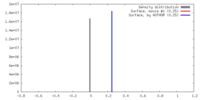
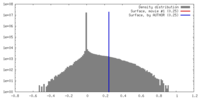
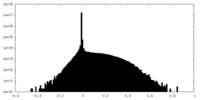
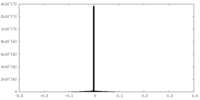
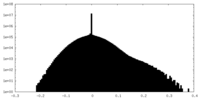
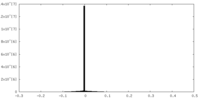
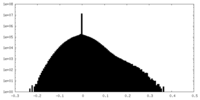
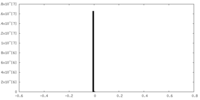
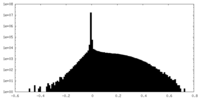
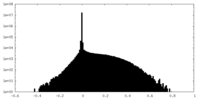
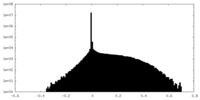
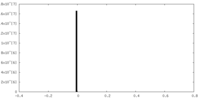
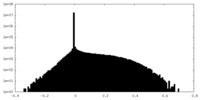
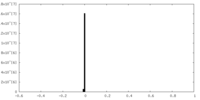
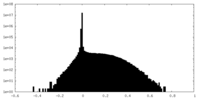
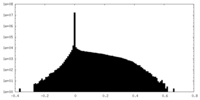
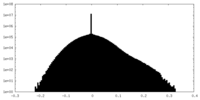
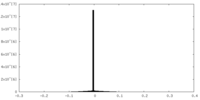
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
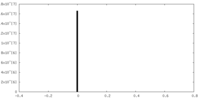
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
+Additional map: Conformation V, sharpened with a B-factor of -300
+Additional map: Half-map 01 for headpiece map
+Additional map: Half-map 02 for headpiece map
+Additional map: Conformation I, sharpened with a B-factor of -300
+Additional map: Conformation II, sharpened with a B-factor of -300
+Additional map: Conformation III, sharpened with a B-factor of -300
+Additional map: Conformation IV, sharpened with a B-factor of -300
+Additional map: Conformation VI, sharpened with a B-factor of -300
+Additional map: Full map, 6.4 A resolution, sharpened with a B-factor of -146
+Additional map: Half-map 01 for full map
+Additional map: Half-map 02 for full map
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Alpha-v Beta-8 Integrin in complex with the Fabs 68 and 8B8
| Entire | Name: Alpha-v Beta-8 Integrin in complex with the Fabs 68 and 8B8 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Alpha-v Beta-8 Integrin in complex with the Fabs 68 and 8B8
| Supramolecule | Name: Alpha-v Beta-8 Integrin in complex with the Fabs 68 and 8B8 type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#6 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 312 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Integrin alpha-v
| Macromolecule | Name: Integrin alpha-v / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 106.758266 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: FNLDVDSPAE YSGPEGSYFG FAVDFFVPSA SSRMFLLVGA PKANTTQPGI VEGGQVLKCD WSSTRRCQPI EFDATGNRDY AKDDPLEFK SHQWFGASVR SKQDKILACA PLYHWRTEMK QEREPVGTCF LQDGTKTVEY APCRSQDIDA DGQGFCQGGF S IDFTKADR ...String: FNLDVDSPAE YSGPEGSYFG FAVDFFVPSA SSRMFLLVGA PKANTTQPGI VEGGQVLKCD WSSTRRCQPI EFDATGNRDY AKDDPLEFK SHQWFGASVR SKQDKILACA PLYHWRTEMK QEREPVGTCF LQDGTKTVEY APCRSQDIDA DGQGFCQGGF S IDFTKADR VLLGGPGSFY WQGQLISDQV AEIVSKYDPN VYSIKYNNQL ATRTAQAIFD DSYLGYSVAV GDFNGDGIDD FV SGVPRAA RTLGMVYIYD GKNMSSLYNF TGEQMAAYFG FSVAATDING DDYADVFIGA PLFMDRGSDG KLQEVGQVSV SLQ RASGDF QTTKLNGFEV FARFGSAIAP LGDLDQDGFN DIAIAAPYGG EDKKGIVYIF NGRSTGLNAV PSQILEGQWA ARSM PPSFG YSMKGATDID KNGYPDLIVG AFGVDRAILY RARPVITVNA GLEVYPSILN QDNKTCSLPG TALKVSCFNV RFCLK ADGK GVLPRKLNFQ VELLLDKLKQ KGAIRRALFL YSRSPSHSKN MTISRGGLMQ CEELIAYLRD ESEFRDKLTP ITIFME YRL DYRTAADTTG LQPILNQFTP ANISRQAHIL LDCGEDNVCK PKLEVSVDSD QKKIYIGDDN PLTLIVKAQN QGEGAYE AE LIVSIPLQAD FIGVVRNNEA LARLSCAFKT ENQTRQVVCD LGNPMKAGTQ LLAGLRFSVH QQSEMDTSVK FDLQIQSS N LFDKVSPVVS HKVDLAVLAA VEIRGVSSPD HVFLPIPNWE HKENPETEED VGPVVQHIYE LRNNGPSSFS KAMLHLQWP YKYNNNTLLY ILHYDIDGPM NCTSDMEINP LRIKISSLQT TEKNDTVAGQ GERDHLITKR DLALSEGDIH TLGCGVAQCL KIVCQVGRL DRGKSAILYV KSLLWTETFM NKENQNHSYS LKSSASFNVI EFPYKNLPIE DITNSTLVTT NVTWGIQPAP M PVPVW UniProtKB: Integrin alpha-V |
-Macromolecule #2: Integrin beta-8
| Macromolecule | Name: Integrin beta-8 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 70.837234 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: EDNRCASSNA ASCARCLALG PECGWCVQED FISGGSRSER CDIVSNLISK GCSVDSIEYP SVHVIIPTEN EINTQVTPGE VSIQLRPGA EANFMLKVHP LKKYPVDLYY LVDVSASMHN NIEKLNSVGN DLSRKMAFFS RDFRLGFGSY VDKTVSPYIS I HPERIHNQ ...String: EDNRCASSNA ASCARCLALG PECGWCVQED FISGGSRSER CDIVSNLISK GCSVDSIEYP SVHVIIPTEN EINTQVTPGE VSIQLRPGA EANFMLKVHP LKKYPVDLYY LVDVSASMHN NIEKLNSVGN DLSRKMAFFS RDFRLGFGSY VDKTVSPYIS I HPERIHNQ CSDYNLDCMP PHGYIHVLSL TENITEFEKA VHRQKISGNI DTPEGGFDAM LQAAVCESHI GWRKEAKRLL LV MTDQTSH LALDSKLAGI VVPNDGNCHL KNNVYVKSTT MEHPSLGQLS EKLIDNNINV IFAVQGKQFH WYKDLLPLLP GTI AGEIES KAANLNNLVV EAYQKLISEV KVQVENQVQG IYFNITAICP DGSRKPGMEG CRNVTSNDEV LFNVTVTMKK CDVT GGKNY AIIKPIGFNE TAKIHIHRNC SCQCEDNRGP KGKCVDETFL DSKCFQCDEN KCHFDEDQFS SESCKSHKDQ PVCSG RGVC VCGKCSCHKI KLGKVYGKYC EKDDFSCPYH HGNLCAGHGE CEAGRCQCFS GWEGDRCQCP SAAAQHCVNS KGQVCS GRG TCVCGRCECT DPRSIGRFCE HCPTCYTACK ENWNCMQCLH PHNLSQAILD QCKTSCALME QQHYVDQTSE CFSSPS UniProtKB: Integrin beta-8 |
-Macromolecule #3: 8B8 heavy chain Fab
| Macromolecule | Name: 8B8 heavy chain Fab / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 23.314826 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: EVQLVESGPG LVKPSQSLSL TCSVTGYYIT SSYYWNWIRQ FPGNELEWMG YISYDGSNSY NPSLKNRISI TRDTSKNQFF LKLNSVTTE DIATYFCVRE DYDSFDYWGQ GTTLTVSSAK TTAPSVYPLA PVCGDTTGSS VTLGCLVKGY FPEPVTLTWN S GSLSSGVH ...String: EVQLVESGPG LVKPSQSLSL TCSVTGYYIT SSYYWNWIRQ FPGNELEWMG YISYDGSNSY NPSLKNRISI TRDTSKNQFF LKLNSVTTE DIATYFCVRE DYDSFDYWGQ GTTLTVSSAK TTAPSVYPLA PVCGDTTGSS VTLGCLVKGY FPEPVTLTWN S GSLSSGVH TFPAVLQSDL YTLSSSVTVT SSTWPSQSIT CNVAHPASST KVDKK |
-Macromolecule #4: 8B8 light chain Fab
| Macromolecule | Name: 8B8 light chain Fab / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 23.241596 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: EIVLTQSPAI MSAFPGEKVT MTCSASSSVS YIHWYQQKSG TSPKRWIYDT SKLASGVPAR FSGSGSGTSY SLTISSMEAE DAATYYCHQ WTSNPATFGG GTKLEIKAAD AAPTVSIFPP SSEQLTSGGA SVVCFLNNFY PKDINVKWKI DGSERQNGVL N SWTDQDSK ...String: EIVLTQSPAI MSAFPGEKVT MTCSASSSVS YIHWYQQKSG TSPKRWIYDT SKLASGVPAR FSGSGSGTSY SLTISSMEAE DAATYYCHQ WTSNPATFGG GTKLEIKAAD AAPTVSIFPP SSEQLTSGGA SVVCFLNNFY PKDINVKWKI DGSERQNGVL N SWTDQDSK DSTYSMSSTL TLTKDEYERH NSYTCEATHK TSTSPIVKSF NRNEC |
-Macromolecule #5: 68 heavy chain Fab
| Macromolecule | Name: 68 heavy chain Fab / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 22.680303 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: EVQLQQSGAE LMKPGASVKI SCKATGYTFS TYWIEWIKQR PGHGLEWIGD ILPGSGTTNY NEKFKGRATV TADRSSNTAY MQLSSLTSE DSAVYYCARW GWDSYWGQGT LVTVSSASTK GPSVFPLAPS SKSTSGGTAA LGCLVKDYFP EPVTVSWNSG A LTSGVHTF ...String: EVQLQQSGAE LMKPGASVKI SCKATGYTFS TYWIEWIKQR PGHGLEWIGD ILPGSGTTNY NEKFKGRATV TADRSSNTAY MQLSSLTSE DSAVYYCARW GWDSYWGQGT LVTVSSASTK GPSVFPLAPS SKSTSGGTAA LGCLVKDYFP EPVTVSWNSG A LTSGVHTF PAVLQSSGLY SLSSVVTVPS SSLGTQTYIC NVNHKPSNTK VDKK |
-Macromolecule #6: 68 light chain Fab
| Macromolecule | Name: 68 light chain Fab / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 23.420795 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: DIEMTQSPSS LSASLGDRVT ISCSASQGIS NYLNWYQQKP DGTVKLLIYY TSSLHSGVPS RFSGSGSGTD YSLTISNLEP EDIATYYCQ QYSELPYTFG GGTKLEIKRT VAAPSVFIFP PSDEQLKSGT ASVVCLLNNF YPREAKVQWK VDNALQSGNS Q ESVTEQDS ...String: DIEMTQSPSS LSASLGDRVT ISCSASQGIS NYLNWYQQKP DGTVKLLIYY TSSLHSGVPS RFSGSGSGTD YSLTISNLEP EDIATYYCQ QYSELPYTFG GGTKLEIKRT VAAPSVFIFP PSDEQLKSGT ASVVCLLNNF YPREAKVQWK VDNALQSGNS Q ESVTEQDS KDSTYSLSST LTLSKADYEK HKVYACEVTH QGLSSPVTKS FNRGEC |
-Macromolecule #10: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 10 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 6.8 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 400 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 60 sec. |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 293 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI POLARA 300 |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 713 / Average exposure time: 6.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 41.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



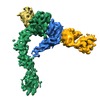



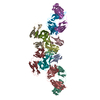

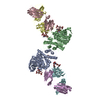











 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)