+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-7445 | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
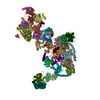
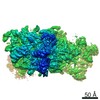
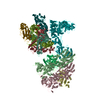
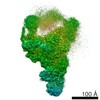
| Title | Yeast nucleolar pre-60S ribosomal subunit (state 3) | ||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | LSU processome state 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Pre-60S / ribosome biogenesis / LSU processome / ribosome | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationsnoRNA release from pre-rRNA / exonucleolytic trimming to generate mature 5'-end of 5.8S rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / endonucleolytic cleavage in ITS1 upstream of 5.8S rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / PeBoW complex / rRNA primary transcript binding / ATP-dependent activity, acting on RNA / maturation of 5.8S rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / pre-mRNA 5'-splice site binding / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit assembly / maturation of 5.8S rRNA ...snoRNA release from pre-rRNA / exonucleolytic trimming to generate mature 5'-end of 5.8S rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / endonucleolytic cleavage in ITS1 upstream of 5.8S rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / PeBoW complex / rRNA primary transcript binding / ATP-dependent activity, acting on RNA / maturation of 5.8S rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / pre-mRNA 5'-splice site binding / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit assembly / maturation of 5.8S rRNA / cleavage in ITS2 between 5.8S rRNA and LSU-rRNA of tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / preribosome, small subunit precursor / proteasome binding / Major pathway of rRNA processing in the nucleolus and cytosol / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / ribosomal large subunit binding / GTP hydrolysis and joining of the 60S ribosomal subunit / negative regulation of mRNA splicing, via spliceosome / preribosome, large subunit precursor / Formation of a pool of free 40S subunits / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) independent of the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) enhanced by the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / L13a-mediated translational silencing of Ceruloplasmin expression / ribosomal large subunit export from nucleus / 90S preribosome / ribonucleoprotein complex binding / protein-RNA complex assembly / maturation of LSU-rRNA / proteasome complex / ribosomal large subunit biogenesis / maturation of LSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / maturation of SSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / macroautophagy / protein catabolic process / maturation of SSU-rRNA / small-subunit processome / rRNA processing / nuclear envelope / ribosome biogenesis / ribosomal small subunit biogenesis / ribosomal large subunit assembly / 5S rRNA binding / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / protein-macromolecule adaptor activity / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / cytoplasmic translation / RNA helicase activity / negative regulation of translation / rRNA binding / structural constituent of ribosome / RNA helicase / ribosome / mRNA binding / nucleolus / ATP hydrolysis activity / DNA binding / RNA binding / zinc ion binding / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / identical protein binding / nucleus / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||||||||||||||
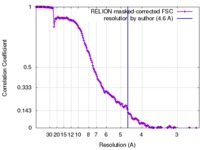
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.6 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Sanghai ZA / Miller L | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, United States,  Switzerland, 5 items Switzerland, 5 items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2018 Journal: Nature / Year: 2018Title: Modular assembly of the nucleolar pre-60S ribosomal subunit. Authors: Zahra Assur Sanghai / Linamarie Miller / Kelly R Molloy / Jonas Barandun / Mirjam Hunziker / Malik Chaker-Margot / Junjie Wang / Brian T Chait / Sebastian Klinge /  Abstract: Early co-transcriptional events during eukaryotic ribosome assembly result in the formation of precursors of the small (40S) and large (60S) ribosomal subunits. A multitude of transient assembly ...Early co-transcriptional events during eukaryotic ribosome assembly result in the formation of precursors of the small (40S) and large (60S) ribosomal subunits. A multitude of transient assembly factors regulate and chaperone the systematic folding of pre-ribosomal RNA subdomains. However, owing to a lack of structural information, the role of these factors during early nucleolar 60S assembly is not fully understood. Here we report cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) reconstructions of the nucleolar pre-60S ribosomal subunit in different conformational states at resolutions of up to 3.4 Å. These reconstructions reveal how steric hindrance and molecular mimicry are used to prevent both premature folding states and binding of later factors. This is accomplished by the concerted activity of 21 ribosome assembly factors that stabilize and remodel pre-ribosomal RNA and ribosomal proteins. Among these factors, three Brix-domain proteins and their binding partners form a ring-like structure at ribosomal RNA (rRNA) domain boundaries to support the architecture of the maturing particle. The existence of mutually exclusive conformations of these pre-60S particles suggests that the formation of the polypeptide exit tunnel is achieved through different folding pathways during subsequent stages of ribosome assembly. These structures rationalize previous genetic and biochemical data and highlight the mechanisms that drive eukaryotic ribosome assembly in a unidirectional manner. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_7445.map.gz emd_7445.map.gz | 388.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-7445-v30.xml emd-7445-v30.xml emd-7445.xml emd-7445.xml | 60.4 KB 60.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_7445_fsc.xml emd_7445_fsc.xml | 17 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_7445.png emd_7445.png | 19.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-7445.cif.gz emd-7445.cif.gz | 14 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7445 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7445 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7445 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7445 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6cb1MC  7324C  6c0fC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_7445.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_7445.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | LSU processome state 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.3 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Yeast nucleolar pre-60S ribosomal subunit
+Supramolecule #1: Yeast nucleolar pre-60S ribosomal subunit
+Macromolecule #1: 35S pre-ribosomal RNA miscRNA
+Macromolecule #2: 5.8S rRNA
+Macromolecule #3: ITS2
+Macromolecule #4: Ribosome biogenesis protein NSA1
+Macromolecule #5: 60S ribosomal protein L4-A
+Macromolecule #6: Protein MAK16
+Macromolecule #7: 60S ribosomal protein L6-A
+Macromolecule #8: 60S ribosomal protein L7-A
+Macromolecule #9: 60S ribosomal protein L8-A
+Macromolecule #10: Ribosome production factor 1
+Macromolecule #11: Proteasome-interacting protein CIC1
+Macromolecule #12: 60S ribosomal protein L13-A
+Macromolecule #13: 60S ribosomal protein L14-A
+Macromolecule #14: 60S ribosomal protein L15-A
+Macromolecule #15: 60S ribosomal protein L16-A
+Macromolecule #16: 60S ribosomal protein L17-A
+Macromolecule #17: 60S ribosomal protein L18-A
+Macromolecule #18: 60S ribosomal protein L20-A
+Macromolecule #19: 60S ribosomal protein L25
+Macromolecule #20: 60S ribosomal protein L26-A
+Macromolecule #21: 60S ribosomal protein L27-A
+Macromolecule #22: Nucleolar protein 16
+Macromolecule #23: Ribosome biogenesis protein BRX1
+Macromolecule #24: 60S ribosomal protein L30
+Macromolecule #25: Ribosome biogenesis protein YTM1
+Macromolecule #26: 60S ribosomal protein L32
+Macromolecule #27: 60S ribosomal protein L33-A
+Macromolecule #28: 60S ribosomal protein L34-A
+Macromolecule #29: 60S ribosomal protein L35-A
+Macromolecule #30: 60S ribosomal protein L36-A
+Macromolecule #31: 60S ribosomal protein L37-A
+Macromolecule #32: 60S ribosomal protein L38
+Macromolecule #33: rRNA-processing protein EBP2
+Macromolecule #34: Pescadillo homolog
+Macromolecule #35: Ribosome biogenesis protein 15
+Macromolecule #36: ATP-dependent RNA helicase HAS1
+Macromolecule #37: Ribosome biogenesis protein ERB1
+Macromolecule #38: Ribosome biogenesis protein RLP7
+Macromolecule #39: BRX1 associated peptide
+Macromolecule #40: Ribosomal RNA-processing protein 1
+Macromolecule #41: ZINC ION
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.6 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Material: COPPER / Mesh: 400 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: LACEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 30 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 295 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Average electron dose: 1.56 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: OTHER |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-6cb1: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller

















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)