+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6zwm | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
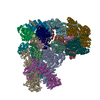
| Title | cryo-EM structure of human mTOR complex 2, overall refinement | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSFERASE / mTOR / Kinase / Complex / Inositol | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationTORC2 signaling / regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation / RNA polymerase III type 2 promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / RNA polymerase III type 1 promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / positive regulation of cytoplasmic translational initiation / T-helper 1 cell lineage commitment / positive regulation of pentose-phosphate shunt / regulation of locomotor rhythm / positive regulation of wound healing, spreading of epidermal cells / TORC2 complex ...TORC2 signaling / regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation / RNA polymerase III type 2 promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / RNA polymerase III type 1 promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / positive regulation of cytoplasmic translational initiation / T-helper 1 cell lineage commitment / positive regulation of pentose-phosphate shunt / regulation of locomotor rhythm / positive regulation of wound healing, spreading of epidermal cells / TORC2 complex / cellular response to leucine starvation / TFIIIC-class transcription factor complex binding / regulation of membrane permeability / heart valve morphogenesis / negative regulation of lysosome organization / nucleus localization / RNA polymerase III type 3 promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / TORC1 complex / positive regulation of transcription of nucleolar large rRNA by RNA polymerase I / regulation of cellular response to oxidative stress / calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade / regulation of osteoclast differentiation / voluntary musculoskeletal movement / TORC1 signaling / positive regulation of keratinocyte migration / phosphatidic acid binding / cellular response to L-leucine / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / MTOR signalling / cellular response to nutrient / cellular response to methionine / Energy dependent regulation of mTOR by LKB1-AMPK / regulation of autophagosome assembly / energy reserve metabolic process / negative regulation of cell size / ruffle organization / negative regulation of Ras protein signal transduction / phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate binding / cellular response to osmotic stress / phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate binding / anoikis / cardiac muscle cell development / negative regulation of protein localization to nucleus / embryo development ending in birth or egg hatching / regulation of establishment of cell polarity / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase III / negative regulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade / regulation of myelination / positive regulation of actin filament polymerization / regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / regulation of cell size / negative regulation of macroautophagy / positive regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation / lysosome organization / Macroautophagy / positive regulation of myotube differentiation / behavioral response to pain / oligodendrocyte differentiation / Constitutive Signaling by AKT1 E17K in Cancer / mTORC1-mediated signalling / germ cell development / phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate binding / CD28 dependent PI3K/Akt signaling / : / HSF1-dependent transactivation / positive regulation of TOR signaling / neuronal action potential / response to amino acid / TOR signaling / 'de novo' pyrimidine nucleobase biosynthetic process / endomembrane system / regulation of macroautophagy / positive regulation of translational initiation / cellular response to nutrient levels / positive regulation of lamellipodium assembly / phosphorylation / phagocytic vesicle / positive regulation of lipid biosynthetic process / heart morphogenesis / positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition / cardiac muscle contraction / regulation of cellular response to heat / phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding / positive regulation of stress fiber assembly / cytoskeleton organization / positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation / T cell costimulation / substantia nigra development / cellular response to starvation / cellular response to amino acid starvation / post-embryonic development / positive regulation of glycolytic process / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / negative regulation of autophagy / response to nutrient / response to nutrient levels / VEGFR2 mediated vascular permeability / regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator / Regulation of PTEN gene transcription / positive regulation of translation Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Scaiola, A. / Mangia, F. / Imseng, S. / Boehringer, D. / Ban, N. / Maier, T. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Switzerland, 3items Switzerland, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2020 Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2020Title: The 3.2-Å resolution structure of human mTORC2. Authors: Alain Scaiola / Francesca Mangia / Stefan Imseng / Daniel Boehringer / Karolin Berneiser / Mitsugu Shimobayashi / Edward Stuttfeld / Michael N Hall / Nenad Ban / Timm Maier /  Abstract: The protein kinase mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is the central regulator of cell growth. Aberrant mTOR signaling is linked to cancer, diabetes, and neurological disorders. mTOR exerts its ...The protein kinase mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is the central regulator of cell growth. Aberrant mTOR signaling is linked to cancer, diabetes, and neurological disorders. mTOR exerts its functions in two distinct multiprotein complexes, mTORC1 and mTORC2. Here, we report a 3.2-Å resolution cryo-EM reconstruction of mTORC2. It reveals entangled folds of the defining Rictor and the substrate-binding SIN1 subunits, identifies the carboxyl-terminal domain of Rictor as the source of the rapamycin insensitivity of mTORC2, and resolves mechanisms for mTORC2 regulation by complex destabilization. Two previously uncharacterized small-molecule binding sites are visualized, an inositol hexakisphosphate (InsP6) pocket in mTOR and an mTORC2-specific nucleotide binding site in Rictor, which also forms a zinc finger. Structural and biochemical analyses suggest that InsP6 and nucleotide binding do not control mTORC2 activity directly but rather have roles in folding or ternary interactions. These insights provide a firm basis for studying mTORC2 signaling and for developing mTORC2-specific inhibitors. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6zwm.cif.gz 6zwm.cif.gz | 1.3 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6zwm.ent.gz pdb6zwm.ent.gz | 1 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6zwm.json.gz 6zwm.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  6zwm_validation.pdf.gz 6zwm_validation.pdf.gz | 1.8 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  6zwm_full_validation.pdf.gz 6zwm_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.8 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  6zwm_validation.xml.gz 6zwm_validation.xml.gz | 177.9 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  6zwm_validation.cif.gz 6zwm_validation.cif.gz | 273.4 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zw/6zwm https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zw/6zwm ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zw/6zwm ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zw/6zwm | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 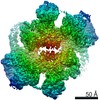 11488MC  6zwoC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 2 types, 4 molecules ABEF
| #1: Protein | Mass: 289257.969 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MTOR, FRAP, FRAP1, FRAP2, RAFT1, RAPT1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MTOR, FRAP, FRAP1, FRAP2, RAFT1, RAPT1 / Production host:  References: UniProt: P42345, non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase #3: Protein | Mass: 192472.922 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RICTOR, KIAA1999 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RICTOR, KIAA1999 / Production host:  |
|---|
-Target of rapamycin complex ... , 2 types, 4 molecules CDGH
| #2: Protein | Mass: 35910.090 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MLST8, GBL, LST8 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MLST8, GBL, LST8 / Production host:  #4: Protein | Mass: 59206.738 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: MAFLDNPTIILAHIRQSHVTSDDTGMCEMVLIDHDVDLEKIHPPSMPGDSGSEIQGSNGE TQGYVYAQSVDITSSWDFGIRRRSNTAQRLERLRKERQNQIKCKNIQWKERNSKQSAQEL KSLFEKKSLKEKPPISGKQSILSVRLEQCPLQLNNPFNEYSKFDGKGHVGTTATKKIDVY ...Details: MAFLDNPTIILAHIRQSHVTSDDTGMCEMVLIDHDVDLEKIHPPSMPGDSGSEIQGSNGE TQGYVYAQSVDITSSWDFGIRRRSNTAQRLERLRKERQNQIKCKNIQWKERNSKQSAQEL KSLFEKKSLKEKPPISGKQSILSVRLEQCPLQLNNPFNEYSKFDGKGHVGTTATKKIDVY LPLHSSQDRLLPMTVVTMASARVQDLIGLICWQYTSEGREPKLNDNVSAYCLHIAEDDGE VDTDFPPLDSNEPIHKFGFSTLALVEKYSSPGLTSKESLFVRINAAHGFSLIQVDNTKVT MKEILLKAVKRRKGSQKVSGPQYRLEKQSEPNVAVDLDSTLESQSAWEFCLVRENSSRAD GVFEEDSQIDIATVQDMLSSHHYKSFKVSMIHRLRFTTDVQLGISGDKVEIDPVTNQKAS TKFWIKQKPISIDSDLLCACDLAEEKSPSHAIFKLTYLSNHDYKHLYFESDAATVNEIVL KVNYILESRASTARADYFAQKQRKLNRRTSFSFQKEKKSGQQ Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MAPKAP1, MIP1, SIN1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MAPKAP1, MIP1, SIN1 / Production host:  |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 4 types, 10 molecules 





| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-AGS / #6: Chemical | #7: Chemical | #8: Chemical | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: human mTOR complex 2 / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#3 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 1.15 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8.5 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.37 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 400 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 70 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: EPU / Version: 2 / Category: image acquisition |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 293038 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj