[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
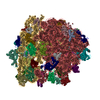
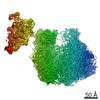
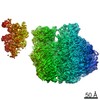
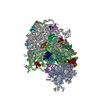
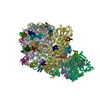
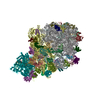
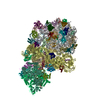
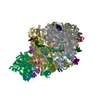
Yorodumi- PDB-6ztl: E. coli 70S-RNAP expressome complex in collided state bound to NusG -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6ztl | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | E. coli 70S-RNAP expressome complex in collided state bound to NusG | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | GENE REGULATION / Transcription / Translation / Expressome / Ribosome / RNA polymerase | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationDNA-templated transcription elongation / RNA polymerase complex / submerged biofilm formation / cellular response to cell envelope stress / regulation of DNA-templated transcription initiation / bacterial-type flagellum assembly / transcription antitermination factor activity, RNA binding / ornithine decarboxylase inhibitor activity / bacterial-type RNA polymerase core enzyme binding / cytosolic DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex ...DNA-templated transcription elongation / RNA polymerase complex / submerged biofilm formation / cellular response to cell envelope stress / regulation of DNA-templated transcription initiation / bacterial-type flagellum assembly / transcription antitermination factor activity, RNA binding / ornithine decarboxylase inhibitor activity / bacterial-type RNA polymerase core enzyme binding / cytosolic DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / misfolded RNA binding / Group I intron splicing / RNA folding / bacterial-type flagellum-dependent cell motility / transcriptional attenuation / nitrate assimilation / endoribonuclease inhibitor activity / positive regulation of ribosome biogenesis / RNA-binding transcription regulator activity / negative regulation of cytoplasmic translation / four-way junction DNA binding / DnaA-L2 complex / translation repressor activity / negative regulation of translational initiation / regulation of mRNA stability / negative regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication initiation / mRNA regulatory element binding translation repressor activity / positive regulation of RNA splicing / assembly of large subunit precursor of preribosome / cytosolic ribosome assembly / response to reactive oxygen species / regulation of DNA-templated transcription elongation / ribosome assembly / transcription elongation factor complex / transcription antitermination / DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / DNA endonuclease activity / regulation of cell growth / cell motility / DNA-templated transcription initiation / DNA-templated transcription termination / response to radiation / maintenance of translational fidelity / mRNA 5'-UTR binding / ribonucleoside binding / DNA-directed RNA polymerase / DNA-directed RNA polymerase activity / regulation of translation / large ribosomal subunit / ribosome biogenesis / transferase activity / ribosome binding / response to heat / ribosomal small subunit biogenesis / ribosomal small subunit assembly / protein-containing complex assembly / ribosomal large subunit assembly / 5S rRNA binding / small ribosomal subunit / small ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic small ribosomal subunit / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / cytoplasmic translation / tRNA binding / protein dimerization activity / negative regulation of translation / rRNA binding / structural constituent of ribosome / ribosome / translation / ribonucleoprotein complex / hydrolase activity / response to antibiotic / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / mRNA binding / DNA-templated transcription / magnesium ion binding / DNA binding / RNA binding / zinc ion binding / membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  synthetic construct (others) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Webster, M.W. / Takacs, M. / Weixlbaumer, A. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  France, 5items France, 5items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2020 Journal: Science / Year: 2020Title: Structural basis of transcription-translation coupling and collision in bacteria. Authors: Michael William Webster / Maria Takacs / Chengjin Zhu / Vita Vidmar / Ayesha Eduljee / Mo'men Abdelkareem / Albert Weixlbaumer /  Abstract: Prokaryotic messenger RNAs (mRNAs) are translated as they are transcribed. The lead ribosome potentially contacts RNA polymerase (RNAP) and forms a supramolecular complex known as the expressome. The ...Prokaryotic messenger RNAs (mRNAs) are translated as they are transcribed. The lead ribosome potentially contacts RNA polymerase (RNAP) and forms a supramolecular complex known as the expressome. The basis of expressome assembly and its consequences for transcription and translation are poorly understood. Here, we present a series of structures representing uncoupled, coupled, and collided expressome states determined by cryo-electron microscopy. A bridge between the ribosome and RNAP can be formed by the transcription factor NusG, which stabilizes an otherwise-variable interaction interface. Shortening of the intervening mRNA causes a substantial rearrangement that aligns the ribosome entrance channel to the RNAP exit channel. In this collided complex, NusG linkage is no longer possible. These structures reveal mechanisms of coordination between transcription and translation and provide a framework for future study. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6ztl.cif.gz 6ztl.cif.gz | 3.9 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6ztl.ent.gz pdb6ztl.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6ztl.json.gz 6ztl.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zt/6ztl https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zt/6ztl ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zt/6ztl ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zt/6ztl | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  11419MC  6ztjC  6ztmC  6ztnC  6ztoC  6ztpC  6zu1C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10846 (Title: E. coli 70S-RNAP expressome complex in collided state (with NusG, 34nt intervening mRNA) [7712 multi-frame micrographs in TIFF format] EMPIAR-10846 (Title: E. coli 70S-RNAP expressome complex in collided state (with NusG, 34nt intervening mRNA) [7712 multi-frame micrographs in TIFF format]Data size: 2.3 TB Data #1: E. coli 70S-RNAP expressome complex in collided state (with NusG, 34nt intervening mRNA) [7712 multi-frame micrographs in TIFF format] [micrographs - multiframe]) |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 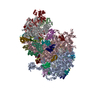
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-RNA chain , 6 types, 6 molecules AAAVAWAXBABB
| #1: RNA chain | Mass: 499888.406 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #22: RNA chain | Mass: 15789.517 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
| #23: RNA chain | Mass: 24832.918 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
| #24: RNA chain | Mass: 24751.018 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
| #25: RNA chain | Mass: 941820.562 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #26: RNA chain | Mass: 38790.090 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-30S ribosomal protein ... , 20 types, 20 molecules ABACADAEAFAGAHAIAJAKALAMANAOAPAQARASATAU
| #2: Protein | Mass: 26781.670 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #3: Protein | Mass: 26031.316 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 23514.199 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #5: Protein | Mass: 17617.455 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #6: Protein | Mass: 15197.032 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #7: Protein | Mass: 17637.445 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #8: Protein | Mass: 14146.557 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #9: Protein | Mass: 14886.270 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #10: Protein | Mass: 11755.597 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #11: Protein | Mass: 13870.975 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #12: Protein | Mass: 13814.249 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #13: Protein | Mass: 13128.467 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #14: Protein | Mass: 11606.560 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #15: Protein | Mass: 10290.816 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #16: Protein | Mass: 9207.572 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #17: Protein | Mass: 9724.491 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #18: Protein | Mass: 9005.472 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #19: Protein | Mass: 10455.355 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #20: Protein | Mass: 9708.464 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #21: Protein | Mass: 8524.039 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
+50S ribosomal protein ... , 28 types, 28 molecules BCBDBEBFBGBHBKBLBMBNBOBPBQBRBSBTBUBVBWBXBYBZB1B2B3B4B5B6
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules CNCT
| #55: DNA chain | Mass: 12063.754 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
|---|---|
| #56: DNA chain | Mass: 11872.596 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
-DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit ... , 4 types, 5 molecules CACBCCCDCE
| #57: Protein | Mass: 36558.680 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #58: Protein | | Mass: 150820.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: rpoB, groN, nitB, rif, ron, stl, stv, tabD, b3987, JW3950 Plasmid: pEcrpoABC(-XH)Z / Production host:  #59: Protein | | Mass: 155366.781 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #60: Protein | | Mass: 10249.547 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|
-Protein , 1 types, 1 molecules CF
| #61: Protein | Mass: 20560.523 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: nusG, A6592_25585, A6V01_22710, A8C65_22140, A9819_22730, A9P13_25180, A9R57_05240, A9X72_23950, AC067_25565, AC789_1c43770, ACN002_4069, ACN68_05355, ACN81_23140, ACU57_23215, ACU90_26230, ...Gene: nusG, A6592_25585, A6V01_22710, A8C65_22140, A9819_22730, A9P13_25180, A9R57_05240, A9X72_23950, AC067_25565, AC789_1c43770, ACN002_4069, ACN68_05355, ACN81_23140, ACU57_23215, ACU90_26230, AM270_23415, AM446_26285, AM464_13235, AML07_02765, AML35_27155, APT94_08685, APZ14_17375, ARC77_16990, AU473_00875, AUQ13_12310, AUS26_26490, AW059_24245, AW106_22725, AWB10_24980, AWG90_024840, AWP75_07120, B7C53_21495, B9M99_23250, B9T59_11605, BANRA_02652, BANRA_02965, BANRA_04868, BANRA_05054, BB545_03125, BE963_11245, BEN53_24665, BER14_24185, BHF03_13055, BHF46_22020, BHS81_23795, BHS87_22260, BIQ87_22825, BIU72_18845, BIZ41_20425, BJJ90_25150, BK248_06370, BK292_28055, BK296_22625, BK334_23885, BK373_27240, BK375_25285, BK383_27750, BMT91_03315, BN17_39461, BOH76_00570, BON63_20075, BON65_15050, BON66_14345, BON69_07640, BON71_08905, BON72_17240, BON75_02205, BON76_16185, BON83_01585, BON86_02250, BON87_25635, BON92_00555, BON94_22220, BON95_12895, BON96_11035, BTQ04_24460, BTQ06_27300, BUE81_05395, BvCms12BK_01423, BvCms2454_04763, BvCms28BK_04512, BvCms35BK_02101, BvCmsC61A_02144, BvCmsHHP001_05230, BvCmsHHP019_04457, BvCmsHHP056_02613, BvCmsKKP036_03586, BvCmsKKP061_02988, BvCmsKSNP073_02860, BvCmsKSNP081_04473, BvCmsKSNP120_03442, BvCmsKSP011_02762, BvCmsKSP024_02914, BvCmsKSP026_03368, BvCmsKSP045_04193, BvCmsKSP058_05150, BvCmsKSP067_02572, BvCmsKSP076_03394, BvCmsNSNP036_01151, BvCmsNSP006_02609, BvCmsNSP007_05025, BvCmsNSP047_00265, BvCmsNSP072_02887, BvCmsOUP014_03194, BvCmsSINP011_03926, BvCmsSINP022_04149, BvCmsSIP019_00806, BvCmsSIP044_03280, BVL39_05395, BW690_26720, BWI89_17415, BWP17_22740, BXT93_25190, BZL31_04420, BZL69_05760, C2M16_25145, C2U48_12750, C4M78_26060, C5715_03885, C5N07_24575, C5P01_26085, C5P44_24205, C6669_07630, C6B13_24055, C7235_23740, C7B02_25750, C7B06_24590, C7B07_24515, C7B08_25795, C7B18_24885, C9098_22125, C9114_22875, C9141_23580, C9160_23410, C9162_26315, C9201_22170, C9306_18330, C9E25_22050, C9E67_28690, C9Z03_20290, C9Z23_22460, C9Z28_21960, C9Z29_22205, C9Z37_20890, C9Z39_11545, C9Z68_22005, C9Z70_22895, C9Z78_23210, C9Z89_21250, CA593_06055, CDC27_21525, CDL37_18180, CF006_23900, CG692_19490, CI641_013295, CI693_09880, CI694_22430, CIG45_23855, CJU63_23510, CMR93_21685, CO706_19475, COD30_25685, COD46_23680, CQB02_21475, CQP61_26065, CR538_24245, CR539_01640, CRD98_23200, CRE06_24015, CRM83_18660, CRX46_23015, CSB64_25615, CV83915_02071, CVH05_03840, CWM24_27465, CWS33_24585, D0X26_26090, D2184_25125, D2185_24315, D2188_26625, D3821_09130, D3822_07045, D3O91_23455, D3P01_24300, D3Y67_18010, D4M06_24755, D4V08_22465, D6T60_24420, D6X76_25425, D7K63_24265, D7K66_23575, D9D20_23600, D9D31_17400, D9D43_22285, D9E34_21740, D9E35_23840, D9F17_24210, D9G11_22910, D9G42_23575, D9G48_16785, D9H36_23700, D9H53_22650, D9H68_20300, D9H70_22035, D9H94_18920, D9I18_21340, D9I87_21115, D9I88_18975, D9I97_19355, D9J03_21550, D9J11_22250, D9J44_24490, D9J60_24680, D9J78_24465, D9K48_24855, D9K54_12200, D9L89_22830, D9X97_23540, DAH18_24890, DAH26_25975, DAH30_23810, DAH32_23215, DAH34_21590, DAH37_22535, DAH43_24845, DB359_25595, DBQ99_24575, DD762_22315, DEN86_24465, DEN89_26545, DEN97_23745, DEO04_24340, DEO19_24590, DIV22_03710, DJ492_21155, DJ503_21480, DL455_22945, DL545_23715, DL800_27635, DM102_24845, DM129_21405, DMI04_23160, DN627_23120, DN700_22935, DNB37_22335, DND16_22055, DNQ45_05150, DNX30_24180, DOY56_23490, DP258_23400, DP277_21350, DQE83_24500, DQF57_23755, DQO13_23745, DS732_01515, DTL43_13735, DTL90_24565, DTM10_25890, DTM45_24265, DU309_24235, DU321_23455, DWB25_23615, DXT69_22770, DXT71_22275, DXT73_22975, DXX80_014070, E0I42_21930, E0K84_22915, E0L12_22075, E2112_20390, E2115_21525, E2116_21360, E2119_22370, E2127_20870, E2128_03155, E2129_21325, E2134_22760, E2135_19300, E2855_04995, E2863_04087, E4K55_23315, E5P22_12620, E5P28_08855, E5P37_21480, E5S42_21570, E5S46_22920, E5S47_23055, E5S58_21655, E5S61_22405, EA223_18780, EAI42_07555, EAI46_11730, EAI52_22765, EAX79_24725, EB509_19910, EB510_23015, EB515_23215, EC1094V2_4288, EC3234A_76c00020, EC3426_00293, EC382_20035, EC95NR1_03447, ECONIH1_23440, ECs4905, ECTO6_04524, ED225_22815, ED600_17570, ED607_18465, ED611_23905, ED648_18875, ED903_15555, ED944_23285, EEA45_21070, EEP23_09520, EF173_24425, EHH55_00685, EHJ36_22675, EI021_22100, EI028_22550, EI032_21280, EIA08_23380, EIA21_22555, EIZ93_16305, EJC75_19605, EKI52_13975, EL75_4207, EL79_4413, EL80_4320, ELT20_20690, ELT49_22095, ELT58_20800, ELU85_23620, ELV08_18720, ELV15_18010, ELV28_22220, ELY05_18135, EO241_25805, EPT01_21710, EPU41_22430, EQ820_22900, EQ823_21595, EQ825_24495, EQ830_22075, ERL57_22710, ERS085365_04268, ERS085366_03833, ERS085374_04594, ERS085379_04702, ERS085386_04623, ERS085404_04521, ERS085416_04255, ERS139211_00029, ERS150873_04413, ERS150876_04842, EST51_23890, EVY14_16870, EXM29_02430, ExPECSC019_03691, ExPECSC038_04333, EXX06_24555, EXX13_24135, EXX23_22335, EXX24_23200, EXX53_20975, EXX55_24470, EXX71_22285, EXX78_23980, EXX87_25010, EYD11_21620, EYX82_16660, EYY27_22340, EYY34_19835, EYY78_22630, F1E13_23780, F1E19_21855, F7F18_24025, F7F23_23365, F7F29_25900, F7G01_23380, F7G03_24045, FAF34_028990, FKO60_24845, FNJ69_19080, FNJ83_24770, FORC82_4527, FQ915_26180, FQR64_21830, FRV13_16245, FV293_23400, FV295_22235, FV438_22405, FWK02_12320, FY127_17780, FZ043_01110, GJ11_25170, HmCms184_03867, HmCmsJML074_03188, HmCmsJML079_04908, HmCmsJML204_03263, HMPREF3040_01771, HW43_01555, MJ49_09455, MS6198_46010, NCTC10082_02087, NCTC10090_02786, NCTC10429_00094, NCTC10764_02978, NCTC10766_02647, NCTC10865_05901, NCTC10974_05357, NCTC11022_04295, NCTC11112_02275, NCTC11126_05446, NCTC11181_01971, NCTC11341_02768, NCTC12950_05220, NCTC13127_06170, NCTC13148_04401, NCTC13846_04507, NCTC7922_04992, NCTC7927_05255, NCTC8009_08439, NCTC8179_05103, NCTC8450_00357, NCTC8500_05331, NCTC8622_01622, NCTC8960_02346, NCTC9007_05346, NCTC9036_04655, NCTC9044_02298, NCTC9045_05548, NCTC9050_02824, NCTC9055_01673, NCTC9058_02141, NCTC9062_03438, NCTC9077_05942, NCTC9111_04961, NCTC9117_05910, NCTC9119_05061, NCTC9701_05002, NCTC9702_05645, NCTC9703_04220, NCTC9706_02009, NCTC9777_01124, NCTC9969_04938, PGD_00616, PU06_15460, RG28_25315, RK56_017435, RX35_03749, SAMEA3472043_04873, SAMEA3472044_04880, SAMEA3472047_03493, SAMEA3472055_04940, SAMEA3472056_05316, SAMEA3472070_05100, SAMEA3472080_04808, SAMEA3472090_05013, SAMEA3472108_04978, SAMEA3472110_05075, SAMEA3472112_05160, SAMEA3472114_04960, SAMEA3472147_04113, SAMEA3484427_04977, SAMEA3484429_04980, SAMEA3484434_04732, SAMEA3485101_05504, SAMEA3485113_04488, SAMEA3752372_05072, SAMEA3752553_04898, SAMEA3752557_04837, SAMEA3752559_04862, SAMEA3752620_04706, SAMEA3753064_05336, SAMEA3753097_04838, SAMEA3753164_04793, SAMEA3753290_00011, SAMEA3753300_04891, SK85_04313, UC41_25620, UN86_14210, UN91_25475, WQ89_24645, WR15_01460, YDC107_2696 Plasmid: pSKB2_(His)6-HRV3C-NusG / Production host:  |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 445 molecules 
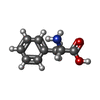



| #62: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #63: Chemical | ChemComp-PHE / | #64: Chemical | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 90 % / Chamber temperature: 283 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 700 nm |
| Specimen holder | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 42 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 40 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 684211 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 45774 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL / Target criteria: Correlation coefficient | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj