[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
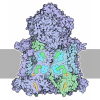
Yorodumi- PDB-6ziy: Respiratory complex I from Thermus thermophilus, NADH dataset, ma... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6ziy | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Respiratory complex I from Thermus thermophilus, NADH dataset, major state | ||||||
 Components Components | (NADH-quinone oxidoreductase subunit ...) x 15 | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / Respiratory chain / complex I / NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase / electron transfer / proton translocation | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationTranslocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions / NADH dehydrogenase (quinone) (non-electrogenic) activity / NADH dehydrogenase complex / molybdopterin cofactor binding / oxidoreductase activity, acting on NAD(P)H, quinone or similar compound as acceptor / iron-sulfur cluster assembly / ubiquinone binding / electron transport coupled proton transport / NADH dehydrogenase activity / respiratory chain complex I ...Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions / NADH dehydrogenase (quinone) (non-electrogenic) activity / NADH dehydrogenase complex / molybdopterin cofactor binding / oxidoreductase activity, acting on NAD(P)H, quinone or similar compound as acceptor / iron-sulfur cluster assembly / ubiquinone binding / electron transport coupled proton transport / NADH dehydrogenase activity / respiratory chain complex I / NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity / quinone binding / ATP synthesis coupled electron transport / ferric iron binding / aerobic respiration / 2 iron, 2 sulfur cluster binding / NAD binding / FMN binding / 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding / iron ion binding / metal ion binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.25 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Kaszuba, K. / Tambalo, M. / Gallagher, G.T. / Sazanov, L.A. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 1items United Kingdom, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2020 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2020Title: Key role of quinone in the mechanism of respiratory complex I. Authors: Javier Gutiérrez-Fernández / Karol Kaszuba / Gurdeep S Minhas / Rozbeh Baradaran / Margherita Tambalo / David T Gallagher / Leonid A Sazanov /    Abstract: Complex I is the first and the largest enzyme of respiratory chains in bacteria and mitochondria. The mechanism which couples spatially separated transfer of electrons to proton translocation in ...Complex I is the first and the largest enzyme of respiratory chains in bacteria and mitochondria. The mechanism which couples spatially separated transfer of electrons to proton translocation in complex I is not known. Here we report five crystal structures of T. thermophilus enzyme in complex with NADH or quinone-like compounds. We also determined cryo-EM structures of major and minor native states of the complex, differing in the position of the peripheral arm. Crystal structures show that binding of quinone-like compounds (but not of NADH) leads to a related global conformational change, accompanied by local re-arrangements propagating from the quinone site to the nearest proton channel. Normal mode and molecular dynamics analyses indicate that these are likely to represent the first steps in the proton translocation mechanism. Our results suggest that quinone binding and chemistry play a key role in the coupling mechanism of complex I. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6ziy.cif.gz 6ziy.cif.gz | 793.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6ziy.ent.gz pdb6ziy.ent.gz | 616.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6ziy.json.gz 6ziy.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zi/6ziy https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zi/6ziy ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zi/6ziy ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zi/6ziy | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  11231MC  6i0dC  6i1pC  6q8oC  6q8wC  6q8xC  6y11C  6zjlC  6zjnC  6zjyC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-NADH-quinone oxidoreductase subunit ... , 15 types, 15 molecules 12345697AJKLMNH
| #1: Protein | Mass: 48693.715 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q56222, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 20309.162 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q56221, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 86656.203 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q56223, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 46428.027 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q56220, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
| #5: Protein | Mass: 23893.254 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q56219, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
| #6: Protein | Mass: 20262.564 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q56218, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
| #7: Protein | Mass: 20106.309 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q56224, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
| #8: Protein | Mass: 14812.074 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q5SKZ7, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
| #9: Protein | Mass: 13154.656 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q56217, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
| #10: Protein | Mass: 18563.330 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q56225, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
| #11: Protein | Mass: 10002.788 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q56226, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
| #12: Protein | Mass: 65189.930 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q56227, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
| #13: Protein | Mass: 49247.117 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q56228, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
| #14: Protein | Mass: 44463.895 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q56229, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
| #15: Protein | Mass: 41034.523 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q60019, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
-Non-polymers , 4 types, 11 molecules 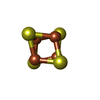
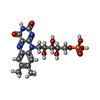
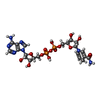
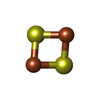


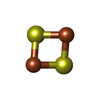
| #16: Chemical | ChemComp-SF4 / #17: Chemical | ChemComp-FMN / | #18: Chemical | ChemComp-NAI / | #19: Chemical | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Respiratory complex I from Thermus thermophilus / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#15 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.53 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 |
| Buffer solution | pH: 6 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 6 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES / Details: with 5 mM NADH |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R0.6/1 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 295 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 4000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 2500 nm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 2 sec. / Electron dose: 34 e/Å2 / Detector mode: INTEGRATING / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 3 / Num. of real images: 2184 |
| Image scans | Sampling size: 14 µm / Width: 4096 / Height: 4096 / Movie frames/image: 34 / Used frames/image: 1-34 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 205000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.25 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 44500 / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 6Y11 Accession code: 6Y11 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller













 PDBj
PDBj