+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6up7 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | neurotensin receptor and arrestin2 complex | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / GPCR signaling | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationG protein-coupled neurotensin receptor activity / neuropeptide receptor binding / inositol phosphate catabolic process / symmetric synapse / angiotensin receptor binding / D-aspartate import across plasma membrane / positive regulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid secretion / TGFBR3 regulates TGF-beta signaling / Activation of SMO / regulation of membrane depolarization ...G protein-coupled neurotensin receptor activity / neuropeptide receptor binding / inositol phosphate catabolic process / symmetric synapse / angiotensin receptor binding / D-aspartate import across plasma membrane / positive regulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid secretion / TGFBR3 regulates TGF-beta signaling / Activation of SMO / regulation of membrane depolarization / positive regulation of arachidonate secretion / negative regulation of interleukin-8 production / L-glutamate import across plasma membrane / regulation of respiratory gaseous exchange / neuropeptide hormone activity / positive regulation of inhibitory postsynaptic potential / arrestin family protein binding / negative regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure / G protein-coupled receptor internalization / negative regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / positive regulation of glutamate secretion / Lysosome Vesicle Biogenesis / temperature homeostasis / : / response to lipid / positive regulation of cardiac muscle hypertrophy / stress fiber assembly / Golgi Associated Vesicle Biogenesis / positive regulation of inositol phosphate biosynthetic process / positive regulation of Rho protein signal transduction / detection of temperature stimulus involved in sensory perception of pain / pseudopodium / negative regulation of interleukin-6 production / positive regulation of receptor internalization / negative regulation of Notch signaling pathway / enzyme inhibitor activity / neuropeptide signaling pathway / transport vesicle / insulin-like growth factor receptor binding / clathrin-coated pit / axon terminus / negative regulation of protein ubiquitination / GTPase activator activity / Activated NOTCH1 Transmits Signal to the Nucleus / cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / Peptide ligand-binding receptors / positive regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / blood vessel diameter maintenance / dendritic shaft / adult locomotory behavior / learning / Signaling by high-kinase activity BRAF mutants / MAP2K and MAPK activation / G protein-coupled receptor binding / G protein-coupled receptor activity / cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane / terminal bouton / positive regulation of protein phosphorylation / Signaling by RAF1 mutants / Signaling by moderate kinase activity BRAF mutants / Paradoxical activation of RAF signaling by kinase inactive BRAF / Signaling downstream of RAS mutants / endocytic vesicle membrane / Signaling by BRAF and RAF1 fusions / Cargo recognition for clathrin-mediated endocytosis / protein transport / Clathrin-mediated endocytosis / Thrombin signalling through proteinase activated receptors (PARs) / cytoplasmic vesicle / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / G alpha (s) signalling events / perikaryon / G alpha (q) signalling events / dendritic spine / chemical synaptic transmission / molecular adaptor activity / proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / transcription coactivator activity / positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / Ub-specific processing proteases / nuclear body / protein ubiquitination / positive regulation of apoptotic process / receptor ligand activity / membrane raft / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / Golgi membrane / negative regulation of gene expression / lysosomal membrane / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / positive regulation of gene expression / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / negative regulation of apoptotic process / chromatin / protein-containing complex binding / cell surface / endoplasmic reticulum / Golgi apparatus Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.2 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Qu, Q.H. / Huang, W. / Masureel, M. / Janetzko, J. / Kobilka, B.K. / Skiniotis, G. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2020 Journal: Nature / Year: 2020Title: Structure of the neurotensin receptor 1 in complex with β-arrestin 1. Authors: Weijiao Huang / Matthieu Masureel / Qianhui Qu / John Janetzko / Asuka Inoue / Hideaki E Kato / Michael J Robertson / Khanh C Nguyen / Jeffrey S Glenn / Georgios Skiniotis / Brian K Kobilka /   Abstract: Arrestin proteins bind to active, phosphorylated G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), thereby preventing G-protein coupling, triggering receptor internalization and affecting various downstream ...Arrestin proteins bind to active, phosphorylated G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), thereby preventing G-protein coupling, triggering receptor internalization and affecting various downstream signalling pathways. Although there is a wealth of structural information detailing the interactions between GPCRs and G proteins, less is known about how arrestins engage GPCRs. Here we report a cryo-electron microscopy structure of full-length human neurotensin receptor 1 (NTSR1) in complex with truncated human β-arrestin 1 (βarr1(ΔCT)). We find that phosphorylation of NTSR1 is critical for the formation of a stable complex with βarr1(ΔCT), and identify phosphorylated sites in both the third intracellular loop and the C terminus that may promote this interaction. In addition, we observe a phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate molecule forming a bridge between the membrane side of NTSR1 transmembrane segments 1 and 4 and the C-lobe of arrestin. Compared with a structure of a rhodopsin-arrestin-1 complex, in our structure arrestin is rotated by approximately 85° relative to the receptor. These findings highlight both conserved aspects and plasticity among arrestin-receptor interactions. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6up7.cif.gz 6up7.cif.gz | 134.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6up7.ent.gz pdb6up7.ent.gz | 92.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6up7.json.gz 6up7.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  6up7_validation.pdf.gz 6up7_validation.pdf.gz | 760.1 KB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  6up7_full_validation.pdf.gz 6up7_full_validation.pdf.gz | 765.8 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  6up7_validation.xml.gz 6up7_validation.xml.gz | 24.1 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  6up7_validation.cif.gz 6up7_validation.cif.gz | 36.1 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/up/6up7 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/up/6up7 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/up/6up7 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/up/6up7 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 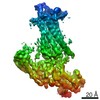 20836MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein/peptide | Mass: 819.007 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 39062.840 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ARRB1, ARR1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ARRB1, ARR1 / Production host:  |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 37360.656 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: missing regions were not modeled due to local low resolution/flexibility. Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NTSR1, NTRR / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NTSR1, NTRR / Production host:  |
| #4: Protein/peptide | Mass: 783.958 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: actual sequence for this poly-A exists, however, the local resolution for this region is not sufficient to register the amino acids. Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  |
| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-PIO / [( |
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: NTSR_Arrestin / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#4 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: OTHER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 56 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 254725 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj