[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6ty4: FAK structure with AMP-PNP from single particle analysis of 2D cr... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6ty4 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
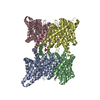
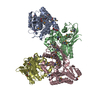
| Title | FAK structure with AMP-PNP from single particle analysis of 2D crystals | |||||||||
 Components Components | Focal adhesion kinase 1 | |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CELL ADHESION / Kinase / Focal Adhesion / Membrane | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationApoptotic cleavage of cellular proteins / NCAM signaling for neurite out-growth / RAF/MAP kinase cascade / Turbulent (oscillatory, disturbed) flow shear stress activates signaling by PIEZO1 and integrins in endothelial cells / RHO GTPases Activate WASPs and WAVEs / Regulation of actin dynamics for phagocytic cup formation / negative regulation of protein autophosphorylation / radial glia-guided pyramidal neuron migration / positive regulation of protein tyrosine kinase activity / calcium-dependent cysteine-type endopeptidase activity ...Apoptotic cleavage of cellular proteins / NCAM signaling for neurite out-growth / RAF/MAP kinase cascade / Turbulent (oscillatory, disturbed) flow shear stress activates signaling by PIEZO1 and integrins in endothelial cells / RHO GTPases Activate WASPs and WAVEs / Regulation of actin dynamics for phagocytic cup formation / negative regulation of protein autophosphorylation / radial glia-guided pyramidal neuron migration / positive regulation of protein tyrosine kinase activity / calcium-dependent cysteine-type endopeptidase activity / positive regulation of substrate-dependent cell migration, cell attachment to substrate / Integrin signaling / GRB2:SOS provides linkage to MAPK signaling for Integrins / : / MET activates PTK2 signaling / Extra-nuclear estrogen signaling / EPHB-mediated forward signaling / p130Cas linkage to MAPK signaling for integrins / VEGFA-VEGFR2 Pathway / signal complex assembly / response to pH / wound healing, spreading of cells / angiogenesis involved in wound healing / negative regulation of anoikis / positive regulation of protein binding / negative regulation of cell-substrate adhesion / positive regulation of focal adhesion assembly / regulation of cell adhesion / response to muscle stretch / molecular function activator activity / actin filament organization / non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity / non-specific protein-tyrosine kinase / sarcolemma / integrin binding / epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway / protein autophosphorylation / protease binding / protein tyrosine kinase activity / cell cortex / positive regulation of cell migration / ciliary basal body / focal adhesion / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / centrosome / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / ATP binding / identical protein binding / nucleus / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 5.96 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Acebron, I. / Righetto, R. / Biyani, N. / Chami, M. / Boskovic, J. / Stahlberg, H. / Lietha, D. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Spain, Spain,  Switzerland, 2items Switzerland, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2020 Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2020Title: Structural basis of Focal Adhesion Kinase activation on lipid membranes. Authors: Iván Acebrón / Ricardo D Righetto / Christina Schoenherr / Svenja de Buhr / Pilar Redondo / Jayne Culley / Carlos F Rodríguez / Csaba Daday / Nikhil Biyani / Oscar Llorca / Adam Byron / ...Authors: Iván Acebrón / Ricardo D Righetto / Christina Schoenherr / Svenja de Buhr / Pilar Redondo / Jayne Culley / Carlos F Rodríguez / Csaba Daday / Nikhil Biyani / Oscar Llorca / Adam Byron / Mohamed Chami / Frauke Gräter / Jasminka Boskovic / Margaret C Frame / Henning Stahlberg / Daniel Lietha /     Abstract: Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) is a key component of the membrane proximal signaling layer in focal adhesion complexes, regulating important cellular processes, including cell migration, proliferation, ...Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) is a key component of the membrane proximal signaling layer in focal adhesion complexes, regulating important cellular processes, including cell migration, proliferation, and survival. In the cytosol, FAK adopts an autoinhibited state but is activated upon recruitment into focal adhesions, yet how this occurs or what induces structural changes is unknown. Here, we employ cryo-electron microscopy to reveal how FAK associates with lipid membranes and how membrane interactions unlock FAK autoinhibition to promote activation. Intriguingly, initial binding of FAK to the membrane causes steric clashes that release the kinase domain from autoinhibition, allowing it to undergo a large conformational change and interact itself with the membrane in an orientation that places the active site toward the membrane. In this conformation, the autophosphorylation site is exposed and multiple interfaces align to promote FAK oligomerization on the membrane. We show that interfaces responsible for initial dimerization and membrane attachment are essential for FAK autophosphorylation and resulting cellular activity including cancer cell invasion, while stable FAK oligomerization appears to be needed for optimal cancer cell proliferation in an anchorage-independent manner. Together, our data provide structural details of a key membrane bound state of FAK that is primed for efficient autophosphorylation and activation, hence revealing the critical event in integrin mediated FAK activation and signaling at focal adhesions. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6ty4.cif.gz 6ty4.cif.gz | 236.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6ty4.ent.gz pdb6ty4.ent.gz | 189.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6ty4.json.gz 6ty4.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ty/6ty4 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ty/6ty4 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ty/6ty4 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ty/6ty4 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  10616MC  6ty3C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10347 (Title: FAK structure from single particle analysis of 2D crystals EMPIAR-10347 (Title: FAK structure from single particle analysis of 2D crystalsData size: 1.8 TB Data #1: Dose-weighted aligned movie averages of the FAK AMP-PNP dataset [micrographs - single frame] Data #2: Unaligned movies of the FAK AMP-PNP dataset [micrographs - multiframe] Data #3: Stack of particles extracted from the FAK AMP-PNP dataset [picked particles - single frame - unprocessed] Data #4: Dose-weighted aligned movie averages of the FAK APO Polara dataset [micrographs - single frame] Data #5: Dose-weighted aligned movie averages of the FAK APO Titan dataset [micrographs - single frame] Data #6: Unaligned movies of the FAK APO Titan dataset [micrographs - multiframe] Data #7: Stack of particles extracted from the FAK APO Titan and Polara datasets [picked particles - single frame - unprocessed]) |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 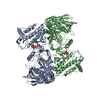
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 75476.445 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)References: UniProt: Q00944, non-specific protein-tyrosine kinase #2: Chemical | #3: Chemical | Has ligand of interest | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: 2D ARRAY / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Focal adhesion kinase / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.15 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 5.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 5.96 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 548394 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | 3D fitting-ID: 1 / Pdb chain-ID: A / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj