+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6tgy | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
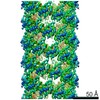
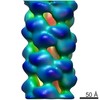
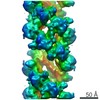
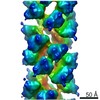
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of p62-PB1 filament (L-type) | ||||||||||||
 Components Components | Sequestosome-1 | ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | APOPTOSIS / Autophagy | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationbrown fat cell proliferation / protein localization to perinuclear region of cytoplasm / protein targeting to vacuole involved in autophagy / regulation of Ras protein signal transduction / aggrephagy / response to mitochondrial depolarisation / Lewy body / negative regulation of toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway / amphisome / regulation of protein complex stability ...brown fat cell proliferation / protein localization to perinuclear region of cytoplasm / protein targeting to vacuole involved in autophagy / regulation of Ras protein signal transduction / aggrephagy / response to mitochondrial depolarisation / Lewy body / negative regulation of toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway / amphisome / regulation of protein complex stability / endosome organization / autophagy of mitochondrion / pexophagy / membraneless organelle assembly / phagophore assembly site / ubiquitin-modified protein reader activity / regulation of mitochondrion organization / regulation of canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / Nuclear events mediated by NFE2L2 / aggresome / endosomal transport / K63-linked polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding / intracellular membraneless organelle / negative regulation of ferroptosis / temperature homeostasis / cellular response to stress / autolysosome / molecular sequestering activity / immune system process / mitophagy / energy homeostasis / sperm midpiece / inclusion body / ionotropic glutamate receptor binding / signaling adaptor activity / positive regulation of autophagy / negative regulation of protein ubiquitination / protein sequestering activity / SH2 domain binding / autophagosome / p75NTR recruits signalling complexes / NF-kB is activated and signals survival / Pexophagy / NRIF signals cell death from the nucleus / protein kinase C binding / ubiquitin binding / sarcomere / positive regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / response to ischemia / PINK1-PRKN Mediated Mitophagy / positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / macroautophagy / P-body / protein catabolic process / molecular condensate scaffold activity / PML body / receptor tyrosine kinase binding / autophagy / Interleukin-1 signaling / protein import into nucleus / Signaling by ALK fusions and activated point mutants / KEAP1-NFE2L2 pathway / intracellular protein localization / late endosome / signaling receptor activity / Neddylation / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / protein-macromolecule adaptor activity / transcription by RNA polymerase II / cell differentiation / intracellular signal transduction / positive regulation of apoptotic process / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle / apoptotic process / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / protein kinase binding / protein-containing complex binding / glutamatergic synapse / enzyme binding / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / endoplasmic reticulum / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / mitochondrion / extracellular exosome / zinc ion binding / nucleoplasm / identical protein binding / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Jakobi, A.J. / Huber, S.T. / Mortensen, S.A. / Sachse, C. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 3items Germany, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2020 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2020Title: Structural basis of p62/SQSTM1 helical filaments and their role in cellular cargo uptake. Authors: Arjen J Jakobi / Stefan T Huber / Simon A Mortensen / Sebastian W Schultz / Anthimi Palara / Tanja Kuhm / Birendra Kumar Shrestha / Trond Lamark / Wim J H Hagen / Matthias Wilmanns / Terje ...Authors: Arjen J Jakobi / Stefan T Huber / Simon A Mortensen / Sebastian W Schultz / Anthimi Palara / Tanja Kuhm / Birendra Kumar Shrestha / Trond Lamark / Wim J H Hagen / Matthias Wilmanns / Terje Johansen / Andreas Brech / Carsten Sachse /    Abstract: p62/SQSTM1 is an autophagy receptor and signaling adaptor with an N-terminal PB1 domain that forms the scaffold of phase-separated p62 bodies in the cell. The molecular determinants that govern PB1 ...p62/SQSTM1 is an autophagy receptor and signaling adaptor with an N-terminal PB1 domain that forms the scaffold of phase-separated p62 bodies in the cell. The molecular determinants that govern PB1 domain filament formation in vitro remain to be determined and the role of p62 filaments inside the cell is currently unclear. We here determine four high-resolution cryo-EM structures of different human and Arabidopsis PB1 domain assemblies and observed a filamentous ultrastructure of p62/SQSTM1 bodies using correlative cellular EM. We show that oligomerization or polymerization, driven by a double arginine finger in the PB1 domain, is a general requirement for lysosomal targeting of p62. Furthermore, the filamentous assembly state of p62 is required for autophagosomal processing of the p62-specific cargo KEAP1. Our results show that using such mechanisms, p62 filaments can be critical for cargo uptake in autophagy and are an integral part of phase-separated p62 bodies. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6tgy.cif.gz 6tgy.cif.gz | 33.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6tgy.ent.gz pdb6tgy.ent.gz | 22 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6tgy.json.gz 6tgy.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  6tgy_validation.pdf.gz 6tgy_validation.pdf.gz | 1.3 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  6tgy_full_validation.pdf.gz 6tgy_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.3 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  6tgy_validation.xml.gz 6tgy_validation.xml.gz | 21 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  6tgy_validation.cif.gz 6tgy_validation.cif.gz | 28.3 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tg/6tgy https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tg/6tgy ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tg/6tgy ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tg/6tgy | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 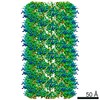 10501MC  6tgnC  6tgpC  6tgsC  6th3C C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 | x 120
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 13704.609 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SQSTM1, ORCA, OSIL / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SQSTM1, ORCA, OSIL / Production host:  |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: p62-PB1 domain filament (L-type) / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 / Details: 50 mM TRIS (pH 7.5), 100 mM NaCl, 4 mM DTT |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 400 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/1 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 283 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 2277 |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 40 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Helical symmerty | Angular rotation/subunit: 77.29 ° / Axial rise/subunit: 4.787 Å / Axial symmetry: C2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 51853 / Symmetry type: HELICAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL / Target criteria: Correlation coefficient | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 2KKC Accession code: 2KKC / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj








