[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6t63: A model of the EIAV CA-SP hexamer (C2) from Gag-deltaMA tubes ass... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6t63 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
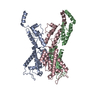
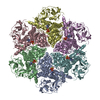
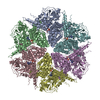
| Title | A model of the EIAV CA-SP hexamer (C2) from Gag-deltaMA tubes assembled at pH6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components | Gag polyprotein | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRAL PROTEIN / Retrovirus / lentivirus / Equine infectious anemia virus / EIAV / Gag / capsid / IP6 / phytic acid / inositolhexakiphosphate | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationviral budding via host ESCRT complex / viral nucleocapsid / structural constituent of virion / nucleic acid binding / zinc ion binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Equine infectious anemia virus Equine infectious anemia virus | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / subtomogram averaging / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.8 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Dick, R.A. / Xu, C. / Morado, D.R. / Kravchuk, V. / Ricana, C.L. / Lyddon, T.D. / Broad, A.M. / Feathers, J.R. / Johnson, M.C. / Vogt, V.M. ...Dick, R.A. / Xu, C. / Morado, D.R. / Kravchuk, V. / Ricana, C.L. / Lyddon, T.D. / Broad, A.M. / Feathers, J.R. / Johnson, M.C. / Vogt, V.M. / Perilla, J.R. / Briggs, J.A.G. / Schur, F.K.M. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Austria, Austria,  United States, United States,  United Kingdom, United Kingdom,  Germany, 10items Germany, 10items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: PLoS Pathog / Year: 2020 Journal: PLoS Pathog / Year: 2020Title: Structures of immature EIAV Gag lattices reveal a conserved role for IP6 in lentivirus assembly. Authors: Robert A Dick / Chaoyi Xu / Dustin R Morado / Vladyslav Kravchuk / Clifton L Ricana / Terri D Lyddon / Arianna M Broad / J Ryan Feathers / Marc C Johnson / Volker M Vogt / Juan R Perilla / ...Authors: Robert A Dick / Chaoyi Xu / Dustin R Morado / Vladyslav Kravchuk / Clifton L Ricana / Terri D Lyddon / Arianna M Broad / J Ryan Feathers / Marc C Johnson / Volker M Vogt / Juan R Perilla / John A G Briggs / Florian K M Schur /     Abstract: Retrovirus assembly is driven by the multidomain structural protein Gag. Interactions between the capsid domains (CA) of Gag result in Gag multimerization, leading to an immature virus particle that ...Retrovirus assembly is driven by the multidomain structural protein Gag. Interactions between the capsid domains (CA) of Gag result in Gag multimerization, leading to an immature virus particle that is formed by a protein lattice based on dimeric, trimeric, and hexameric protein contacts. Among retroviruses the inter- and intra-hexamer contacts differ, especially in the N-terminal sub-domain of CA (CANTD). For HIV-1 the cellular molecule inositol hexakisphosphate (IP6) interacts with and stabilizes the immature hexamer, and is required for production of infectious virus particles. We have used in vitro assembly, cryo-electron tomography and subtomogram averaging, atomistic molecular dynamics simulations and mutational analyses to study the HIV-related lentivirus equine infectious anemia virus (EIAV). In particular, we sought to understand the structural conservation of the immature lentivirus lattice and the role of IP6 in EIAV assembly. Similar to HIV-1, IP6 strongly promoted in vitro assembly of EIAV Gag proteins into virus-like particles (VLPs), which took three morphologically highly distinct forms: narrow tubes, wide tubes, and spheres. Structural characterization of these VLPs to sub-4Å resolution unexpectedly showed that all three morphologies are based on an immature lattice with preserved key structural components, highlighting the structural versatility of CA to form immature assemblies. A direct comparison between EIAV and HIV revealed that both lentiviruses maintain similar immature interfaces, which are established by both conserved and non-conserved residues. In both EIAV and HIV-1, IP6 regulates immature assembly via conserved lysine residues within the CACTD and SP. Lastly, we demonstrate that IP6 stimulates in vitro assembly of immature particles of several other retroviruses in the lentivirus genus, suggesting a conserved role for IP6 in lentiviral assembly. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6t63.cif.gz 6t63.cif.gz | 712 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6t63.ent.gz pdb6t63.ent.gz | 569.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6t63.json.gz 6t63.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/t6/6t63 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/t6/6t63 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/t6/6t63 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/t6/6t63 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  10383MC  6t61C  6t64C C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 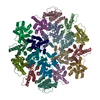
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 54881.535 Da / Num. of mol.: 18 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Equine infectious anemia virus / Gene: gag / Production host: Equine infectious anemia virus / Gene: gag / Production host:  Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: subtomogram averaging |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Equine infectious anemia virus / Type: VIRUS Details: Gag construct was expressed in E.coli and purified using the SUMO-tag system. Assembly was performed at pH6. Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Equine infectious anemia virus Equine infectious anemia virus | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details of virus | Empty: YES / Enveloped: NO / Isolate: OTHER / Type: VIRUS-LIKE PARTICLE | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural host | Organism: Equus caballus | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Virus shell | Name: Capsid / Diameter: 350 nm | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES Details: Virus-like-particles (tubular) of EIAV Gag deltaMAdeltap9 (referred to as Gag deltaMA) assembled at pH6. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: 20mA / Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: C-flat-2/2 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK II / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 90 % / Chamber temperature: 15 K / Details: 1-2 seconds blot time, offset -3mm |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS / Details: nanoprobe |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 130000 X / Nominal defocus max: -3500 nm / Nominal defocus min: -1500 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm / Alignment procedure: ZEMLIN TABLEAU |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 1.4 sec. / Electron dose: 3.4 e/Å2 / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 Details: Data was acquired using a dose-symmetric tilt acquisition scheme, as described in Hagen et al, 2017, J. Struct. Biol, 197(2):191-8 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Quantum LS / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
| Image scans | Width: 3708 / Height: 3838 / Movie frames/image: 21 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image processing | Details: Tilt series were low-pass filtered according to their cumulative dose using exposure filters that were calculated using an exposure-dependent amplitude attenuation function and critical ...Details: Tilt series were low-pass filtered according to their cumulative dose using exposure filters that were calculated using an exposure-dependent amplitude attenuation function and critical exposure constants (as published in Grant & Grigorieff, Elife, 2015). Tilt series were aligned and reconstructed in IMOD. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Details: CTF-correction was performed using NOVACTF / Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C2 (2 fold cyclic) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 112929 / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EM volume selection | Method: Subvolumes were defined according to their position on the VLPs Details: Subtomogram extraction positions were defined in Amira using the electron microscopy toolbox by determing the radii and the spline of the VLPs. Initially, positions were oversampled and ...Details: Subtomogram extraction positions were defined in Amira using the electron microscopy toolbox by determing the radii and the spline of the VLPs. Initially, positions were oversampled and subsequently cleaned during alignments using cross-correlation and distance thresholds. Num. of tomograms: 56 / Num. of volumes extracted: 357324 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: OTHER / Space: REAL / Target criteria: Cross-correlation coefficient Details: Rigid body fitting was done in Chimera. Missing residues were built de novo in Coot. Refinement was performed iteratively in Phenix and Coot. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 2EIA Accession code: 2EIA / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj

