+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6p07 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
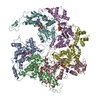
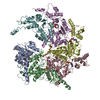
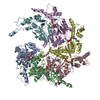
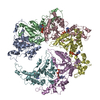
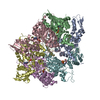
| Title | Spastin hexamer in complex with substrate | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MOTOR PROTEIN / AAA+ ATPase / Homohexamer / Microtubule Severing Enzyme | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmicrotubule-severing ATPase / microtubule severing ATPase activity / microtubule severing / mitotic chromosome movement towards spindle pole / positive regulation of microtubule depolymerization / mitotic spindle elongation / protein hexamerization / regulation of synapse structure or activity / isomerase activity / lipid droplet ...microtubule-severing ATPase / microtubule severing ATPase activity / microtubule severing / mitotic chromosome movement towards spindle pole / positive regulation of microtubule depolymerization / mitotic spindle elongation / protein hexamerization / regulation of synapse structure or activity / isomerase activity / lipid droplet / adult locomotory behavior / spindle / nervous system development / chromosome / microtubule binding / microtubule / cell differentiation / cell division / centrosome / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / identical protein binding / membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
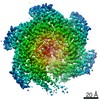
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Sandate, C.R. / Szyk, A. / Zehr, E. / Roll-Mecak, A. / Lander, G.C. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2019 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2019Title: An allosteric network in spastin couples multiple activities required for microtubule severing. Authors: Colby R Sandate / Agnieszka Szyk / Elena A Zehr / Gabriel C Lander / Antonina Roll-Mecak /  Abstract: The AAA+ ATPase spastin remodels microtubule arrays through severing and its mutation is the most common cause of hereditary spastic paraplegias (HSP). Polyglutamylation of the tubulin C-terminal ...The AAA+ ATPase spastin remodels microtubule arrays through severing and its mutation is the most common cause of hereditary spastic paraplegias (HSP). Polyglutamylation of the tubulin C-terminal tail recruits spastin to microtubules and modulates severing activity. Here, we present a ~3.2 Å resolution cryo-EM structure of the Drosophila melanogaster spastin hexamer with a polyglutamate peptide bound in its central pore. Two electropositive loops arranged in a double-helical staircase coordinate the substrate sidechains. The structure reveals how concurrent nucleotide and substrate binding organizes the conserved spastin pore loops into an ordered network that is allosterically coupled to oligomerization, and suggests how tubulin tail engagement activates spastin for microtubule disassembly. This allosteric coupling may apply generally in organizing AAA+ protein translocases into their active conformations. We show that this allosteric network is essential for severing and is a hotspot for HSP mutations. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6p07.cif.gz 6p07.cif.gz | 329 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6p07.ent.gz pdb6p07.ent.gz | 261.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6p07.json.gz 6p07.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/p0/6p07 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/p0/6p07 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/p0/6p07 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/p0/6p07 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  20226MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 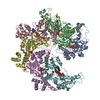
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 54183.473 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Mutation: E583Q Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: spas, D-spastin, Dmel\CG5977, Dspastin, Spas, Spastin, CG5977, Dmel_CG5977 Production host:  References: UniProt: A0A126GV13, UniProt: A0A0B4LHJ5*PLUS, microtubule-severing ATPase #2: Protein/peptide | | Mass: 1954.722 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  #3: Chemical | ChemComp-ATP / #4: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #5: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: complex of spastin homohexamer bound to polyglutmate peptide Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#2 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 294 kDa/nm / Experimental value: YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 1.2 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: Grids were plasma-cleaned using a Solarus plasma cleaner (Gatan, Inc.) Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil, UltrAuFoil, R1.2/1.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 90 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K Details: Sample was blotted approximately 4 seconds using Whatman No. 1 filter paper before plunge-freezing. |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 36000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 70 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Temperature (max): 70 K / Temperature (min): 70 K |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 12 sec. / Electron dose: 52 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 2 / Num. of real images: 2534 |
| Image scans | Sampling size: 5 µm / Width: 3710 / Height: 3838 / Movie frames/image: 48 / Used frames/image: 1-48 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.12_2829: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Image processing | Details: Collected in counting mode, 48 frames movie-1, exposure time 12 s (250 ms frames), exposure rate of ~5.6 e- pixel-1 s-1, total exposure of ~52 e- angstrom-2 (1.08 e- angstrom-2 frame-1). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Details: CTF correction performed per-particle in CryoSparc / Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 2736865 / Details: Template-picked particles | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
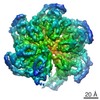
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 488385 / Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj








