+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6o7k | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
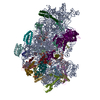
| Title | 30S initiation complex | |||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | RIBOSOME / 30S Initiation complex with IF1 / IF2 and P/I tRNA | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationtranslation initiation factor activity / small ribosomal subunit / small ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic small ribosomal subunit / cytoplasmic translation / tRNA binding / rRNA binding / structural constituent of ribosome / ribosome / translation ...translation initiation factor activity / small ribosomal subunit / small ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic small ribosomal subunit / cytoplasmic translation / tRNA binding / rRNA binding / structural constituent of ribosome / ribosome / translation / ribonucleoprotein complex / GTPase activity / mRNA binding / GTP binding / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.2 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Frank, J. / Gonzalez Jr., R.L. / kaledhonkar, S. / Fu, Z. / Caban, K. / Li, W. / Chen, B. / Sun, M. | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 4items United States, 4items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2019 Journal: Nature / Year: 2019Title: Late steps in bacterial translation initiation visualized using time-resolved cryo-EM. Authors: Sandip Kaledhonkar / Ziao Fu / Kelvin Caban / Wen Li / Bo Chen / Ming Sun / Ruben L Gonzalez / Joachim Frank /  Abstract: The initiation of bacterial translation involves the tightly regulated joining of the 50S ribosomal subunit to an initiator transfer RNA (fMet-tRNA)-containing 30S ribosomal initiation complex to ...The initiation of bacterial translation involves the tightly regulated joining of the 50S ribosomal subunit to an initiator transfer RNA (fMet-tRNA)-containing 30S ribosomal initiation complex to form a 70S initiation complex, which subsequently matures into a 70S elongation-competent complex. Rapid and accurate formation of the 70S initiation complex is promoted by initiation factors, which must dissociate from the 30S initiation complex before the resulting 70S elongation-competent complex can begin the elongation of translation. Although comparisons of the structures of the 30S and 70S initiation complexes have revealed that the ribosome, initiation factors and fMet-tRNA can acquire different conformations in these complexes, the timing of conformational changes during formation of the 70S initiation complex, the structures of any intermediates formed during these rearrangements, and the contributions that these dynamics might make to the mechanism and regulation of initiation remain unknown. Moreover, the absence of a structure of the 70S elongation-competent complex formed via an initiation-factor-catalysed reaction has precluded an understanding of the rearrangements to the ribosome, initiation factors and fMet-tRNA that occur during maturation of a 70S initiation complex into a 70S elongation-competent complex. Here, using time-resolved cryogenic electron microscopy, we report the near-atomic-resolution view of how a time-ordered series of conformational changes drive and regulate subunit joining, initiation factor dissociation and fMet-tRNA positioning during formation of the 70S elongation-competent complex. Our results demonstrate the power of time-resolved cryogenic electron microscopy to determine how a time-ordered series of conformational changes contribute to the mechanism and regulation of one of the most fundamental processes in biology. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6o7k.cif.gz 6o7k.cif.gz | 1.3 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6o7k.ent.gz pdb6o7k.ent.gz | 959.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6o7k.json.gz 6o7k.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o7/6o7k https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o7/6o7k ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o7/6o7k ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o7/6o7k | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  0643MC  0661C  0662C  6o9jC  6o9kC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Translation initiation factor IF- ... , 2 types, 2 molecules 5f
| #1: Protein | Mass: 8116.468 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 54866.508 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-RNA chain , 3 types, 3 molecules gvN
| #3: RNA chain | Mass: 498725.406 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #24: RNA chain | Mass: 24786.785 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #25: RNA chain | Mass: 1900.198 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-30S ribosomal protein ... , 20 types, 20 molecules Prqtswuy1zj32hlknmpo
| #4: Protein | Mass: 9263.946 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #5: Protein | Mass: 11196.988 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #6: Protein | Mass: 12487.200 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #7: Protein | Mass: 13636.961 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #8: Protein | Mass: 12625.753 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #9: Protein | Mass: 11489.390 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #10: Protein | Mass: 10159.621 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #11: Protein | Mass: 9207.572 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #12: Protein | Mass: 6466.477 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #13: Protein | Mass: 9057.626 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #14: Protein | Mass: 24253.943 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #15: Protein | Mass: 9506.190 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #16: Protein | Mass: 6067.081 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #17: Protein | Mass: 23078.785 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #18: Protein | Mass: 23383.002 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #19: Protein | Mass: 15804.282 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #20: Protein | Mass: 11669.371 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #21: Protein | Mass: 16861.523 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #22: Protein | Mass: 14015.361 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #23: Protein | Mass: 14554.882 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-Details
| Has protein modification | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: 70S elongation competent ribosome / Type: RIBOSOME / Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Details: unspecified |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F30 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TECNAI F30 |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: DARK FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 35 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: MDFF / Category: model fitting |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 86367 / Symmetry type: POINT |
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL |
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 2AVY 2avy Accession code: 2AVY / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj






























