[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-6339: Molecular architecture of the Ub-PCNA/Pol eta complex bound to DNA -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-6339 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
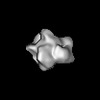
| Title | Molecular architecture of the Ub-PCNA/Pol eta complex bound to DNA | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Reconstruction of Ub-PCNA/Pol eta/DNA ternary complex | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Translesion synthesis / DNA damage tolerance / Y-Family polymerase / PCNA monoubiquitination | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of deoxyribonuclease activity / dinucleotide insertion or deletion binding / PCNA-p21 complex / mitotic telomere maintenance via semi-conservative replication / purine-specific mismatch base pair DNA N-glycosylase activity / nuclear lamina / Polymerase switching / positive regulation of DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity / Processive synthesis on the lagging strand / MutLalpha complex binding ...positive regulation of deoxyribonuclease activity / dinucleotide insertion or deletion binding / PCNA-p21 complex / mitotic telomere maintenance via semi-conservative replication / purine-specific mismatch base pair DNA N-glycosylase activity / nuclear lamina / Polymerase switching / positive regulation of DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity / Processive synthesis on the lagging strand / MutLalpha complex binding / PCNA complex / Telomere C-strand (Lagging Strand) Synthesis / Removal of the Flap Intermediate / Mismatch repair (MMR) directed by MSH2:MSH3 (MutSbeta) / Mismatch repair (MMR) directed by MSH2:MSH6 (MutSalpha) / Transcription of E2F targets under negative control by DREAM complex / Polymerase switching on the C-strand of the telomere / replisome / Processive synthesis on the C-strand of the telomere / response to L-glutamate / response to UV-C / Removal of the Flap Intermediate from the C-strand / error-free translesion synthesis / response to dexamethasone / DNA synthesis involved in DNA repair / histone acetyltransferase binding / DNA polymerase processivity factor activity / leading strand elongation / G1/S-Specific Transcription / nuclear replication fork / replication fork processing / SUMOylation of DNA replication proteins / cellular response to UV-C / pyrimidine dimer repair / PCNA-Dependent Long Patch Base Excision Repair / error-prone translesion synthesis / response to cadmium ion / estrous cycle / mismatch repair / regulation of DNA repair / translesion synthesis / cyclin-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme complex / base-excision repair, gap-filling / DNA polymerase binding / epithelial cell differentiation / liver regeneration / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Genes Involved in G2 Cell Cycle Arrest / positive regulation of DNA replication / nuclear estrogen receptor binding / replication fork / Translesion synthesis by REV1 / positive regulation of DNA repair / Translesion synthesis by POLK / Translesion synthesis by POLI / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in GG-NER / male germ cell nucleus / Termination of translesion DNA synthesis / response to radiation / Translesion Synthesis by POLH / Recognition of DNA damage by PCNA-containing replication complex / receptor tyrosine kinase binding / HDR through Homologous Recombination (HRR) / cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus / Dual Incision in GG-NER / cellular response to hydrogen peroxide / Dual incision in TC-NER / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / cellular response to UV / response to estradiol / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / site of double-strand break / heart development / chromatin organization / DNA-directed DNA polymerase / damaged DNA binding / DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity / DNA replication / chromosome, telomeric region / nuclear body / DNA repair / chromatin binding / centrosome / chromatin / protein-containing complex binding / enzyme binding / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / extracellular exosome / zinc ion binding / nucleoplasm / identical protein binding / nucleus / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / negative staining / Resolution: 22.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Lau WCY / Li Y / Zhang Q / Huen MSY | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Rep / Year: 2015 Journal: Sci Rep / Year: 2015Title: Molecular architecture of the Ub-PCNA/Pol η complex bound to DNA. Authors: Wilson C Y Lau / Yinyin Li / Qinfen Zhang / Michael S Y Huen /  Abstract: Translesion synthesis (TLS) is the mechanism by which DNA polymerases replicate through unrepaired DNA lesions. TLS is activated by monoubiquitination of the homotrimeric proliferating cell nuclear ...Translesion synthesis (TLS) is the mechanism by which DNA polymerases replicate through unrepaired DNA lesions. TLS is activated by monoubiquitination of the homotrimeric proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) at lysine-164, followed by the switch from replicative to specialized polymerases at DNA damage sites. Pol η belongs to the Y-Family of specialized polymerases that can efficiently bypass UV-induced lesions. Like other members of the Y-Family polymerases, its recruitment to the damaged sites is mediated by the interaction with monoubiquitinated PCNA (Ub-PCNA) via its ubiquitin-binding domain and non-canonical PCNA-interacting motif in the C-terminal region. The structural determinants underlying the direct recognition of Ub-PCNA by Pol η, or Y-Family polymerases in general, remain largely unknown. Here we report a structure of the Ub-PCNA/Pol η complex bound to DNA determined by single-particle electron microscopy (EM). The overall obtained structure resembles that of the editing PCNA/PolB complex. Analysis of the map revealed the conformation of ubiquitin that binds the C-terminal domain of Pol η. Our present study suggests that the Ub-PCNA/Pol η interaction requires the formation of a structured binding interface, which is dictated by the inherent flexibility of Ub-PCNA. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_6339.map.gz emd_6339.map.gz | 3.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-6339-v30.xml emd-6339-v30.xml emd-6339.xml emd-6339.xml | 10.9 KB 10.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  400_6339.gif 400_6339.gif 80_6339.gif 80_6339.gif | 43.4 KB 4 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6339 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6339 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6339 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6339 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
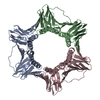
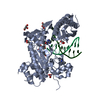
| Related structure data |  3ja9MC 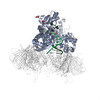 3jaaMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_6339.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 4.2 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_6339.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 4.2 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Reconstruction of Ub-PCNA/Pol eta/DNA ternary complex | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 2.14 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Ub-PCNA/Pol eta/DNA
| Entire | Name: Ub-PCNA/Pol eta/DNA |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: Ub-PCNA/Pol eta/DNA
| Supramolecule | Name: Ub-PCNA/Pol eta/DNA / type: sample / ID: 1000 / Details: The sample was monodisperse Oligomeric state: Monomeric catalytic core of Pol eta binds to one homotrimeric Ub-PCNA Number unique components: 2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental: 200 KDa / Theoretical: 200 KDa / Method: Chemical crosslinking, SDS-PAGE |
-Macromolecule #1: Monoubiquitinated PCNA
| Macromolecule | Name: Monoubiquitinated PCNA / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Oligomeric state: trimer / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human |
| Molecular weight | Experimental: 120 KDa / Theoretical: 120 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #2: Pol eta
| Macromolecule | Name: Pol eta / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Oligomeric state: Monomer / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | negative staining |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.1 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 / Details: 50mM Tris-HCl, 5mM MgCl2 |
| Staining | Type: NEGATIVE Details: Grids with adsorbed protein floated on two 20ul drops of 2% w/v uranyl acetate solution for 30 seconds |
| Grid | Details: Continuous carbon coated copper grids (Ted Pella), glow-discharged for 30 seconds |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: NONE / Instrument: OTHER |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | JEOL 2010 |
|---|---|
| Date | Nov 12, 2014 |
| Image recording | Category: CCD / Film or detector model: GATAN ULTRASCAN 4000 (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 18 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source: LAB6 |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 50000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: SIDE ENTRY, EUCENTRIC |
- Image processing
Image processing
| CTF correction | Details: Particles |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Algorithm: OTHER / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 22.0 Å / Resolution method: OTHER / Software - Name: EMAN2 / Number images used: 7330 |
| Final two d classification | Number classes: 227 |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | PDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Software | Name:  Chimera Chimera |
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
| Output model |  PDB-3ja9:  PDB-3jaa: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






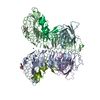
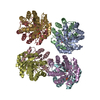
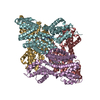
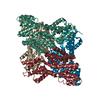


















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)