[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
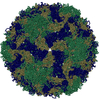
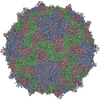
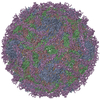
Yorodumi- PDB-5lk7: Single particle reconstruction of slow bee paralysis virus virion... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5lk7 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
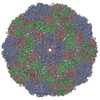
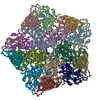
| Title | Single particle reconstruction of slow bee paralysis virus virion at pH 5.5 | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRUS / icosahedral virus / honebee virus / iflavirus | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationhost cell membrane / viral capsid / RNA helicase activity / cysteine-type endopeptidase activity / viral RNA genome replication / RNA-directed RNA polymerase activity / DNA-templated transcription / structural molecule activity / proteolysis / RNA binding / ATP binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Slow bee paralysis virus Slow bee paralysis virus | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.42 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Kalynych, S. / Fuzik, T. / Plevka, P. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2017 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2017Title: Cryo-EM study of slow bee paralysis virus at low pH reveals iflavirus genome release mechanism. Authors: Sergei Kalynych / Tibor Füzik / Antonín Přidal / Joachim de Miranda / Pavel Plevka /   Abstract: Viruses from the family Iflaviridae are insect pathogens. Many of them, including slow bee paralysis virus (SBPV), cause lethal diseases in honeybees and bumblebees, resulting in agricultural losses. ...Viruses from the family Iflaviridae are insect pathogens. Many of them, including slow bee paralysis virus (SBPV), cause lethal diseases in honeybees and bumblebees, resulting in agricultural losses. Iflaviruses have nonenveloped icosahedral virions containing single-stranded RNA genomes. However, their genome release mechanism is unknown. Here, we show that low pH promotes SBPV genome release, indicating that the virus may use endosomes to enter host cells. We used cryo-EM to study a heterogeneous population of SBPV virions at pH 5.5. We determined the structures of SBPV particles before and after genome release to resolutions of 3.3 and 3.4 Å, respectively. The capsids of SBPV virions in low pH are not expanded. Thus, SBPV does not appear to form "altered" particles with pores in their capsids before genome release, as is the case in many related picornaviruses. The egress of the genome from SBPV virions is associated with a loss of interpentamer contacts mediated by N-terminal arms of VP2 capsid proteins, which result in the expansion of the capsid. Pores that are 7 Å in diameter form around icosahedral threefold symmetry axes. We speculate that they serve as channels for the genome release. Our findings provide an atomic-level characterization of the genome release mechanism of iflaviruses. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5lk7.cif.gz 5lk7.cif.gz | 160.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5lk7.ent.gz pdb5lk7.ent.gz | 123.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5lk7.json.gz 5lk7.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/lk/5lk7 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/lk/5lk7 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/lk/5lk7 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/lk/5lk7 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 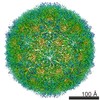 4063MC  4064C  5lk8C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 | x 60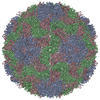
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 30307.211 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Slow bee paralysis virus / References: UniProt: A7LM73 Slow bee paralysis virus / References: UniProt: A7LM73 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 29824.205 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Slow bee paralysis virus / References: UniProt: A7LM73 Slow bee paralysis virus / References: UniProt: A7LM73 |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 47623.910 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Slow bee paralysis virus / References: UniProt: A7LM73 Slow bee paralysis virus / References: UniProt: A7LM73 |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Slow bee paralysis virus / Type: VIRUS / Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Slow bee paralysis virus Slow bee paralysis virus |
| Details of virus | Empty: NO / Enveloped: NO / Isolate: SPECIES / Type: VIRION |
| Natural host | Organism: Apis mellifera / Strain: 3 |
| Virus shell | Name: icosahedral |
| Buffer solution | pH: 5.5 / Details: 30 mM Sodium Acetate 50 mM Sodium Chloride |
| Specimen | Conc.: 1.8 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES Details: sample was purifed froim natural source and dialyzed overnight into sodium acetate buffer |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/1 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Details: blot force 0, blot time 2 s. |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 75000 X / Nominal defocus max: 3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 0.5 sec. / Electron dose: 21 e/Å2 / Detector mode: INTEGRATING / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 5325 |
| Image scans | Width: 4096 / Height: 4096 / Movie frames/image: 7 / Used frames/image: 1-7 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 4712 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.42 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 10350 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 49.7 / Protocol: OTHER / Space: RECIPROCAL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj
