+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 | データベース: PDB / ID: 5fwp | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
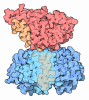
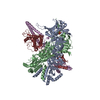
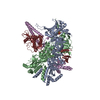
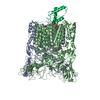
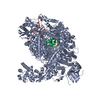
| タイトル | Atomic cryoEM structure of Hsp90-Cdc37-Cdk4 complex | |||||||||
 要素 要素 |
| |||||||||
 キーワード キーワード | CHAPERONE / HSP90 / CDC37 / CDK4 / KINASE / UNFOLDING | |||||||||
| 機能・相同性 |  機能・相同性情報 機能・相同性情報cyclin D3-CDK4 complex / cyclin D1-CDK4 complex / cyclin D2-CDK4 complex / Evasion of Oncogene Induced Senescence Due to Defective p16INK4A binding to CDK4 / Evasion of Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence Due to Defective p16INK4A binding to CDK4 / regulation of transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II / Evasion of Oncogene Induced Senescence Due to Defective p16INK4A binding to CDK4 and CDK6 / Evasion of Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence Due to Defective p16INK4A binding to CDK4 and CDK6 / Drug-mediated inhibition of CDK4/CDK6 activity / regulation of type II interferon-mediated signaling pathway ...cyclin D3-CDK4 complex / cyclin D1-CDK4 complex / cyclin D2-CDK4 complex / Evasion of Oncogene Induced Senescence Due to Defective p16INK4A binding to CDK4 / Evasion of Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence Due to Defective p16INK4A binding to CDK4 / regulation of transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II / Evasion of Oncogene Induced Senescence Due to Defective p16INK4A binding to CDK4 and CDK6 / Evasion of Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence Due to Defective p16INK4A binding to CDK4 and CDK6 / Drug-mediated inhibition of CDK4/CDK6 activity / regulation of type II interferon-mediated signaling pathway / regulation of type B pancreatic cell proliferation / HSP90-CDC37 chaperone complex / negative regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process / Aryl hydrocarbon receptor signalling / aryl hydrocarbon receptor complex / cellular response to ionomycin / histone methyltransferase binding / Transcriptional regulation by RUNX2 / dynein axonemal particle / cellular response to phorbol 13-acetate 12-myristate / receptor ligand inhibitor activity / positive regulation of type 2 mitophagy / regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity / protein kinase regulator activity / ATP-dependent protein binding / positive regulation of protein localization to cell surface / protein folding chaperone complex / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase regulator activity / post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression / Respiratory syncytial virus genome replication / telomerase holoenzyme complex assembly / positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway / Uptake and function of diphtheria toxin / Drug-mediated inhibition of ERBB2 signaling / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to trastuzumab / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to sapitinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to tesevatinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to neratinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to osimertinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to afatinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to AEE788 / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to lapatinib / Drug resistance in ERBB2 TMD/JMD mutants / PTK6 Regulates Cell Cycle / regulation of type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway / dendritic growth cone / TPR domain binding / Defective binding of RB1 mutants to E2F1,(E2F2, E2F3) / Assembly and release of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) virions / protein phosphatase activator activity / The NLRP3 inflammasome / Sema3A PAK dependent Axon repulsion / regulation of protein ubiquitination / HSF1-dependent transactivation / positive regulation of G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / bicellular tight junction / response to unfolded protein / cyclin-dependent kinase / HSF1 activation / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity / Attenuation phase / chaperone-mediated protein complex assembly / RHOBTB2 GTPase cycle / axonal growth cone / telomere maintenance via telomerase / protein targeting / Purinergic signaling in leishmaniasis infection / cyclin-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme complex / : / regulation of G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / supramolecular fiber organization / DNA polymerase binding / heat shock protein binding / Signaling by ERBB2 / protein folding chaperone / peptide binding / negative regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / cellular response to interleukin-4 / ESR-mediated signaling / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / Constitutive Signaling by Overexpressed ERBB2 / cyclin binding / placenta development / nitric-oxide synthase regulator activity / Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of Cyclin D / positive regulation of cell differentiation / ATP-dependent protein folding chaperone / Signaling by ERBB2 TMD/JMD mutants / Hsp90 protein binding / G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / Constitutive Signaling by EGFRvIII / Signaling by ERBB2 ECD mutants / Signaling by ERBB2 KD Mutants / Oncogene Induced Senescence / DDX58/IFIH1-mediated induction of interferon-alpha/beta / Regulation of actin dynamics for phagocytic cup formation / Transcriptional regulation of white adipocyte differentiation / Regulation of necroptotic cell death / Meiotic recombination / histone deacetylase binding 類似検索 - 分子機能 | |||||||||
| 生物種 |  HOMO SAPIENS (ヒト) HOMO SAPIENS (ヒト) | |||||||||
| 手法 | 電子顕微鏡法 / 単粒子再構成法 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 7.2 Å | |||||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Verba, K.A. / Wang, R.Y.R. / Arakawa, A. / Liu, Y. / Yokoyama, S. / Agard, D.A. | |||||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: Science / 年: 2016 ジャーナル: Science / 年: 2016タイトル: Atomic structure of Hsp90-Cdc37-Cdk4 reveals that Hsp90 traps and stabilizes an unfolded kinase. 著者: Kliment A Verba / Ray Yu-Ruei Wang / Akihiko Arakawa / Yanxin Liu / Mikako Shirouzu / Shigeyuki Yokoyama / David A Agard /   要旨: The Hsp90 molecular chaperone and its Cdc37 cochaperone help stabilize and activate more than half of the human kinome. However, both the mechanism by which these chaperones assist their "client" ...The Hsp90 molecular chaperone and its Cdc37 cochaperone help stabilize and activate more than half of the human kinome. However, both the mechanism by which these chaperones assist their "client" kinases and the reason why some kinases are addicted to Hsp90 while closely related family members are independent are unknown. Our structural understanding of these interactions is lacking, as no full-length structures of human Hsp90, Cdc37, or either of these proteins with a kinase have been elucidated. Here we report a 3.9 angstrom cryo-electron microscopy structure of the Hsp90-Cdc37-Cdk4 kinase complex. Surprisingly, the two lobes of Cdk4 are completely separated with the β4-β5 sheet unfolded. Cdc37 mimics part of the kinase N lobe, stabilizing an open kinase conformation by wedging itself between the two lobes. Finally, Hsp90 clamps around the unfolded kinase β5 strand and interacts with exposed N- and C-lobe interfaces, protecting the kinase in a trapped unfolded state. On the basis of this structure and an extensive amount of previously collected data, we propose unifying conceptual and mechanistic models of chaperone-kinase interactions. | |||||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
| ムービー |
 ムービービューア ムービービューア |
|---|---|
| 構造ビューア | 分子:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
- ダウンロード
ダウンロード
| PDBx/mmCIF形式 |  5fwp.cif.gz 5fwp.cif.gz | 593.1 KB | 表示 |  PDBx/mmCIF形式 PDBx/mmCIF形式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB形式 |  pdb5fwp.ent.gz pdb5fwp.ent.gz | 475.6 KB | 表示 |  PDB形式 PDB形式 |
| PDBx/mmJSON形式 |  5fwp.json.gz 5fwp.json.gz | ツリー表示 |  PDBx/mmJSON形式 PDBx/mmJSON形式 | |
| その他 |  その他のダウンロード その他のダウンロード |
-検証レポート
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fw/5fwp https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fw/5fwp ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fw/5fwp ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fw/5fwp | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-関連構造データ
| 関連構造データ |  3340MC 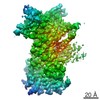 3337C 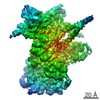 3338C  3339C  3341C  3342C  3343C  3344C 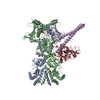 5fwkC 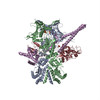 5fwlC 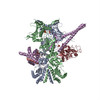 5fwmC C: 同じ文献を引用 ( M: このデータのモデリングに利用したマップデータ |
|---|---|
| 類似構造データ |
- リンク
リンク
- 集合体
集合体
| 登録構造単位 | 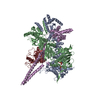
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- 要素
要素
| #1: タンパク質 | 分子量: 83645.539 Da / 分子数: 2 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 詳細: ATP / 由来: (組換発現)  HOMO SAPIENS (ヒト) / プラスミド: PFASTBACHT HOMO SAPIENS (ヒト) / プラスミド: PFASTBACHT発現宿主:  参照: UniProt: P08238 #2: タンパク質 | | 分子量: 44622.363 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  HOMO SAPIENS (ヒト) / プラスミド: PFASTBACHT HOMO SAPIENS (ヒト) / プラスミド: PFASTBACHT発現宿主:  参照: UniProt: Q16543 #3: タンパク質 | | 分子量: 34520.629 Da / 分子数: 1 / Fragment: KINASE DOMAIN / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  HOMO SAPIENS (ヒト) / プラスミド: PFASTBACHT HOMO SAPIENS (ヒト) / プラスミド: PFASTBACHT発現宿主:  参照: UniProt: P11802 #4: 化合物 | #5: 化合物 | Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-実験情報
-実験
| 実験 | 手法: 電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
| EM実験 | 試料の集合状態: PARTICLE / 3次元再構成法: 単粒子再構成法 |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 構成要素 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分子量 | 値: 0.245 MDa / 実験値: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 緩衝液 | pH: 7.5 詳細: 20mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 150 mM NaCl, 10 mM KCl, 10 mM MgCl2, 20 mM Na2MoO4, 2mM DTT, 0.085mM DDM | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 試料 | 濃度: 0.27 mg/ml / 包埋: NO / シャドウイング: NO / 染色: NO / 凍結: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 試料支持 | 詳細: HOLEY CARBON | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 急速凍結 | 装置: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / 凍結剤: ETHANE / Temp: 95 K / 湿度: 90 % / 凍結前の試料温度: 293 K / 詳細: LIQUID ETHANE / 手法: Single blot from 4 to 6 seconds, at 20C |
- 電子顕微鏡撮影
電子顕微鏡撮影
| 実験機器 |  モデル: Titan Krios / 画像提供: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| 顕微鏡 | モデル: FEI TITAN KRIOS / 日付: 2014年11月25日 |
| 電子銃 | 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: OTHER |
| 電子レンズ | モード: BRIGHT FIELD / 倍率(公称値): 22500 X / 最大 デフォーカス(公称値): 3800 nm / 最小 デフォーカス(公称値): 1400 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| 試料ホルダ | 試料ホルダーモデル: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| 撮影 | 平均露光時間: 7.6 sec. / 電子線照射量: 44 e/Å2 フィルム・検出器のモデル: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) 実像数: 3718 / 詳細: 38 frames |
- 解析
解析
| EMソフトウェア |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 画像処理 | 詳細: Image stacks were corrected for motion and summed as described previously, resulting in binned sums (1.315A/pix). For particle picking the images were binned to 5.2A/pix and Gaussian bandpass ...詳細: Image stacks were corrected for motion and summed as described previously, resulting in binned sums (1.315A/pix). For particle picking the images were binned to 5.2A/pix and Gaussian bandpass filtered between 15A and 500A using EMAN2. SamViewer template based picking was then used to pick particles from all the micrographs, followed by manual review of all the picks. After such procedure 802877 particles were picked in total and extracted from images binned to 2.6A/pix. CTFFIND4 was used to estimate defocus parameters for all the images. Relion 1.4 was used for all the following steps unless noted otherwise. Reference free 2D classification into 300 classes for 75 iterations was performed followed by manual examination of the resulting class averages. Low resolution/signal to noise/feature class averages and contributing particles were discarded, resulting in 670000 particles left. The resulting particles were 3D classified into 4 classes resulting in two classes having high-resolution features (390000 particles). At this stage particles were extracted from 1.315A/pix micrographs and all the following processing was done with these particles. Using 3D Auto-refine in Relion 1.4, a reconstruction was obtained from 390000 particles resulting from 3D classification above (using highest resolution 3D class as initial model, low pass filtered to 20A). Using the resulting parameters, the particles were further drift corrected per particle and dose weighted using the Particle Polishing feature. The B-factor weighing curve was fit by a polynomial (with a rationale that such a curve should be smooth) and used to generate new weighting parameters for Particle Polishing, with which 390000 particles were then polished. All further data processing was done using the polished particles. Re-refinement of the 390000 particles after polishing yielded the map at about 4A resolution (determined using gold standard FSC in the PostProcessing tab). The 390000 particles were then 3D classified into four different classes without particle re-alignment, using the alignment parameters from 4A reconstruction. Particles contributing to each of the four classes were grouped and a full 3D refinement with a spherical 200A mask was performed with each of the four groups of particles using the same initial model, low pass filtered to 20A. This is one of the resulting reconstructions. | ||||||||||||
| 粒子像の選択 | 選択した粒子像数: 114683 | ||||||||||||
| 対称性 | 点対称性: C1 (非対称) | ||||||||||||
| 3次元再構成 | 手法: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / 解像度: 7.2 Å / 粒子像の数: 114683 / ピクセルサイズ(実測値): 1.315 Å 詳細: SUBMISSION BASED ON EXPERIMENTAL DATA FROM EMDB EMD-3340. (DEPOSITION ID: 14281). Refinement type: HALF-MAPS REFINED INDEPENDENTLY / 対称性のタイプ: POINT | ||||||||||||
| 原子モデル構築 | B value: 141 / プロトコル: FLEXIBLE FIT / 空間: REAL 詳細: Cdc37 crystal structure from PDB:1US7 was fit into EMD-3340 manually and then with UCSF Chimera "Fit In Map" tool. The model was truncated at residue 260, as there was no reliable density for ...詳細: Cdc37 crystal structure from PDB:1US7 was fit into EMD-3340 manually and then with UCSF Chimera "Fit In Map" tool. The model was truncated at residue 260, as there was no reliable density for the rest of the crystal structure. PDB:5FWK and the above fit crystal structure for residues 148-260 were loaded in Coot. The residues 133-147 were built in by hand into the Cdc37 Reconstruction and residues 245-260 (helix) were rotated as a rigid body. To relieve atomic clashes or bond length/angle distortions at the linker regions, the resulting model was subjected to "Cartesian space relax" protocol within EMD-3340 map using Rosetta. Final model was selected using the combined score of Rosetta all-atom physically-realistic score and electron density score. | ||||||||||||
| 原子モデル構築 |
| ||||||||||||
| 精密化 | 最高解像度: 7.2 Å | ||||||||||||
| 精密化ステップ | サイクル: LAST / 最高解像度: 7.2 Å
|
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー





 PDBj
PDBj