[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-3j4r: Pseudo-atomic model of the AKAP18-PKA Complex in a linear conform... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 3j4r | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
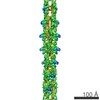
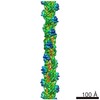
| Title | Pseudo-atomic model of the AKAP18-PKA Complex in a linear conformation derived from electron microscopy | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSFERASE / A-kinase anchoring protein / cAMP-Dependent Kinase / RII / PKA regulatory subunit II / phosphorylation / anchoring / intrinsic disorder | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcAMP-dependent protein kinase regulator activity / PKA activation in glucagon signalling / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase / HDL assembly / DARPP-32 events / Rap1 signalling / PKA activation / Regulation of insulin secretion / Vasopressin regulates renal water homeostasis via Aquaporins / GPER1 signaling ...cAMP-dependent protein kinase regulator activity / PKA activation in glucagon signalling / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase / HDL assembly / DARPP-32 events / Rap1 signalling / PKA activation / Regulation of insulin secretion / Vasopressin regulates renal water homeostasis via Aquaporins / GPER1 signaling / Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP1) regulates insulin secretion / Hedgehog 'off' state / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / MAPK6/MAPK4 signaling / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / GLI3 is processed to GLI3R by the proteasome / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / exocytic vesicle / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / regulation of membrane repolarization / Interleukin-3, Interleukin-5 and GM-CSF signaling / High laminar flow shear stress activates signaling by PIEZO1 and PECAM1:CDH5:KDR in endothelial cells / CD209 (DC-SIGN) signaling / RET signaling / Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / nucleotide-activated protein kinase complex / Mitochondrial protein degradation / VEGFA-VEGFR2 Pathway / positive regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport / Ion homeostasis / cAMP-dependent protein kinase inhibitor activity / cAMP-dependent protein kinase / regulation of protein processing / cAMP-dependent protein kinase activity / cellular response to parathyroid hormone stimulus / protein localization to lipid droplet / regulation of bicellular tight junction assembly / cAMP-dependent protein kinase complex / regulation of osteoblast differentiation / cellular response to cold / sperm capacitation / AMP binding / ciliary base / protein kinase A binding / negative regulation of glycolytic process through fructose-6-phosphate / protein kinase A catalytic subunit binding / protein kinase A regulatory subunit binding / intracellular potassium ion homeostasis / mesoderm formation / action potential / lateral plasma membrane / plasma membrane raft / axoneme / negative regulation of cAMP/PKA signal transduction / cAMP/PKA signal transduction / sperm flagellum / postsynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / cAMP binding / regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process / negative regulation of TORC1 signaling / T-tubule / protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity / cellular response to glucagon stimulus / positive regulation of gluconeogenesis / acrosomal vesicle / protein export from nucleus / positive regulation of phagocytosis / cellular response to cAMP / positive regulation of protein export from nucleus / hippocampal mossy fiber to CA3 synapse / sarcoplasmic reticulum / negative regulation of smoothened signaling pathway / neuromuscular junction / neural tube closure / cellular response to glucose stimulus / peptidyl-serine phosphorylation / positive regulation of cholesterol biosynthetic process / positive regulation of insulin secretion / modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / mRNA processing / kinase activity / manganese ion binding / cellular response to heat / adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / sperm midpiece / protein kinase activity / regulation of cell cycle / apical plasma membrane / postsynapse / nuclear speck / protein domain specific binding / protein serine kinase activity / protein serine/threonine kinase activity / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / synapse / centrosome Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / negative staining / Resolution: 35 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Reichow, S.L. / Gonen, T. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2013 Journal: Elife / Year: 2013Title: Intrinsic disorder within an AKAP-protein kinase A complex guides local substrate phosphorylation. Authors: F Donelson Smith / Steve L Reichow / Jessica L Esseltine / Dan Shi / Lorene K Langeberg / John D Scott / Tamir Gonen /  Abstract: Anchoring proteins sequester kinases with their substrates to locally disseminate intracellular signals and avert indiscriminate transmission of these responses throughout the cell. Mechanistic ...Anchoring proteins sequester kinases with their substrates to locally disseminate intracellular signals and avert indiscriminate transmission of these responses throughout the cell. Mechanistic understanding of this process is hampered by limited structural information on these macromolecular complexes. A-kinase anchoring proteins (AKAPs) spatially constrain phosphorylation by cAMP-dependent protein kinases (PKA). Electron microscopy and three-dimensional reconstructions of type-II PKA-AKAP18γ complexes reveal hetero-pentameric assemblies that adopt a range of flexible tripartite configurations. Intrinsically disordered regions within each PKA regulatory subunit impart the molecular plasticity that affords an ∼16 nanometer radius of motion to the associated catalytic subunits. Manipulating flexibility within the PKA holoenzyme augmented basal and cAMP responsive phosphorylation of AKAP-associated substrates. Cell-based analyses suggest that the catalytic subunit remains within type-II PKA-AKAP18γ complexes upon cAMP elevation. We propose that the dynamic movement of kinase sub-structures, in concert with the static AKAP-regulatory subunit interface, generates a solid-state signaling microenvironment for substrate phosphorylation. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.01319.001. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  3j4r.cif.gz 3j4r.cif.gz | 323.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb3j4r.ent.gz pdb3j4r.ent.gz | 259 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  3j4r.json.gz 3j4r.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j4/3j4r https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j4/3j4r ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j4/3j4r ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j4/3j4r | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5756MC  5755C  3j4qC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 39478.773 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: SEE REMARK 999 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 45644.266 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #3: Protein | Mass: 40628.555 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Sequence details | AKAP18 IN THIS ENTRY IS FROM HOMO SAPIENS, BUT THE MODELED SEQUENCE IS FROM RATTUS NORVEGICUS | |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | Name: 25 mM HEPES, pH 7.4, 200 mM NaCl, 0.5 mM EDTA, 1 mM DTT pH: 7.4 Details: 25 mM HEPES, pH 7.4, 200 mM NaCl, 0.5 mM EDTA, 1 mM DTT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.005 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: YES / Vitrification applied: NO / Details: Stain 0.75% (w/v) uranyl formate | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EM staining | Type: NEGATIVE / Material: Uranyl Formate | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: 200 mesh copper grid with thin carbon support |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TECNAI 12 / Date: May 1, 2012 |
|---|---|
| Electron gun | Electron source: LAB6 / Accelerating voltage: 120 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 52000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Cs: 6.3 mm Astigmatism: Objective lens astigmatism was corrected at 100,000 times magnification Camera length: 0 mm |
| Specimen holder | Specimen holder model: OTHER / Specimen holder type: Single-Tilt / Temperature: 298 K / Tilt angle max: 50 ° / Tilt angle min: 0 ° |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 15 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GENERIC GATAN |
| Image scans | Num. digital images: 1335 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Relative weight: 1 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Details: Each Micrograph | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Method: Angular Reconstitution and Refinement / Resolution: 35 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 1000 / Nominal pixel size: 4.2 Å / Actual pixel size: 4.2 Å Details: (Single particle details: Images were processed in IMAGIC and ISAC. 3D reconstruction was done in IMAGIC and FREALIGN.) (Single particle--Applied symmetry: C1) Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 UCSF Chimera
UCSF Chimera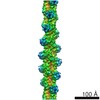

 PDBj
PDBj













