[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-3285: Cryo-electron microscopy structure of ribosome-bound initiation f... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-3285 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
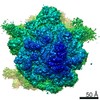
| Title | Cryo-electron microscopy structure of ribosome-bound initiation factor 2 | |||||||||
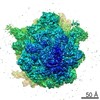
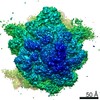
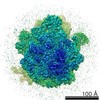
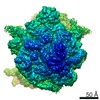
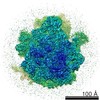
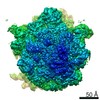
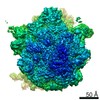
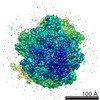
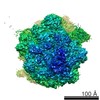
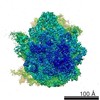
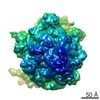
 Map data Map data | Initiation Factor 2 was stalled on Escherichia coli 70S ribosomes by the non-hydrolysable GTP analogue GDPNP in the presence of fMet-tRNAiMet and mRNA. | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Initiation Factor 2 / ribosome / translation / translation initiation / IF2 / translational GTPase / GTPase | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationguanosine tetraphosphate binding / stringent response / : / transcription antitermination factor activity, RNA binding / ornithine decarboxylase inhibitor activity / ribosomal small subunit binding / misfolded RNA binding / Group I intron splicing / RNA folding / transcriptional attenuation ...guanosine tetraphosphate binding / stringent response / : / transcription antitermination factor activity, RNA binding / ornithine decarboxylase inhibitor activity / ribosomal small subunit binding / misfolded RNA binding / Group I intron splicing / RNA folding / transcriptional attenuation / endoribonuclease inhibitor activity / positive regulation of ribosome biogenesis / RNA-binding transcription regulator activity / translational termination / negative regulation of cytoplasmic translation / four-way junction DNA binding / DnaA-L2 complex / translation repressor activity / regulation of mRNA stability / negative regulation of translational initiation / negative regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication initiation / translation initiation factor activity / mRNA regulatory element binding translation repressor activity / response to cold / positive regulation of RNA splicing / assembly of large subunit precursor of preribosome / cytosolic ribosome assembly / response to reactive oxygen species / regulation of DNA-templated transcription elongation / ribosome assembly / transcription elongation factor complex / transcription antitermination / DNA endonuclease activity / regulation of cell growth / translational initiation / DNA-templated transcription termination / response to radiation / maintenance of translational fidelity / mRNA 5'-UTR binding / regulation of translation / large ribosomal subunit / ribosome biogenesis / transferase activity / ribosome binding / ribosomal small subunit biogenesis / ribosomal small subunit assembly / ribosomal large subunit assembly / 5S rRNA binding / small ribosomal subunit / small ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic small ribosomal subunit / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / cytoplasmic translation / tRNA binding / negative regulation of translation / rRNA binding / structural constituent of ribosome / ribosome / translation / hydrolase activity / response to antibiotic / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / GTPase activity / mRNA binding / GTP binding / DNA binding / RNA binding / zinc ion binding / membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.6 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Sprink T / Ramrath DJF / Yamamoto H / Yamamoto K / Loerke J / Ismer J / Hildebrand PW / Scheerer P / Buerger J / Mielke T / Spahn CMT | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2016 Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2016Title: Structures of ribosome-bound initiation factor 2 reveal the mechanism of subunit association. Authors: Thiemo Sprink / David J F Ramrath / Hiroshi Yamamoto / Kaori Yamamoto / Justus Loerke / Jochen Ismer / Peter W Hildebrand / Patrick Scheerer / Jörg Bürger / Thorsten Mielke / Christian M T Spahn /  Abstract: Throughout the four phases of protein biosynthesis-initiation, elongation, termination, and recycling-the ribosome is controlled and regulated by at least one specified translational guanosine ...Throughout the four phases of protein biosynthesis-initiation, elongation, termination, and recycling-the ribosome is controlled and regulated by at least one specified translational guanosine triphosphatase (trGTPase). Although the structural basis for trGTPase interaction with the ribosome has been solved for the last three steps of translation, the high-resolution structure for the key initiation trGTPase, initiation factor 2 (IF2), complexed with the ribosome, remains elusive. We determine the structure of IF2 complexed with a nonhydrolyzable guanosine triphosphate analog and initiator fMet-tRNAi (Met) in the context of the Escherichia coli ribosome to 3.7-Å resolution using cryo-electron microscopy. The structural analysis reveals previously unseen intrinsic conformational modes of the 70S initiation complex, establishing the mutual interplay of IF2 and initator transfer RNA (tRNA) with the ribsosome and providing the structural foundation for a mechanistic understanding of the final steps of translation initiation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_3285.map.gz emd_3285.map.gz | 97.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-3285-v30.xml emd-3285-v30.xml emd-3285.xml emd-3285.xml | 12.8 KB 12.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_3285.png emd_3285.png | 407.1 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3285 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3285 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3285 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3285 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 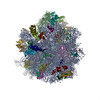 3jcnMC 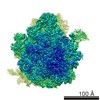 6559C  3jcjC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_3285.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 100.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_3285.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 100.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Initiation Factor 2 was stalled on Escherichia coli 70S ribosomes by the non-hydrolysable GTP analogue GDPNP in the presence of fMet-tRNAiMet and mRNA. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.23 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Initiation Factor 2 was stalled on Escherichia coli 70S ribosomes...
| Entire | Name: Initiation Factor 2 was stalled on Escherichia coli 70S ribosomes by the non-hydrolysable GTP analogue GDPNP in the presence of fMet-tRNAiMet and mRNA. |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: Initiation Factor 2 was stalled on Escherichia coli 70S ribosomes...
| Supramolecule | Name: Initiation Factor 2 was stalled on Escherichia coli 70S ribosomes by the non-hydrolysable GTP analogue GDPNP in the presence of fMet-tRNAiMet and mRNA. type: sample / ID: 1000 / Number unique components: 3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental: 2.5 MDa / Theoretical: 2.6 MDa |
-Supramolecule #1: 70S ribosome
| Supramolecule | Name: 70S ribosome / type: complex / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: 70S Details: Initiation Factor 2 was stalled on Escherichia coli 70S ribosomes by the non-hydrolysable GTP analogue GDPNP in the presence of fMet-tRNAiMet and mRNA. Recombinant expression: No / Ribosome-details: ribosome-prokaryote: ALL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Experimental: 2.5 MDa / Theoretical: 2.6 MDa |
-Macromolecule #1: fMet-tRNAiMet
| Macromolecule | Name: fMet-tRNAiMet / type: rna / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: initiator tRNA Details: Initiation Factor 2 was stalled on Escherichia coli 70S ribosomes by the non-hydrolysable GTP analogue GDPNP in the presence of fMet-tRNAiMet and mRNA. Classification: TRANSFER / Structure: DOUBLE HELIX / Synthetic?: No |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #2: Initiation Factor 2
| Macromolecule | Name: Initiation Factor 2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Name.synonym: IF2 Details: Initiation Factor 2 was stalled on Escherichia coli 70S ribosomes by the non-hydrolysable GTP analogue GDPNP in the presence of fMet-tRNAiMet and mRNA. Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Experimental: 97 KDa / Theoretical: 97 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | UniProtKB: Translation initiation factor IF-2 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Details: 20 mM Hepes-KOH pH 7.5, 15 mM magnesium acetate, 150 mM potassium acetate, 4 mM -mercapthoethanol, 2 mM spermidine and 0.05 mM spermine |
|---|---|
| Grid | Details: Quantifoil R3-3 Cu 300 mesh with 2 nm carbon support film |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK I / Method: blot for 2-4 seconds before plunging |
- Electron microscopy #1
Electron microscopy #1
| Microscopy ID | 1 |
|---|---|
| Microscope | FEI POLARA 300 |
| Date | Aug 26, 2013 |
| Image recording | Category: CCD / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Number real images: 918 / Average electron dose: 20 e/Å2 / Details: Automated data collection using Leginon |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated magnification: 39000 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.0 mm / Nominal defocus max: 7.18 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.64 µm / Nominal magnification: 31000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: GATAN LIQUID NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Electron microscopy #2
Electron microscopy #2
| Microscopy ID | 2 |
|---|---|
| Microscope | FEI POLARA 300 |
| Date | Jun 10, 2015 |
| Image recording | Category: CCD / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Number real images: 2797 / Average electron dose: 20 e/Å2 / Details: Automated data collection using Leginon |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated magnification: 39000 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.0 mm / Nominal defocus max: 7.57 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.19 µm / Nominal magnification: 31000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: GATAN LIQUID NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Details | To avoid overfitting, the data was refined in a resolution-limited scheme using SPIDER |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Details: CTFFIND4 |
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 4.6 Å / Resolution method: OTHER / Software - Name: EMAN2, CTFFIND4, SPIDER, SPARX Details: Final maps were calculated from two datasets. To avoid overfitting, the data was refined in a resolution-limited scheme using SPIDER Number images used: 14872 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



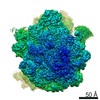
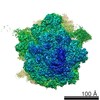
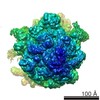
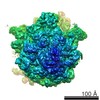










 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)