+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-24581 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
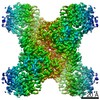
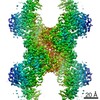
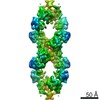
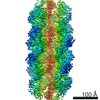
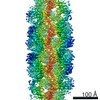
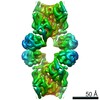
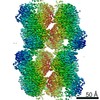
| Title | Yeast CTP Synthase (Ura8) Bundle Bound to Substrates at Low pH | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Yeast CTP Synthase (Ura8) Bundle bound to substrates at low pH | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | glutaminase and amido-ligase / PROTEIN FIBRIL | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcytoophidium / CTP synthase (glutamine hydrolysing) / CTP synthase activity / 'de novo' CTP biosynthetic process / pyrimidine nucleobase biosynthetic process / glutamine metabolic process / ATP binding / identical protein binding / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hansen JM / Lynch EM | |||||||||
| Funding support | 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2021 Journal: Elife / Year: 2021Title: Cryo-EM structures of CTP synthase filaments reveal mechanism of pH-sensitive assembly during budding yeast starvation. Authors: Jesse M Hansen / Avital Horowitz / Eric M Lynch / Daniel P Farrell / Joel Quispe / Frank DiMaio / Justin M Kollman /  Abstract: Many metabolic enzymes self-assemble into micron-scale filaments to organize and regulate metabolism. The appearance of these assemblies often coincides with large metabolic changes as in ...Many metabolic enzymes self-assemble into micron-scale filaments to organize and regulate metabolism. The appearance of these assemblies often coincides with large metabolic changes as in development, cancer, and stress. Yeast undergo cytoplasmic acidification upon starvation, triggering the assembly of many metabolic enzymes into filaments. However, it is unclear how these filaments assemble at the molecular level and what their role is in the yeast starvation response. CTP Synthase (CTPS) assembles into metabolic filaments across many species. Here, we characterize in vitro polymerization and investigate in vivo consequences of CTPS assembly in yeast. Cryo-EM structures reveal a pH-sensitive assembly mechanism and highly ordered filament bundles that stabilize an inactive state of the enzyme, features unique to yeast CTPS. Disruption of filaments in cells with non-assembly or pH-insensitive mutations decreases growth rate, reflecting the importance of regulated CTPS filament assembly in homeotstasis. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_24581.map.gz emd_24581.map.gz | 10.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-24581-v30.xml emd-24581-v30.xml emd-24581.xml emd-24581.xml | 10.7 KB 10.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_24581.png emd_24581.png | 90.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-24581.cif.gz emd-24581.cif.gz | 5.5 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24581 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24581 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24581 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24581 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_24581_validation.pdf.gz emd_24581_validation.pdf.gz | 351.4 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_24581_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_24581_full_validation.pdf.gz | 351 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_24581_validation.xml.gz emd_24581_validation.xml.gz | 8.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_24581_validation.cif.gz emd_24581_validation.cif.gz | 9.4 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24581 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24581 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24581 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24581 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7rnrMC  7rkhC  7rl0C  7rl5C  7rmcC  7rmfC  7rmkC  7rmoC  7rmvC  7rnlC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_24581.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_24581.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Yeast CTP Synthase (Ura8) Bundle bound to substrates at low pH | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
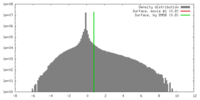
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.05 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : CTP Synthase Bundle assembled with Substrates
| Entire | Name: CTP Synthase Bundle assembled with Substrates |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: CTP Synthase Bundle assembled with Substrates
| Supramolecule | Name: CTP Synthase Bundle assembled with Substrates / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: CTP synthase
| Macromolecule | Name: CTP synthase / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 20 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: CTP synthase (glutamine hydrolysing) |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 62.439168 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MKYVVVSGGV ISGIGKGVLA SSTGMLLKTL GLKVTSIKID PYMNIDAGTM SPLEHGECFV LDDGGETDLD LGNYERYLGI TLSRDHNIT TGKIYSHVIS RERRGDYLGK TVQIVPHLTN AIQDWIQRVS KIPVDDTGLE PDVCIIELGG TVGDIESAPF V EALRQFQF ...String: MKYVVVSGGV ISGIGKGVLA SSTGMLLKTL GLKVTSIKID PYMNIDAGTM SPLEHGECFV LDDGGETDLD LGNYERYLGI TLSRDHNIT TGKIYSHVIS RERRGDYLGK TVQIVPHLTN AIQDWIQRVS KIPVDDTGLE PDVCIIELGG TVGDIESAPF V EALRQFQF EVGRENFALI HVSLVPVIHG EQKTKPTQAA IKDLRSLGLI PDMIACRCSE ELNRSTIDKI AMFCHVGPEQ VV NVHDVNS TYHVPLLLLK QHMIDYLHSR LKLGEVPLTL EDKERGSQLL TNWENMTKNL DDSDDVVKIA LVGKYTNLKD SYL SVTKSL EHASMKCRRQ LEILWVEASN LEPETQEVDK NKFHDSWNKL SSADGILVPG GFGTRGIEGM ILAAKWARES GVPF LGVCL GLQVAAIEFA RNVIGRPNSS STEFLDETLL APEDQVVITM RLGLRPTIFQ PNSEWSNIRK LYGEVNEVHE RHRHR YEIN PKIVNDMESR GFIFVGKDET GQRCEIFELK GHPYYVGTQY HPEYTSKVLE PSRPFWGLVA AASGTLGEVI KDINL UniProtKB: CTP synthase |
-Macromolecule #2: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 20 / Formula: ATP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 507.181 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ATP: |
-Macromolecule #3: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 40 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #4: URIDINE 5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: URIDINE 5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 20 / Formula: UTP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 484.141 Da |
| Chemical component information | 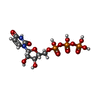 ChemComp-UTP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 6 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 90.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C2 (2 fold cyclic) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.3 Å / Resolution method: OTHER / Details: FSCref0.5 (Phenix Density Modification) / Number images used: 21220 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






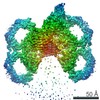

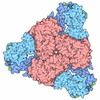

 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)