[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
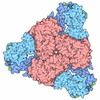
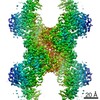
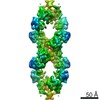
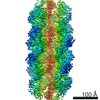
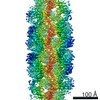
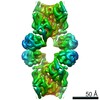
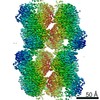
Yorodumi- PDB-7rkh: Yeast CTP Synthase (URA8) tetramer bound to ATP/UTP at neutral pH -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7rkh | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Yeast CTP Synthase (URA8) tetramer bound to ATP/UTP at neutral pH | |||||||||
 Components Components | CTP synthase | |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PROTEIN FIBRIL / glutaminase / amido-ligase / nucleotide metabolism | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationCTP synthase (glutamine hydrolysing) / CTP synthase activity / cytoophidium / 'de novo' CTP biosynthetic process / pyrimidine nucleobase biosynthetic process / glutamine metabolic process / ATP binding / identical protein binding / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.8 Å | |||||||||
| Model details | cryo-EM D2 reconstruction | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hansen, J.M. / Lynch, E.M. / Farrell, D.P. / DiMaio, F. / Quispe, J. / Kollman, J.M. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2021 Journal: Elife / Year: 2021Title: Cryo-EM structures of CTP synthase filaments reveal mechanism of pH-sensitive assembly during budding yeast starvation. Authors: Jesse M Hansen / Avital Horowitz / Eric M Lynch / Daniel P Farrell / Joel Quispe / Frank DiMaio / Justin M Kollman /  Abstract: Many metabolic enzymes self-assemble into micron-scale filaments to organize and regulate metabolism. The appearance of these assemblies often coincides with large metabolic changes as in ...Many metabolic enzymes self-assemble into micron-scale filaments to organize and regulate metabolism. The appearance of these assemblies often coincides with large metabolic changes as in development, cancer, and stress. Yeast undergo cytoplasmic acidification upon starvation, triggering the assembly of many metabolic enzymes into filaments. However, it is unclear how these filaments assemble at the molecular level and what their role is in the yeast starvation response. CTP Synthase (CTPS) assembles into metabolic filaments across many species. Here, we characterize in vitro polymerization and investigate in vivo consequences of CTPS assembly in yeast. Cryo-EM structures reveal a pH-sensitive assembly mechanism and highly ordered filament bundles that stabilize an inactive state of the enzyme, features unique to yeast CTPS. Disruption of filaments in cells with non-assembly or pH-insensitive mutations decreases growth rate, reflecting the importance of regulated CTPS filament assembly in homeotstasis. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7rkh.cif.gz 7rkh.cif.gz | 790.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7rkh.ent.gz pdb7rkh.ent.gz | 667.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7rkh.json.gz 7rkh.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/rk/7rkh https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/rk/7rkh ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/rk/7rkh ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/rk/7rkh | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 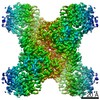 24497MC  7rl0C  7rl5C  7rmcC  7rmfC  7rmkC  7rmoC  7rmvC  7rnlC  7rnrC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 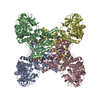
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
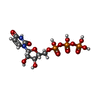
| #1: Protein | Mass: 62439.168 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: 6XHIS c-ter Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: PACBIOSEQ_LOCUS3439, SCNYR20_0009027000 / Plasmid: pET28b / Production host:  References: UniProt: A0A6A5PYW3, CTP synthase (glutamine hydrolysing) #2: Chemical | ChemComp-UTP / #3: Chemical | ChemComp-ATP / #4: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / Has ligand of interest | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Yeast CTP Synthase (URA8) tetramer bound to ATP/UTP at neutral pH Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 256 kDa/nm / Experimental value: YES |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 400 divisions/in. / Grid type: C-flat |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 130000 X / Nominal defocus max: 5500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 90 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 50 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: D2 (2x2 fold dihedral) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.8 Å / Resolution method: OTHER / Num. of particles: 76963 / Details: FSCref0.5 (Phenix Density modification) / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj