[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-24494: Cryo-EM Structure of Adeno-Associated Virus Serotype 9 with Engin... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-24494 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
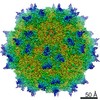
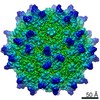
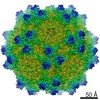
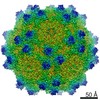
| Title | Cryo-EM Structure of Adeno-Associated Virus Serotype 9 with Engineered Peptide Domain PHP.B (AAV9-PHP.B) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Adeno-Associated Virus Serotype 9 with Engineered Peptide Domain PHP.B (AAV9-PHP.B) | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Gene Therapy / Adeno-associated virus / AAV / VIRUS | |||||||||
| Function / homology | Phospholipase A2-like domain / Phospholipase A2-like domain / Parvovirus coat protein VP2 / Parvovirus coat protein VP1/VP2 / Parvovirus coat protein VP2 / Capsid/spike protein, ssDNA virus / T=1 icosahedral viral capsid / structural molecule activity / Capsid protein VP1 Function and homology information Function and homology information | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Adeno-associated virus 9 Adeno-associated virus 9 | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.27 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Fluck EC / Pumroy RA | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Virol / Year: 2021 Journal: J Virol / Year: 2021Title: Context-Specific Function of the Engineered Peptide Domain of PHP.B. Authors: R Alexander Martino / Edwin C Fluck / Jacqueline Murphy / Qiang Wang / Henry Hoff / Ruth A Pumroy / Claudia Y Lee / Joshua J Sims / Soumitra Roy / Vera Y Moiseenkova-Bell / James M Wilson /  Abstract: One approach to improve the utility of adeno-associated virus (AAV)-based gene therapy is to engineer the AAV capsid to (i) overcome poor transport through tissue barriers and (ii) redirect the ...One approach to improve the utility of adeno-associated virus (AAV)-based gene therapy is to engineer the AAV capsid to (i) overcome poor transport through tissue barriers and (ii) redirect the broadly tropic AAV to disease-relevant cell types. Peptide- or protein-domain insertions into AAV surface loops can achieve both engineering goals by introducing a new interaction surface on the AAV capsid. However, we understand little about the impact of insertions on capsid structure and the extent to which engineered inserts depend on a specific capsid context to function. Here, we examine insert-capsid interactions for the engineered variant AAV9-PHP.B. The 7-amino-acid peptide insert in AAV9-PHP.B facilitates transport across the murine blood-brain barrier via binding to the receptor Ly6a. When transferred to AAV1, the engineered peptide does not bind Ly6a. Comparative structural analysis of AAV1-PHP.B and AAV9-PHP.B revealed that the inserted 7-amino-acid loop is highly flexible and has remarkably little impact on the surrounding capsid conformation. Our work demonstrates that Ly6a binding requires interactions with both the PHP.B peptide and specific residues from the AAV9 HVR VIII region. An AAV1-based vector that incorporates a larger region of AAV9-PHP.B-including the 7-amino-acid loop and adjacent HVR VIII amino acids-can bind to Ly6a and localize to brain tissue. However, unlike AAV9-PHP.B, this AAV1-based vector does not penetrate the blood-brain barrier. Here we discuss the implications for AAV capsid engineering and the transfer of engineered activities between serotypes. Targeting AAV vectors to specific cellular receptors is a promising strategy for enhancing expression in target cells or tissues while reducing off-target transgene expression. The AAV9-PHP.B/Ly6a interaction provides a model system with a robust biological readout that can be interrogated to better understand the biology of AAV vectors' interactions with target receptors. In this work, we analyzed the sequence and structural features required to successfully transfer the Ly6a receptor-binding epitope from AAV9-PHP.B to another capsid of clinical interest, AAV1. We found that AAV1- and AAV9-based vectors targeted to the same receptor exhibited different brain-transduction profiles. Our work suggests that, in addition to attachment-receptor binding, the capsid context in which this binding occurs is important for a vector's performance. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_24494.map.gz emd_24494.map.gz | 288.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-24494-v30.xml emd-24494-v30.xml emd-24494.xml emd-24494.xml | 14.2 KB 14.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
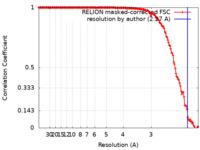
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_24494_fsc.xml emd_24494_fsc.xml | 15.2 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
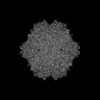
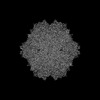
| Images |  emd_24494.png emd_24494.png | 152.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-24494.cif.gz emd-24494.cif.gz | 6.1 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24494 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24494 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24494 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24494 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_24494_validation.pdf.gz emd_24494_validation.pdf.gz | 747.9 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_24494_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_24494_full_validation.pdf.gz | 747.4 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_24494_validation.xml.gz emd_24494_validation.xml.gz | 14.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_24494_validation.cif.gz emd_24494_validation.cif.gz | 19.8 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24494 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24494 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24494 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24494 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7rk8MC  7rk9C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_24494.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 307.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_24494.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 307.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Adeno-Associated Virus Serotype 9 with Engineered Peptide Domain PHP.B (AAV9-PHP.B) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.06 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
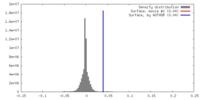
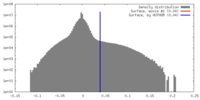
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Adeno-associated virus 9
| Entire | Name:   Adeno-associated virus 9 Adeno-associated virus 9 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Adeno-associated virus 9
| Supramolecule | Name: Adeno-associated virus 9 / type: virus / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all Details: AAV9-PHP.B trans plasmid with cis plasmid encoding the CB7-EGFP reporter gene to produce vectors in HEK293 cells via triple transfection. NCBI-ID: 235455 / Sci species name: Adeno-associated virus 9 / Virus type: SATELLITE / Virus isolate: SEROTYPE / Virus enveloped: No / Virus empty: No |
|---|
-Macromolecule #1: Capsid protein VP1
| Macromolecule | Name: Capsid protein VP1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 60 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Adeno-associated virus 9 Adeno-associated virus 9 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 82.215672 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MAADGYLPDW LEDNLSEGIR EWWALKPGAP QPKANQQHQD NARGLVLPGY KYLGPGNGLD KGEPVNAADA AALEHDKAYD QQLKAGDNP YLKYNHADAE FQERLKEDTS FGGNLGRAVF QAKKRLLEPL GLVEEAAKTA PGKKRPVEQS PQEPDSSAGI G KSGAQPAK ...String: MAADGYLPDW LEDNLSEGIR EWWALKPGAP QPKANQQHQD NARGLVLPGY KYLGPGNGLD KGEPVNAADA AALEHDKAYD QQLKAGDNP YLKYNHADAE FQERLKEDTS FGGNLGRAVF QAKKRLLEPL GLVEEAAKTA PGKKRPVEQS PQEPDSSAGI G KSGAQPAK KRLNFGQTGD TESVPDPQPI GEPPAAPSGV GSLTMASGGG APVADNNEGA DGVGSSSGNW HCDSQWLGDR VI TTSTRTW ALPTYNNHLY KQISNSTSGG SSNDNAYFGY STPWGYFDFN RFHCHFSPRD WQRLINNNWG FRPKRLNFKL FNI QVKEVT DNNGVKTIAN NLTSTVQVFT DSDYQLPYVL GSAHEGCLPP FPADVFMIPQ YGYLTLNDGS QAVGRSSFYC LEYF PSQML RTGNNFQFSY EFENVPFHSS YAHSQSLDRL MNPLIDQYLY YLSKTINGSG QNQQTLKFSV AGPSNMAVQG RNYIP GPSY RQQRVSTTVT QNNNSEFAWP GASSWALNGR NSLMNPGPAM ASHKEGEDRF FPLSGSLIFG KQGTGRDNVD ADKVMI TNE EEIKTTNPVA TESYGQVATN HQSAQTLAVP FKAQAQTGWV QNQGILPGMV WQDRDVYLQG PIWAKIPHTD GNFHPSP LM GGFGMKHPPP QILIKNTPVP ADPPTAFNKD KLNSFITQYS TGQVSVEIEW ELQKENSKRW NPEIQYTSNY YKSNNVEF A VNTEGVYSEP RPIGTRYLTR NL UniProtKB: Capsid protein VP1 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 Component:
Details: Supplemented with 0.001% Pluronic F68 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid | Model: PELCO Ultrathin Carbon with Lacey Carbon / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: LACEY / Support film - Film thickness: 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Number real images: 1380 / Average electron dose: 38.1 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Sample stage | Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-7rk8: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)