+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 |  | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| タイトル | Single particle cryo-EM structure of the Chaetomium thermophilum Nup192-Nic96-Nup53-Nup145N complex (Nup192 residues 1-1756; Nic96 residues 240-301; Nup53 31-67; Nup145N 616-683) | |||||||||||||||
 マップデータ マップデータ | Unsharpened map generated with cryoSPARC NU refine | |||||||||||||||
 試料 試料 |
| |||||||||||||||
 キーワード キーワード | nuclear pore complex / nucleocytoplasmic transport / alpha-helical solenoid / nuclear pore / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | |||||||||||||||
| 機能・相同性 |  機能・相同性情報 機能・相同性情報telomere tethering at nuclear periphery / post-transcriptional tethering of RNA polymerase II gene DNA at nuclear periphery / nuclear pore cytoplasmic filaments / structural constituent of nuclear pore / RNA export from nucleus / nuclear localization sequence binding / 加水分解酵素; プロテアーゼ; ペプチド結合加水分解酵素; セリンエンドペプチターゼ / mRNA transport / nuclear pore / protein import into nucleus ...telomere tethering at nuclear periphery / post-transcriptional tethering of RNA polymerase II gene DNA at nuclear periphery / nuclear pore cytoplasmic filaments / structural constituent of nuclear pore / RNA export from nucleus / nuclear localization sequence binding / 加水分解酵素; プロテアーゼ; ペプチド結合加水分解酵素; セリンエンドペプチターゼ / mRNA transport / nuclear pore / protein import into nucleus / protein transport / nuclear membrane / hydrolase activity / RNA binding 類似検索 - 分子機能 | |||||||||||||||
| 生物種 |  Chaetomium thermophilum var. thermophilum DSM 1495 (菌類) / Chaetomium thermophilum var. thermophilum DSM 1495 (菌類) /  Chaetomium thermophilum (strain DSM 1495 / CBS 144.50 / IMI 039719) (菌類) Chaetomium thermophilum (strain DSM 1495 / CBS 144.50 / IMI 039719) (菌類) | |||||||||||||||
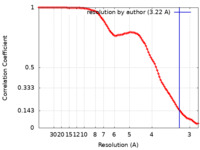
| 手法 | 単粒子再構成法 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 3.22 Å | |||||||||||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Petrovic S / Samanta D / Perriches T / Bley CJ / Thierbach K / Brown B / Nie S / Mobbs GW / Stevens TA / Liu X ...Petrovic S / Samanta D / Perriches T / Bley CJ / Thierbach K / Brown B / Nie S / Mobbs GW / Stevens TA / Liu X / Tomaleri GP / Schaus L / Hoelz A | |||||||||||||||
| 資金援助 |  米国, 4件 米国, 4件
| |||||||||||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: Science / 年: 2022 ジャーナル: Science / 年: 2022タイトル: Architecture of the linker-scaffold in the nuclear pore. 著者: Stefan Petrovic / Dipanjan Samanta / Thibaud Perriches / Christopher J Bley / Karsten Thierbach / Bonnie Brown / Si Nie / George W Mobbs / Taylor A Stevens / Xiaoyu Liu / Giovani Pinton ...著者: Stefan Petrovic / Dipanjan Samanta / Thibaud Perriches / Christopher J Bley / Karsten Thierbach / Bonnie Brown / Si Nie / George W Mobbs / Taylor A Stevens / Xiaoyu Liu / Giovani Pinton Tomaleri / Lucas Schaus / André Hoelz /  要旨: INTRODUCTION In eukaryotic cells, the selective bidirectional transport of macromolecules between the nucleus and cytoplasm occurs through the nuclear pore complex (NPC). Embedded in nuclear envelope ...INTRODUCTION In eukaryotic cells, the selective bidirectional transport of macromolecules between the nucleus and cytoplasm occurs through the nuclear pore complex (NPC). Embedded in nuclear envelope pores, the ~110-MDa human NPC is an ~1200-Å-wide and ~750-Å-tall assembly of ~1000 proteins, collectively termed nucleoporins. Because of the NPC's eightfold rotational symmetry along the nucleocytoplasmic axis, each of the ~34 different nucleoporins occurs in multiples of eight. Architecturally, the NPC's symmetric core is composed of an inner ring encircling the central transport channel and two outer rings anchored on both sides of the nuclear envelope. Because of its central role in the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein, the NPC is commonly targeted in viral infections and its nucleoporin constituents are associated with a plethora of diseases. RATIONALE Although the arrangement of most scaffold nucleoporins in the NPC's symmetric core was determined by quantitative docking of crystal structures into cryo-electron tomographic (cryo-ET) maps of intact NPCs, the topology and molecular details of their cohesion by multivalent linker nucleoporins have remained elusive. Recently, in situ cryo-ET reconstructions of NPCs from various species have indicated that the NPC's inner ring is capable of reversible constriction and dilation in response to variations in nuclear envelope membrane tension, thereby modulating the diameter of the central transport channel by ~200 Å. We combined biochemical reconstitution, high-resolution crystal and single-particle cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure determination, docking into cryo-ET maps, and physiological validation to elucidate the molecular architecture of the linker-scaffold interaction network that not only is essential for the NPC's integrity but also confers the plasticity and robustness necessary to allow and withstand such large-scale conformational changes. RESULTS By biochemically mapping scaffold-binding regions of all fungal and human linker nucleoporins and determining crystal and single-particle cryo-EM structures of linker-scaffold complexes, we completed the characterization of the biochemically tractable linker-scaffold network and established its evolutionary conservation, despite considerable sequence divergence. We determined a series of crystal and single-particle cryo-EM structures of the intact Nup188 and Nup192 scaffold hubs bound to their Nic96, Nup145N, and Nup53 linker nucleoporin binding regions, revealing that both proteins form distinct question mark-shaped keystones of two evolutionarily conserved hetero‑octameric inner ring complexes. Linkers bind to scaffold surface pockets through short defined motifs, with flanking regions commonly forming additional disperse interactions that reinforce the binding. Using a structure‑guided functional analysis in , we confirmed the robustness of linker‑scaffold interactions and established the physiological relevance of our biochemical and structural findings. The near-atomic composite structures resulting from quantitative docking of experimental structures into human and cryo-ET maps of constricted and dilated NPCs structurally disambiguated the positioning of the Nup188 and Nup192 hubs in the intact fungal and human NPC and revealed the topology of the linker-scaffold network. The linker-scaffold gives rise to eight relatively rigid inner ring spokes that are flexibly interconnected to allow for the formation of lateral channels. Unexpectedly, we uncovered that linker‑scaffold interactions play an opposing role in the outer rings by forming tight cross-link staples between the eight nuclear and cytoplasmic outer ring spokes, thereby limiting the dilatory movements to the inner ring. CONCLUSION We have substantially advanced the structural and biochemical characterization of the symmetric core of the and human NPCs and determined near-atomic composite structures. The composite structures uncover the molecular mechanism by which the evolutionarily conserved linker‑scaffold establishes the NPC's integrity while simultaneously allowing for the observed plasticity of the central transport channel. The composite structures are roadmaps for the mechanistic dissection of NPC assembly and disassembly, the etiology of NPC‑associated diseases, the role of NPC dilation in nucleocytoplasmic transport of soluble and integral membrane protein cargos, and the anchoring of asymmetric nucleoporins. [Figure: see text]. | |||||||||||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
| 添付画像 |
|---|
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
-EMDBアーカイブ
| マップデータ |  emd_24057.map.gz emd_24057.map.gz | 59.2 MB |  EMDBマップデータ形式 EMDBマップデータ形式 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ヘッダ (付随情報) |  emd-24057-v30.xml emd-24057-v30.xml emd-24057.xml emd-24057.xml | 26.4 KB 26.4 KB | 表示 表示 |  EMDBヘッダ EMDBヘッダ |
| FSC (解像度算出) |  emd_24057_fsc.xml emd_24057_fsc.xml | 11.6 KB | 表示 |  FSCデータファイル FSCデータファイル |
| 画像 |  emd_24057.png emd_24057.png | 66 KB | ||
| マスクデータ |  emd_24057_msk_1.map emd_24057_msk_1.map | 64 MB |  マスクマップ マスクマップ | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-24057.cif.gz emd-24057.cif.gz | 7.7 KB | ||
| その他 |  emd_24057_additional_1.map.gz emd_24057_additional_1.map.gz emd_24057_half_map_1.map.gz emd_24057_half_map_1.map.gz emd_24057_half_map_2.map.gz emd_24057_half_map_2.map.gz | 59.3 MB 3.9 MB 3.9 MB | ||
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24057 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24057 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24057 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24057 | HTTPS FTP |
-検証レポート
| 文書・要旨 |  emd_24057_validation.pdf.gz emd_24057_validation.pdf.gz | 595.5 KB | 表示 |  EMDB検証レポート EMDB検証レポート |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文書・詳細版 |  emd_24057_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_24057_full_validation.pdf.gz | 595 KB | 表示 | |
| XML形式データ |  emd_24057_validation.xml.gz emd_24057_validation.xml.gz | 15.1 KB | 表示 | |
| CIF形式データ |  emd_24057_validation.cif.gz emd_24057_validation.cif.gz | 20.9 KB | 表示 | |
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24057 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24057 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24057 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24057 | HTTPS FTP |
-関連構造データ
| 関連構造データ |  7mvvMC  7mvtC  7mvuC  7mvwC  7mvxC  7mvyC  7mvzC  7mw0C  7mw1C  7tbiC  7tbjC  7tbkC M: このマップから作成された原子モデル C: 同じ文献を引用 ( |
|---|---|
| 類似構造データ | 類似検索 - 機能・相同性  F&H 検索 F&H 検索 |
- リンク
リンク
| EMDBのページ |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| 「今月の分子」の関連する項目 |
- マップ
マップ
| ファイル |  ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_24057.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 64 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_24057.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 64 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 注釈 | Unsharpened map generated with cryoSPARC NU refine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
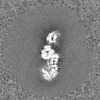
| 投影像・断面図 | 画像のコントロール
画像は Spider により作成 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ボクセルのサイズ | X=Y=Z: 1.4208 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 密度 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 対称性 | 空間群: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 詳細 | EMDB XML:
|
-添付データ
-マスク #1
| ファイル |  emd_24057_msk_1.map emd_24057_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
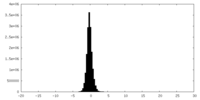
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
| 密度ヒストグラム |
-追加マップ: Map sharpened with PHENIX Autosharpen model based local sharpening
| ファイル | emd_24057_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 注釈 | Map sharpened with PHENIX Autosharpen model based local sharpening | ||||||||||||
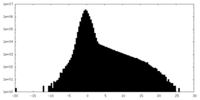
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
| 密度ヒストグラム |
-ハーフマップ: Half-dataset map generated with cryoSPARC
| ファイル | emd_24057_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 注釈 | Half-dataset map generated with cryoSPARC | ||||||||||||
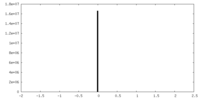
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
| 密度ヒストグラム |
-ハーフマップ: Half-dataset map generated with cryoSPARC
| ファイル | emd_24057_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 注釈 | Half-dataset map generated with cryoSPARC | ||||||||||||
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
| 密度ヒストグラム |
- 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素
-全体 : Nup192-Nic96-Nup53-Nup145N heterotetramer
| 全体 | 名称: Nup192-Nic96-Nup53-Nup145N heterotetramer |
|---|---|
| 要素 |
|
-超分子 #1: Nup192-Nic96-Nup53-Nup145N heterotetramer
| 超分子 | 名称: Nup192-Nic96-Nup53-Nup145N heterotetramer / タイプ: complex / ID: 1 / 親要素: 0 / 含まれる分子: all |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Chaetomium thermophilum var. thermophilum DSM 1495 (菌類) Chaetomium thermophilum var. thermophilum DSM 1495 (菌類) |
| 分子量 | 理論値: 215.7 KDa |
-分子 #1: Nucleoporin NUP192
| 分子 | 名称: Nucleoporin NUP192 / タイプ: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / コピー数: 1 / 光学異性体: LEVO |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Chaetomium thermophilum (strain DSM 1495 / CBS 144.50 / IMI 039719) (菌類) Chaetomium thermophilum (strain DSM 1495 / CBS 144.50 / IMI 039719) (菌類)株: DSM 1495 / CBS 144.50 / IMI 039719 |
| 分子量 | 理論値: 200.047484 KDa |
| 組換発現 | 生物種:  |
| 配列 | 文字列: GPLMSGLNDI FEAQKIEWHE GSAGGSGHMT DLRKLEALQA LHAELVAVRQ HRFEGLQVLE TLLEEQTDAF KALIAKPARD TKDREALGK EPKKLKIGEE EYSLNEDFVN DCLKLADELD LNEKESARIL IDCDAEGDVE TQSRPLWECG VIRFHQERKY L LDCMRLIL ...文字列: GPLMSGLNDI FEAQKIEWHE GSAGGSGHMT DLRKLEALQA LHAELVAVRQ HRFEGLQVLE TLLEEQTDAF KALIAKPARD TKDREALGK EPKKLKIGEE EYSLNEDFVN DCLKLADELD LNEKESARIL IDCDAEGDVE TQSRPLWECG VIRFHQERKY L LDCMRLIL EIAADEDIDA GLQESFGVAA EDKIFGIPPP WERNKENQPT QVKKFIPRCM EAMKGVRSML QCMADKANAR NM LQQASLV RPLDNQETLD FSRLSLVEQH ECLASILHAA VQRHHATIAD FQDFIKILRK WDKYDHFLIH LIPVLAAYIT EFG SPEGMG DLQQARRLND FICKGGDEDS WALPVLGAAV RAWWIAEHNG FYLDDTVQDL RGINLDEEDE QRTKQFLDAL KEGA FDFIL SVAADCKAQE WQDPSQLGAR QWLQRKIPSL PSEPFPFSHF LQHSLMVHLE GFVDATISNL PDVLRKLRTE EDEQR QLRP NHEQDMDLER FLIIISYAYE GRPDAAMSFW EDPDSNLAGF LQWASRRAST PLVSAFCEML RCLADNEECA TAAHNF LLD EGHQASGKMK RSQSLTWSQI FKELEYFTTK VCSERPNPPQ ASMHRPGRPG ADPAEIEPES ALMLECYLRL IAKLATE SE IARKRLIMDE DFNLVDTILK LSVGVIPHRL RACIFYVLKA LMIRKTHEEL DAMWRWVEAW MTNPFSSLPG SQGAPQRI S FLGQTPGPQE CMEMMFREFG TGFEQSNAFI QLLTTLLVPP EGLNSLNDSV PFPEWLGSSI RTLGIEPYVD FVFDVFANR TKDISDPSQL RILRLSCLDF VMVCLVTFNE DLIVLGHESN ISIDDAMAAT NLATYVRLHP FSRVMEWLFN EKVITSLINT IHQDPISLG SASPDSPLVV SILRAIQVMI KALELQETYL HLVRPEVLRY QGEAGVRRKP VANAAYSAFE DGILSHLSLV V DLGKYCNL GHAELTLACL KLLEKISTSS RILSAWSPDS GRLGHRNKAI VQLERNGEGE TISASLSASI MATLDPALAA SG ENYRVKL AILDFLYACL RATPDQPTIA HQLLGFHCEL SKLGIEPKGP FDMQKSLFHS LLNVLITLTV SEEEQGMRGY LVT LKYRVL RILQLLWKSP LSASLVMDEL RATNFLFHML LREVQIQPQL PWDGQLVTGC EFLLSDASLA YIDYLASRAA IFEY IGKEL CSVSQNRIPS IKRQIFDALN GQIFVDEEAP LTIPSIFDFF DFINTDYKWE EIPSPHFTYL KDLDLGPCIL EHKYA GVHY DIRKAQEILA LKRKEYEHSQ LATPEFLETV ELEEKVLIEW LTVRNRANLL LTARLNLLQA WANLLLVMIE SNDFKS TPK MAFLLQALQA ILPTLEAFSS LKSDEAFELA RVAKVLLWKL DFSQDSDAGL DREQFTVGNL IGDKLFQLFQ LCLSAIS QC SGTPELRSLY YSICYRYLTA VVDNDATVAA TPASSTIGPT RSVTNARART LKAITLYGDR LLNVICDDAY GSDTTCQT A AMILLNALVH TSRASSAAGV SPADVDCPII DALNRLNFIG VLVDSLKEIL NEWLAPSSTF DPSLSTNASP SLPIPASPS QQYTSAKLAL LLQLCQTRQG AKYVLQANLF RALEQSGVFA ADPELVEVDS ESGVPRVVAL ERHYALLVAL ARVVGAAVTA RGAHNIVQG RKFLTQHRGL VVHVLKKNAG IGGGVVGNSL ASSINGGSTA TMTRRDEILA QQALEERIEE LAEAFMLLIT A TGFLEYES EQVPSEQPRA HTTFFH UniProtKB: Nucleoporin NUP192 |
-分子 #2: Nucleoporin NIC96
| 分子 | 名称: Nucleoporin NIC96 / タイプ: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / コピー数: 1 / 光学異性体: LEVO |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Chaetomium thermophilum (strain DSM 1495 / CBS 144.50 / IMI 039719) (菌類) Chaetomium thermophilum (strain DSM 1495 / CBS 144.50 / IMI 039719) (菌類)株: DSM 1495 / CBS 144.50 / IMI 039719 |
| 分子量 | 理論値: 7.173938 KDa |
| 組換発現 | 生物種:  |
| 配列 | 文字列: SGTGLGEVDV DTYLSNLQTK TTLSMIADGL ERSARDFDAF LEENVTLEWE AQRKRIYQHF GIK UniProtKB: Nucleoporin NIC96 |
-分子 #3: Nucleoporin NUP53
| 分子 | 名称: Nucleoporin NUP53 / タイプ: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / コピー数: 1 / 光学異性体: LEVO |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Chaetomium thermophilum (strain DSM 1495 / CBS 144.50 / IMI 039719) (菌類) Chaetomium thermophilum (strain DSM 1495 / CBS 144.50 / IMI 039719) (菌類)株: DSM 1495 / CBS 144.50 / IMI 039719 |
| 分子量 | 理論値: 4.173613 KDa |
| 組換発現 | 生物種:  |
| 配列 | 文字列: SQQDGSLRSR KANLETGAFG KSTRRTRSKA ATPAKRED UniProtKB: Nucleoporin NUP53 |
-分子 #4: Nucleoporin NUP145N
| 分子 | 名称: Nucleoporin NUP145N / タイプ: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / コピー数: 1 / 光学異性体: LEVO |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Chaetomium thermophilum (strain DSM 1495 / CBS 144.50 / IMI 039719) (菌類) Chaetomium thermophilum (strain DSM 1495 / CBS 144.50 / IMI 039719) (菌類)株: DSM 1495 / CBS 144.50 / IMI 039719 |
| 分子量 | 理論値: 7.077983 KDa |
| 組換発現 | 生物種:  |
| 配列 | 文字列: SATPLSGKAK VKSRSILPMY KLSPANASRL VTTPQKRAYG FSFSAYGSPT SPSSSASSTP GAFGQSILS UniProtKB: Nucleoporin NUP145 |
-実験情報
-構造解析
| 手法 | クライオ電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
 解析 解析 | 単粒子再構成法 |
| 試料の集合状態 | particle |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 濃度 | 0.5 mg/mL | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 緩衝液 | pH: 8 構成要素:
| ||||||||||||
| 凍結 | 凍結剤: ETHANE / チャンバー内湿度: 100 % / チャンバー内温度: 277 K / 装置: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法
| 顕微鏡 | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| 特殊光学系 | エネルギーフィルター - 名称: GIF Quantum LS |
| 撮影 | フィルム・検出器のモデル: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / 撮影したグリッド数: 1 / 実像数: 4319 / 平均電子線量: 100.0 e/Å2 |
| 電子線 | 加速電圧: 300 kV / 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| 電子光学系 | 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM / 撮影モード: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / 最大 デフォーカス(公称値): 3.0 µm / 最小 デフォーカス(公称値): 1.0 µm / 倍率(公称値): 105000 |
| 試料ステージ | ホルダー冷却材: NITROGEN |
| 実験機器 |  モデル: Titan Krios / 画像提供: FEI Company |
+ 画像解析
画像解析
-原子モデル構築 1
| 精密化 | 空間: REAL / プロトコル: OTHER |
|---|---|
| 得られたモデル |  PDB-7mvv: |
-原子モデル構築 2
| 精密化 | 空間: REAL / プロトコル: OTHER |
|---|---|
| 得られたモデル |  PDB-7mvv: |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー







 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)