[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
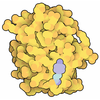
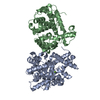
Yorodumi- PDB-1m2z: Crystal structure of a dimer complex of the human glucocorticoid ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 1m2z | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
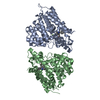
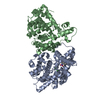
| Title | Crystal structure of a dimer complex of the human glucocorticoid receptor ligand-binding domain bound to dexamethasone and a TIF2 coactivator motif | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HORMONE/HORMONE ACTIVATOR / glucocorticoid receptor / dexamethasone / TIF2 / dimer interface / Hormone binding pocket / charge clamp / coactivator / HORMONE-HORMONE ACTIVATOR COMPLEX | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationRegulation of NPAS4 gene transcription / regulation of glucocorticoid biosynthetic process / nuclear glucocorticoid receptor activity / steroid hormone binding / glucocorticoid metabolic process / response to cortisol / PTK6 Expression / neuroinflammatory response / mammary gland duct morphogenesis / microglia differentiation ...Regulation of NPAS4 gene transcription / regulation of glucocorticoid biosynthetic process / nuclear glucocorticoid receptor activity / steroid hormone binding / glucocorticoid metabolic process / response to cortisol / PTK6 Expression / neuroinflammatory response / mammary gland duct morphogenesis / microglia differentiation / astrocyte differentiation / maternal behavior / adrenal gland development / RNA polymerase II intronic transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / regulation of gluconeogenesis / cellular response to glucocorticoid stimulus / cellular response to steroid hormone stimulus / locomotor rhythm / aryl hydrocarbon receptor binding / motor behavior / cellular response to Thyroglobulin triiodothyronine / regulation of glucose metabolic process / Synthesis of bile acids and bile salts / regulation of lipid metabolic process / estrogen response element binding / Synthesis of bile acids and bile salts via 27-hydroxycholesterol / cellular response to dexamethasone stimulus / Endogenous sterols / Synthesis of bile acids and bile salts via 7alpha-hydroxycholesterol / nuclear receptor-mediated steroid hormone signaling pathway / FOXO-mediated transcription of oxidative stress, metabolic and neuronal genes / cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus / core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / RORA,B,C and NR1D1 (REV-ERBA) regulate gene expression / Expression of BMAL (ARNTL), CLOCK, and NPAS2 / Recycling of bile acids and salts / transcription regulator inhibitor activity / cellular response to hormone stimulus / : / steroid binding / positive regulation of adipose tissue development / Regulation of lipid metabolism by PPARalpha / peroxisome proliferator activated receptor signaling pathway / regulation of cellular response to insulin stimulus / BMAL1:CLOCK,NPAS2 activates circadian expression / SUMOylation of transcription cofactors / response to progesterone / Activation of gene expression by SREBF (SREBP) / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / TBP-class protein binding / nuclear receptor binding / RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / negative regulation of smoothened signaling pathway / synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / SUMOylation of intracellular receptors / chromosome segregation / circadian regulation of gene expression / promoter-specific chromatin binding / Heme signaling / Hsp90 protein binding / PPARA activates gene expression / Transcriptional activation of mitochondrial biogenesis / Cytoprotection by HMOX1 / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / Nuclear Receptor transcription pathway / Transcriptional regulation of white adipocyte differentiation / mRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II / response to wounding / positive regulation of miRNA transcription / DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific / RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex / nuclear receptor activity / spindle / sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding / Regulation of RUNX2 expression and activity / positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process / HATs acetylate histones / MLL4 and MLL3 complexes regulate expression of PPARG target genes in adipogenesis and hepatic steatosis / chromatin organization / DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific / gene expression / transcription regulator complex / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / Potential therapeutics for SARS / DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific / transcription coactivator activity / protein dimerization activity / nuclear speck / nuclear body / RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / mitochondrial matrix / DNA-binding transcription factor activity / protein domain specific binding / cell division / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / apoptotic process / chromatin binding / synapse / centrosome / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / Amore / Resolution: 2.5 Å SYNCHROTRON / Amore / Resolution: 2.5 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Bledsoe, R.B. / Montana, V.G. / Stanley, T.B. / Delves, C.J. / Apolito, C.J. / Mckee, D.D. / Consler, T.G. / Parks, D.J. / Stewart, E.L. / Willson, T.M. ...Bledsoe, R.B. / Montana, V.G. / Stanley, T.B. / Delves, C.J. / Apolito, C.J. / Mckee, D.D. / Consler, T.G. / Parks, D.J. / Stewart, E.L. / Willson, T.M. / Lambert, M.H. / Moore, J.T. / Pearce, K.H. / Xu, H.E. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell(Cambridge,Mass.) / Year: 2002 Journal: Cell(Cambridge,Mass.) / Year: 2002Title: Crystal Structure of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Ligand Binding Domain Reveals a Novel Mode of Receptor Dimerization and Coactivator Recognition Authors: Bledsoe, R.B. / Montana, V.G. / Stanley, T.B. / Delves, C.J. / Apolito, C.J. / Mckee, D.D. / Consler, T.G. / Parks, D.J. / Stewart, E.L. / Willson, T.M. / Lambert, M.H. / Moore, J.T. / Pearce, K.H. / Xu, H.E. | ||||||
| History |
| ||||||
| Remark 400 | COMPOUND THIS STRUCTURE CONTAINS: 1. A NOVEL LBD-LBD DIMER 2. A NOVEL CHARGE CLAMP FOR COACTIVATOR ...COMPOUND THIS STRUCTURE CONTAINS: 1. A NOVEL LBD-LBD DIMER 2. A NOVEL CHARGE CLAMP FOR COACTIVATOR RECOGNITION 3. A UNIQUE STEROID BINDING POCKET | ||||||
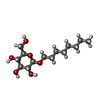
| Remark 600 | HETEROGEN THE ATOMS OF THE DETERGENT, BOG, B-OCTYLGLUCOSIDE, ARE ONLY PARTIALLY SEEN IN THE ...HETEROGEN THE ATOMS OF THE DETERGENT, BOG, B-OCTYLGLUCOSIDE, ARE ONLY PARTIALLY SEEN IN THE STRUCTURE. THE OCTANE CHAIN IS MISSING IN BOG 601. 6 ATOMS OF THE OCTANE CHAIN ARE MISSING IN BOG 701. THE O1 IS MISSING IN BOG 501. |
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  1m2z.cif.gz 1m2z.cif.gz | 130.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb1m2z.ent.gz pdb1m2z.ent.gz | 102.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  1m2z.json.gz 1m2z.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/m2/1m2z https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/m2/1m2z ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/m2/1m2z ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/m2/1m2z | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Similar structure data |
|---|
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 29811.711 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Fragment: Ligand Binding Domain, residues 521-777 / Mutation: F602S Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Plasmid: PET24 / Species (production host): Escherichia coli / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Plasmid: PET24 / Species (production host): Escherichia coli / Production host:  #2: Protein/peptide | Mass: 2448.833 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Fragment: TIF2 coactivator motif, residues 734-754 / Source method: obtained synthetically Details: The peptide was chemically synthesized. The source of the peptide is naturally found in Homo sapiens (human). References: UniProt: Q15596 #3: Sugar | #4: Chemical | #5: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 3.04 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 59.6 % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 293 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop / pH: 8 Details: salts, pH 8.0, VAPOR DIFFUSION, HANGING DROP, temperature 293K | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal grow | *PLUS Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Components of the solutions | *PLUS
|
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  APS APS  / Beamline: 19-BM / Wavelength: 1 Å / Beamline: 19-BM / Wavelength: 1 Å |
| Detector | Type: MACSCIENCE / Detector: CCD / Date: Aug 15, 2002 / Details: Mar CCD 165 mm |
| Radiation | Monochromator: GRAPHITE / Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 1 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 2.5→50 Å / Num. all: 27314 / Num. obs: 27095 / % possible obs: 99.2 % / Observed criterion σ(F): 0 / Observed criterion σ(I): 0 / Redundancy: 10 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 62.5 Å2 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.082 / Rsym value: 0.082 / Net I/σ(I): 35.9 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 2.5→2.59 Å / Redundancy: 10 % / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.718 / Mean I/σ(I) obs: 2.5 / Num. unique all: 2727 / Rsym value: 0.718 |
| Reflection | *PLUS Lowest resolution: 50 Å / % possible obs: 99.4 % |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure: Amore Starting model: GR model built on the PR structure Resolution: 2.5→8 Å / Rfactor Rfree error: 0.006 / Isotropic thermal model: RESTRAINED / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 2 / σ(I): 2 / Stereochemistry target values: Engh & Huber / Details: BULK SOLVENT MODEL USED
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Solvent model: FLAT MODEL / Bsol: 71.2081 Å2 / ksol: 0.379381 e/Å3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 67.2 Å2
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine analyze | Luzzati coordinate error free: 0.42 Å / Luzzati sigma a free: 0.4 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 2.5→8 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Resolution: 2.5→2.65 Å / Rfactor Rfree error: 0.025 / Total num. of bins used: 6
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Xplor file |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | *PLUS Highest resolution: 2.5 Å / Lowest resolution: 50 Å / % reflection Rfree: 10 % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | *PLUS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | *PLUS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints | *PLUS
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj