+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | complex of DNA ligase I and FEN1 on PCNA and DNA | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | DNA / Replication / Complex / Ligase / PCNA / Ligation / FEN1 / Flap Endonuclease I / Okazaki fragment maturation | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationOkazaki fragment processing involved in mitotic DNA replication / flap endonuclease activity / positive regulation of sister chromatid cohesion / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in DNA damage repair and senescence / telomere maintenance via semi-conservative replication / nucleic acid metabolic process / DNA ligase activity / double-stranded DNA exodeoxyribonuclease activity / DNA ligase (ATP) / positive regulation of deoxyribonuclease activity ...Okazaki fragment processing involved in mitotic DNA replication / flap endonuclease activity / positive regulation of sister chromatid cohesion / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in DNA damage repair and senescence / telomere maintenance via semi-conservative replication / nucleic acid metabolic process / DNA ligase activity / double-stranded DNA exodeoxyribonuclease activity / DNA ligase (ATP) / positive regulation of deoxyribonuclease activity / dinucleotide insertion or deletion binding / PCNA-p21 complex / mitotic telomere maintenance via semi-conservative replication / DNA ligase (ATP) activity / 5'-flap endonuclease activity / purine-specific mismatch base pair DNA N-glycosylase activity / MutLalpha complex binding / DNA replication, removal of RNA primer / positive regulation of DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity / nuclear lamina / Polymerase switching / Telomere C-strand (Lagging Strand) Synthesis / UV protection / Processive synthesis on the lagging strand / PCNA complex / DNA ligation / Removal of the Flap Intermediate / Processive synthesis on the C-strand of the telomere / Polymerase switching on the C-strand of the telomere / Mismatch repair (MMR) directed by MSH2:MSH3 (MutSbeta) / Mismatch repair (MMR) directed by MSH2:MSH6 (MutSalpha) / HDR through MMEJ (alt-NHEJ) / Removal of the Flap Intermediate from the C-strand / Transcription of E2F targets under negative control by DREAM complex / lagging strand elongation / replisome / 5'-3' exonuclease activity / exonuclease activity / response to L-glutamate / histone acetyltransferase binding / DNA biosynthetic process / leading strand elongation / DNA polymerase processivity factor activity / G1/S-Specific Transcription / response to dexamethasone / replication fork processing / Early Phase of HIV Life Cycle / nuclear replication fork / SUMOylation of DNA replication proteins / POLB-Dependent Long Patch Base Excision Repair / PCNA-Dependent Long Patch Base Excision Repair / anatomical structure morphogenesis / estrous cycle / mismatch repair / translesion synthesis / response to cadmium ion / DNA polymerase binding / cyclin-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme complex / base-excision repair, gap-filling / epithelial cell differentiation / positive regulation of DNA repair / Translesion synthesis by REV1 / Translesion synthesis by POLK / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Genes Involved in G2 Cell Cycle Arrest / Translesion synthesis by POLI / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in GG-NER / positive regulation of DNA replication / male germ cell nucleus / replication fork / nuclear estrogen receptor binding / liver regeneration / Recognition of DNA damage by PCNA-containing replication complex / Termination of translesion DNA synthesis / double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / Translesion Synthesis by POLH / base-excision repair / HDR through Homologous Recombination (HRR) / Dual Incision in GG-NER / receptor tyrosine kinase binding / memory / cellular response to hydrogen peroxide / Dual incision in TC-NER / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / cellular response to UV / RNA-DNA hybrid ribonuclease activity / cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus / double-strand break repair / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / response to estradiol / manganese ion binding / heart development / double-stranded DNA binding / endonuclease activity / DNA recombination / DNA replication / damaged DNA binding / chromosome, telomeric region / Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds / nuclear body / cell division Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.4 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Blair K / Tehseen M / Raducanu VS / Shahid T / Lancey C / Cruehet R / Hamdan S / De Biasio A | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 1 items United Kingdom, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: Mechanism of human Lig1 regulation by PCNA in Okazaki fragment sealing. Authors: Kerry Blair / Muhammad Tehseen / Vlad-Stefan Raducanu / Taha Shahid / Claudia Lancey / Fahad Rashid / Ramon Crehuet / Samir M Hamdan / Alfredo De Biasio /    Abstract: During lagging strand synthesis, DNA Ligase 1 (Lig1) cooperates with the sliding clamp PCNA to seal the nicks between Okazaki fragments generated by Pol δ and Flap endonuclease 1 (FEN1). We present ...During lagging strand synthesis, DNA Ligase 1 (Lig1) cooperates with the sliding clamp PCNA to seal the nicks between Okazaki fragments generated by Pol δ and Flap endonuclease 1 (FEN1). We present several cryo-EM structures combined with functional assays, showing that human Lig1 recruits PCNA to nicked DNA using two PCNA-interacting motifs (PIPs) located at its disordered N-terminus (PIP) and DNA binding domain (PIP). Once Lig1 and PCNA assemble as two-stack rings encircling DNA, PIP is released from PCNA and only PIP is required for ligation to facilitate the substrate handoff from FEN1. Consistently, we observed that PCNA forms a defined complex with FEN1 and nicked DNA, and it recruits Lig1 to an unoccupied monomer creating a toolbelt that drives the transfer of DNA to Lig1. Collectively, our results provide a structural model on how PCNA regulates FEN1 and Lig1 during Okazaki fragments maturation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_14080.map.gz emd_14080.map.gz | 3.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-14080-v30.xml emd-14080-v30.xml emd-14080.xml emd-14080.xml | 23.9 KB 23.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
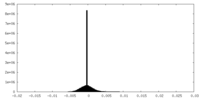
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_14080_fsc.xml emd_14080_fsc.xml | 9.3 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_14080.png emd_14080.png | 85.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-14080.cif.gz emd-14080.cif.gz | 7.4 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_14080_half_map_1.map.gz emd_14080_half_map_1.map.gz emd_14080_half_map_2.map.gz emd_14080_half_map_2.map.gz | 50.8 MB 50.9 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14080 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14080 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14080 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14080 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_14080_validation.pdf.gz emd_14080_validation.pdf.gz | 844.8 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_14080_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_14080_full_validation.pdf.gz | 844.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_14080_validation.xml.gz emd_14080_validation.xml.gz | 16.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_14080_validation.cif.gz emd_14080_validation.cif.gz | 21.2 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-14080 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-14080 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-14080 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-14080 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7qo1MC  7qnzC  8b8tC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_14080.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 65.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_14080.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 65.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.835 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_14080_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_14080_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : complex of DNA ligase I and FEN1 on PCNA and DNA
| Entire | Name: complex of DNA ligase I and FEN1 on PCNA and DNA |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: complex of DNA ligase I and FEN1 on PCNA and DNA
| Supramolecule | Name: complex of DNA ligase I and FEN1 on PCNA and DNA / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #2, #6, #1, #3, #5 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: DNA ligase 1
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA ligase 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: DNA ligase (ATP) |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 84.248555 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: CKESLTEAEV ATEKEGEDGD QPTTPPKPLK TSKAETPTES VSEPEVATKQ ELQEEEEQTK PPRRAPKTLS SFFTPRKPAV KKEVKEEEP GAPGKEGAAE GPLDPSGYNP AKNNYHPVED ACWKPGQKVP YLAVARTFEK IEEVSARLRM VETLSNLLRS V VALSPPDL ...String: CKESLTEAEV ATEKEGEDGD QPTTPPKPLK TSKAETPTES VSEPEVATKQ ELQEEEEQTK PPRRAPKTLS SFFTPRKPAV KKEVKEEEP GAPGKEGAAE GPLDPSGYNP AKNNYHPVED ACWKPGQKVP YLAVARTFEK IEEVSARLRM VETLSNLLRS V VALSPPDL LPVLYLSLNH LGPPQQGLEL GVGDGVLLKA VAQATGRQLE SVRAEAAEKG DVGLVAENSR STQRLMLPPP PL TASGVFS KFRDIARLTG SASTAKKIDI IKGLFVACRH SEARFIARSL SGRLRLGLAE QSVLAALSQA VSLTPPGQEF PPA MVDAGK GKTAEARKTW LEEQGMILKQ TFCEVPDLDR IIPVLLEHGL ERLPEHCKLS PGIPLKPMLA HPTRGISEVL KRFE EAAFT CEYKYDGQRA QIHALEGGEV KIFSRNQEDN TGKYPDIISR IPKIKLPSVT SFILDTEAVA WDREKKQIQP FQVLT TRKR KEVDASEIQV QVCLYAFDLI YLNGESLVRE PLSRRRQLLR ENFVETEGEF VFATSLDTKD IEQIAEFLEQ SVKDSC EGL MVKTLDVDAT YEIAKRSHNW LKLKKDYLDG VGDTLDLVVI GAYLGRGKRA GRYGGFLLAS YDEDSEELQA ICKLGTG FS DEELEEHHQS LKALVLPSPR PYVRIDGAVI PDHWLDPSAV WEVKCADLSL SPIYPAARGL VDSDKGISLR FPRFIRVR E DKQPEQATTS AQVACLYRKQ SQIQNQQGED SGSDPEDTY UniProtKB: DNA ligase 1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen
| Macromolecule | Name: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 29.088061 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GPHMFEARLV QGSILKKVLE ALKDLINEAC WDISSSGVNL QSMDSSHVSL VQLTLRSEGF DTYRCDRNLA MGVNLTSMSK ILKCAGNED IITLRAEDNA DTLALVFEAP NQEKVSDYEM KLMDLDVEQL GIPEQEYSCV VKMPSGEFAR ICRDLSHIGD A VVISCAKD ...String: GPHMFEARLV QGSILKKVLE ALKDLINEAC WDISSSGVNL QSMDSSHVSL VQLTLRSEGF DTYRCDRNLA MGVNLTSMSK ILKCAGNED IITLRAEDNA DTLALVFEAP NQEKVSDYEM KLMDLDVEQL GIPEQEYSCV VKMPSGEFAR ICRDLSHIGD A VVISCAKD GVKFSASGEL GNGNIKLSQT SNVDKEEEAV TIEMNEPVQL TFALRYLNFF TKATPLSSTV TLSMSADVPL VV EYKIADM GHLKYYLAPK IEDEEGS UniProtKB: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen |
-Macromolecule #6: Flap endonuclease 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Flap endonuclease 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 42.617039 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGIQGLAKLI ADVAPSAIRE NDIKSYFGRK VAIDASMSIY QFLIAVRQGG DVLQNEEGET TSHLMGMFYR TIRMMENGIK PVYVFDGKP PQLKSGELAK RSERRAEAEK QLQQAQAAGA EQEVEKFTKR LVKVTKQHND ECKHLLSLMG IPYLDAPSEA E ASCAALVK ...String: MGIQGLAKLI ADVAPSAIRE NDIKSYFGRK VAIDASMSIY QFLIAVRQGG DVLQNEEGET TSHLMGMFYR TIRMMENGIK PVYVFDGKP PQLKSGELAK RSERRAEAEK QLQQAQAAGA EQEVEKFTKR LVKVTKQHND ECKHLLSLMG IPYLDAPSEA E ASCAALVK AGKVYAAATE DMACLTFGSP VLMRHLTASE AKKLPIQEFH LSRILQELGL NQEQFVDLCI LLGSDYCESI RG IGPKRAV DLIQKHKSIE EIVRRLDPNK YPVPENWLHK EAHQLFLEPE VLDPESVELK WSEPNEEELI KFMCGEKQFS EER IRSGVK RLSKSRQGST QGRLDDFFKV TGSLSSAKRK EPEPKGSTKK KAKTGAAGKF KRGK UniProtKB: Flap endonuclease 1 |
-Macromolecule #3: Oligo19ddC
| Macromolecule | Name: Oligo19ddC / type: dna / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 5.802744 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DG)(DC)(DT)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC) (DT)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DOC) |
-Macromolecule #4: Oligo13P
| Macromolecule | Name: Oligo13P / type: dna / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 3.976599 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DG)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DA) (DA)(DC)(DC) |
-Macromolecule #5: Oligo32
| Macromolecule | Name: Oligo32 / type: dna / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 9.845345 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DG)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DC) (DG)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DT) (DC)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DA) (DA)(DG)(DC) |
-Macromolecule #7: ADENOSINE MONOPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE MONOPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: AMP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 347.221 Da |
| Chemical component information | 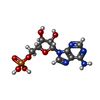 ChemComp-AMP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
| ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid | Model: UltrAuFoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 300 sec. Details: The grid was coated with graphene oxide prior to use. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Min: 77.0 K / Max: 77.0 K |
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Bioquantum / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 5760 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 4092 pixel / Number grids imaged: 1 / Average exposure time: 2.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 18.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 105000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-7qo1: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)