+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structure of ATP synthase from an early photosynthetic bacterium . |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, Vol. 122, Issue 13, Page e2425824122, Year 2025 |
| Publish date | Mar 25, 2025 |
 Authors Authors | Xin Zhang / Jingyi Wu / Zhenzhen Min / Jiamao Wang / Xin Hong / Xinkai Pei / Zihe Rao / Xiaoling Xu /  |
| PubMed Abstract | F-type ATP synthase (FF) catalyzes proton motive force-driven ATP synthesis in mitochondria, chloroplasts, and bacteria. Different from the mitochondrial and bacterial enzymes, FF from photosynthetic ...F-type ATP synthase (FF) catalyzes proton motive force-driven ATP synthesis in mitochondria, chloroplasts, and bacteria. Different from the mitochondrial and bacterial enzymes, FF from photosynthetic organisms have evolved diverse structural and mechanistic details to adapt to the light-dependent reactions. Although complete structure of chloroplast FF has been reported, no high-resolution structure of an FF from photosynthetic bacteria has been available. Here, we report cryo-EM structures of an intact and functionally competent FF from (FF), a filamentous anoxygenic phototrophic bacterium from the earliest branch of photosynthetic organisms. The structures of FF in its ADP-free and ADP-bound forms for three rotational states reveal a previously unrecognized architecture of ATP synthases. A pair of peripheral stalks connect to the F head through a dimer of δ-subunits, and associate with two membrane-embedded a-subunits that are asymmetrically positioned outside and clamp F's c-ring. The two a-subunits constitute two proton inlets on the periplasmic side and two proton outlets on the cytoplasmic side, endowing FF with unique proton translocation pathways that allow more protons being translocated relative to single a-subunit FF. Our findings deepen understanding of the architecture and proton translocation mechanisms of FF synthases and suggest innovative strategies for modulating their activities by altering the number of a-subunit. |
 External links External links |  Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A /  PubMed:40131952 / PubMed:40131952 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.84 - 5.18 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-60868, PDB-9itj: EMDB-60869, PDB-9itk: EMDB-60870, PDB-9itl: EMDB-60871, PDB-9itm: EMDB-60872, PDB-9itn: EMDB-60873, PDB-9ito: EMDB-60874, PDB-9itp: EMDB-60875, PDB-9itq: EMDB-60876, PDB-9itr: EMDB-60877, PDB-9its: EMDB-60878, PDB-9itt: EMDB-60879, PDB-9itu: EMDB-60880, PDB-9itv: EMDB-60881, PDB-9itw: EMDB-60882, PDB-9itx: EMDB-60883, PDB-9ity: EMDB-60884, PDB-9itz: EMDB-60885, PDB-9iu0: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-ATP:  ChemComp-MG:  ChemComp-ADP:  ChemComp-PO4: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / ATP synthesis / proton channels / proton-motive force / proton translocation |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers



























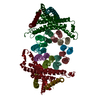











 chloroflexus aurantiacus j-10-fl (bacteria)
chloroflexus aurantiacus j-10-fl (bacteria)