+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9its | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Chloroflexus aurantiacus ADP-bound ATP synthase, state 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components | (ATP synthase ...) x 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / ATP synthesis / proton channels / proton-motive force / proton translocation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationproton motive force-driven plasma membrane ATP synthesis / proton motive force-driven ATP synthesis / proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex, proton-transporting domain / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / ADP binding / lipid binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Chloroflexus aurantiacus J-10-fl (bacteria) Chloroflexus aurantiacus J-10-fl (bacteria) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.89 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhang, X. / Wu, J. / Xu, X. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1items China, 1items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2025 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2025Title: Structure of ATP synthase from an early photosynthetic bacterium . Authors: Xin Zhang / Jingyi Wu / Zhenzhen Min / Jiamao Wang / Xin Hong / Xinkai Pei / Zihe Rao / Xiaoling Xu /  Abstract: F-type ATP synthase (FF) catalyzes proton motive force-driven ATP synthesis in mitochondria, chloroplasts, and bacteria. Different from the mitochondrial and bacterial enzymes, FF from photosynthetic ...F-type ATP synthase (FF) catalyzes proton motive force-driven ATP synthesis in mitochondria, chloroplasts, and bacteria. Different from the mitochondrial and bacterial enzymes, FF from photosynthetic organisms have evolved diverse structural and mechanistic details to adapt to the light-dependent reactions. Although complete structure of chloroplast FF has been reported, no high-resolution structure of an FF from photosynthetic bacteria has been available. Here, we report cryo-EM structures of an intact and functionally competent FF from (FF), a filamentous anoxygenic phototrophic bacterium from the earliest branch of photosynthetic organisms. The structures of FF in its ADP-free and ADP-bound forms for three rotational states reveal a previously unrecognized architecture of ATP synthases. A pair of peripheral stalks connect to the F head through a dimer of δ-subunits, and associate with two membrane-embedded a-subunits that are asymmetrically positioned outside and clamp F's c-ring. The two a-subunits constitute two proton inlets on the periplasmic side and two proton outlets on the cytoplasmic side, endowing FF with unique proton translocation pathways that allow more protons being translocated relative to single a-subunit FF. Our findings deepen understanding of the architecture and proton translocation mechanisms of FF synthases and suggest innovative strategies for modulating their activities by altering the number of a-subunit. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9its.cif.gz 9its.cif.gz | 973.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9its.ent.gz pdb9its.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9its.json.gz 9its.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  9its_validation.pdf.gz 9its_validation.pdf.gz | 1.9 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  9its_full_validation.pdf.gz 9its_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.9 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  9its_validation.xml.gz 9its_validation.xml.gz | 135.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  9its_validation.cif.gz 9its_validation.cif.gz | 216.8 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/it/9its https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/it/9its ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/it/9its ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/it/9its | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  60877MC  9itjC  9itkC  9itlC  9itmC  9itnC  9itoC  9itpC  9itqC  9itrC  9ittC  9ituC 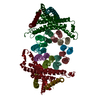 9itvC  9itwC  9itxC  9ityC  9itzC  9iu0C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-ATP synthase ... , 8 types, 26 molecules ABCDEFGRSWYVUXHIJKLMNOPQTZ
| #1: Protein | Mass: 56563.340 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Chloroflexus aurantiacus J-10-fl (bacteria) Chloroflexus aurantiacus J-10-fl (bacteria)References: UniProt: A9WGS6, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase #2: Protein | Mass: 51755.691 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Chloroflexus aurantiacus J-10-fl (bacteria) Chloroflexus aurantiacus J-10-fl (bacteria)References: UniProt: A9WGS4, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase #3: Protein | | Mass: 32118.955 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Chloroflexus aurantiacus J-10-fl (bacteria) Chloroflexus aurantiacus J-10-fl (bacteria)References: UniProt: A9WGS5 #4: Protein | | Mass: 15694.111 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Chloroflexus aurantiacus J-10-fl (bacteria) Chloroflexus aurantiacus J-10-fl (bacteria)References: UniProt: A9WGS3 #5: Protein | Mass: 16552.895 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Chloroflexus aurantiacus J-10-fl (bacteria) Chloroflexus aurantiacus J-10-fl (bacteria)References: UniProt: A9WGS7 #6: Protein | Mass: 18710.455 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Chloroflexus aurantiacus J-10-fl (bacteria) Chloroflexus aurantiacus J-10-fl (bacteria)References: UniProt: A9WGS8 #7: Protein | Mass: 7688.102 Da / Num. of mol.: 10 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Chloroflexus aurantiacus J-10-fl (bacteria) Chloroflexus aurantiacus J-10-fl (bacteria)References: UniProt: A9WGS9 #8: Protein | Mass: 34176.105 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Chloroflexus aurantiacus J-10-fl (bacteria) Chloroflexus aurantiacus J-10-fl (bacteria)References: UniProt: A9WGT0 |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 4 types, 11 molecules 






| #9: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #10: Chemical | #11: Chemical | #12: Chemical | ChemComp-PO4 / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: ATP synthase / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#8 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Chloroflexus aurantiacus J-10-fl (bacteria) Chloroflexus aurantiacus J-10-fl (bacteria) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1600 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.20.1_4487: / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.89 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 85733 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



















 PDBj
PDBj






