+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Snapshots of SOS response reveal structural requisites for LexA autoproteolysis. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | iScience, Vol. 28, Issue 2, Page 111726, Year 2025 |
| Publish date | Feb 21, 2025 |
 Authors Authors | Filippo Vascon / Sofia De Felice / Matteo Gasparotto / Stefan T Huber / Claudio Catalano / Monica Chinellato / Riccardo Mezzetti / Alessandro Grinzato / Francesco Filippini / Lorenzo Maso / Arjen J Jakobi / Laura Cendron /      |
| PubMed Abstract | Antimicrobial resistance poses a severe threat to human health and stands out among the pathogens responsible for this emergency. The SOS response to DNA damage is crucial in bacterial evolution, ...Antimicrobial resistance poses a severe threat to human health and stands out among the pathogens responsible for this emergency. The SOS response to DNA damage is crucial in bacterial evolution, influencing resistance development and adaptability in challenging environments, especially under antibiotic exposure. Recombinase A (RecA) and the transcriptional repressor LexA are the key players that orchestrate this process, determining either the silencing or the active transcription of the genes under their control. By integrating state-of-the-art structural approaches with binding and functional assays, we elucidated the molecular events activating the SOS response in , focusing on the RecA-LexA interaction. Our findings identify the conserved determinants and strength of the interactions that allow RecA to trigger LexA autocleavage and inactivation. These results provide the groundwork for designing novel antimicrobial strategies and exploring the potential translation of -derived approaches, to address the implications of infections. |
 External links External links |  iScience / iScience /  PubMed:39898034 / PubMed:39898034 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (helical sym.) / EM (single particle) / X-ray diffraction |
| Resolution | 1.7 - 4.2 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-19761, PDB-8s70: EMDB-19771, PDB-8s7g:  PDB-8b0v: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-EDO:  ChemComp-CA: 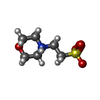 ChemComp-MES:  ChemComp-HOH:  ChemComp-MG:  ChemComp-AGS: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION / transcriptional regulator / serine-lysine protease / DNA BINDING PROTEIN / recombinase / co-protease activator / protease / antibiotic resistance / SOS response |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers






 Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria)
Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria)