+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Dimeric transport mechanism of human vitamin C transporter SVCT1. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Commun, Vol. 15, Issue 1, Page 5569, Year 2024 |
| Publish date | Jul 2, 2024 |
 Authors Authors | Takaaki A Kobayashi / Hiroto Shimada / Fumiya K Sano / Yuzuru Itoh / Sawako Enoki / Yasushi Okada / Tsukasa Kusakizako / Osamu Nureki /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Vitamin C plays important roles as a cofactor in many enzymatic reactions and as an antioxidant against oxidative stress. As some mammals including humans cannot synthesize vitamin C de novo from ...Vitamin C plays important roles as a cofactor in many enzymatic reactions and as an antioxidant against oxidative stress. As some mammals including humans cannot synthesize vitamin C de novo from glucose, its uptake from dietary sources is essential, and is mediated by the sodium-dependent vitamin C transporter 1 (SVCT1). Despite its physiological significance in maintaining vitamin C homeostasis, the structural basis of the substrate transport mechanism remained unclear. Here, we report the cryo-EM structures of human SVCT1 in different states at 2.5-3.5 Å resolutions. The binding manner of vitamin C together with two sodium ions reveals the counter ion-dependent substrate recognition mechanism. Furthermore, comparisons of the inward-open and occluded structures support a transport mechanism combining elevator and distinct rotational motions. Our results demonstrate the molecular mechanism of vitamin C transport with its underlying conformational cycle, potentially leading to future industrial and medical applications. |
 External links External links |  Nat Commun / Nat Commun /  PubMed:38956111 / PubMed:38956111 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.49 - 3.5 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-36201, PDB-8jew: EMDB-36204, PDB-8jez: EMDB-36205, PDB-8jf0: EMDB-36206, PDB-8jf1: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-ASC:  ChemComp-NA:  ChemComp-AV0:  ChemComp-LBN:  ChemComp-CLR:  ChemComp-NAG:  ChemComp-PLM:  ChemComp-HOH:  ChemComp-Y01: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSPORT PROTEIN / Transporter / Membrane protein / Ascorbic acid / Vitamin C / Sodium / Solute carrier |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers










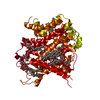
 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)