+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Glycan-dependent cell adhesion mechanism of Tc toxins. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Nat Commun, Vol. 11, Issue 1, Page 2694, Year 2020 |
| 掲載日 | 2020年6月1日 |
 著者 著者 | Daniel Roderer / Felix Bröcker / Oleg Sitsel / Paulina Kaplonek / Franziska Leidreiter / Peter H Seeberger / Stefan Raunser /   |
| PubMed 要旨 | Toxin complex (Tc) toxins are virulence factors of pathogenic bacteria. Tcs are composed of three subunits: TcA, TcB and TcC. TcA facilitates receptor-toxin interaction and membrane permeation, TcB ...Toxin complex (Tc) toxins are virulence factors of pathogenic bacteria. Tcs are composed of three subunits: TcA, TcB and TcC. TcA facilitates receptor-toxin interaction and membrane permeation, TcB and TcC form a toxin-encapsulating cocoon. While the mechanisms of holotoxin assembly and pore formation have been described, little is known about receptor binding of TcAs. Here, we identify heparins/heparan sulfates and Lewis antigens as receptors for different TcAs from insect and human pathogens. Glycan array screening reveals that all tested TcAs bind negatively charged heparins. Cryo-EM structures of Morganella morganii TcdA4 and Xenorhabdus nematophila XptA1 reveal that heparins/heparan sulfates unexpectedly bind to different regions of the shell domain, including receptor-binding domains. In addition, Photorhabdus luminescens TcdA1 binds to Lewis antigens with micromolar affinity. Here, the glycan interacts with the receptor-binding domain D of the toxin. Our results suggest a glycan dependent association mechanism of Tc toxins on the host cell surface. |
 リンク リンク |  Nat Commun / Nat Commun /  PubMed:32483155 / PubMed:32483155 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 3.2 - 5.0 Å |
| 構造データ | 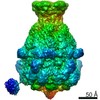 EMDB-10794: EMDB-10796, PDB-6yew: EMDB-10797, PDB-6yey: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | TOXIN / complex / glycan |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について



 Photorhabdus luminescens (バクテリア)
Photorhabdus luminescens (バクテリア)
