+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Protease-associated import systems are widespread in Gram-negative bacteria. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | PLoS Genet, Vol. 15, Issue 10, Page e1008435, Year 2019 |
| Publish date | Oct 15, 2019 |
 Authors Authors | Rhys Grinter / Pok Man Leung / Lakshmi C Wijeyewickrema / Dene Littler / Simone Beckham / Robert N Pike / Daniel Walker / Chris Greening / Trevor Lithgow /   |
| PubMed Abstract | Bacteria have evolved sophisticated uptake machineries in order to obtain the nutrients required for growth. Gram-negative plant pathogens of the genus Pectobacterium obtain iron from the protein ...Bacteria have evolved sophisticated uptake machineries in order to obtain the nutrients required for growth. Gram-negative plant pathogens of the genus Pectobacterium obtain iron from the protein ferredoxin, which is produced by their plant hosts. This iron-piracy is mediated by the ferredoxin uptake system (Fus), a gene cluster encoding proteins that transport ferredoxin into the bacterial cell and process it proteolytically. In this work we show that gene clusters related to the Fus are widespread in bacterial species. Through structural and biochemical characterisation of the distantly related Fus homologues YddB and PqqL from Escherichia coli, we show that these proteins are analogous to components of the Fus from Pectobacterium. The membrane protein YddB shares common structural features with the outer membrane ferredoxin transporter FusA, including a large extracellular substrate binding site. PqqL is an active protease with an analogous periplasmic localisation and iron-dependent expression to the ferredoxin processing protease FusC. Structural analysis demonstrates that PqqL and FusC share specific features that distinguish them from other members of the M16 protease family. Taken together, these data provide evidence that protease associated import systems analogous to the Fus are widespread in Gram-negative bacteria. |
 External links External links |  PLoS Genet / PLoS Genet /  PubMed:31613892 / PubMed:31613892 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | SAS (X-ray synchrotron) / X-ray diffraction |
| Resolution | 2 - 2.6 Å |
| Structure data |  SASDFB6: 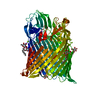 PDB-6ofr:  PDB-6ofs:  PDB-6oft: |
| Chemicals | 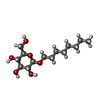 ChemComp-BOG:  ChemComp-MG:  ChemComp-GOL:  ChemComp-HOH:  ChemComp-ZN:  ChemComp-CL:  ChemComp-PO4: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSPORT PROTEIN / Protein Transport / Gram-negative bacteria / Outer membrane / Nutrient Uptake / TonB-Dependent Transporter / HYDROLASE / Protease / M16 Family / Processing Protease |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers




