+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structural basis of ligand recognition and self-activation of orphan GPR52. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nature, Vol. 579, Issue 7797, Page 152-157, Year 2020 |
| Publish date | Feb 19, 2020 |
 Authors Authors | Xi Lin / Mingyue Li / Niandong Wang / Yiran Wu / Zhipu Luo / Shimeng Guo / Gye-Won Han / Shaobai Li / Yang Yue / Xiaohu Wei / Xin Xie / Yong Chen / Suwen Zhao / Jian Wu / Ming Lei / Fei Xu /   |
| PubMed Abstract | GPR52 is a class-A orphan G-protein-coupled receptor that is highly expressed in the brain and represents a promising therapeutic target for the treatment of Huntington's disease and several ...GPR52 is a class-A orphan G-protein-coupled receptor that is highly expressed in the brain and represents a promising therapeutic target for the treatment of Huntington's disease and several psychiatric disorders. Pathological malfunction of GPR52 signalling occurs primarily through the heterotrimeric G protein, but it is unclear how GPR52 and G couple for signal transduction and whether a native ligand or other activating input is required. Here we present the high-resolution structures of human GPR52 in three states: a ligand-free state, a G-coupled self-activation state and a potential allosteric ligand-bound state. Together, our structures reveal that extracellular loop 2 occupies the orthosteric binding pocket and operates as a built-in agonist, conferring an intrinsically high level of basal activity to GPR52. A fully active state is achieved when G is coupled to GPR52 in the absence of an external agonist. The receptor also features a side pocket for ligand binding. These insights into the structure and function of GPR52 could improve our understanding of other self-activated GPCRs, enable the identification of endogenous and tool ligands, and guide drug discovery efforts that target GPR52. |
 External links External links |  Nature / Nature /  PubMed:32076264 PubMed:32076264 |
| Methods | EM (single particle) / X-ray diffraction |
| Resolution | 2.2 - 3.32 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-0902, PDB-6li3:  PDB-6li0:  PDB-6li1:  PDB-6li2: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-EN6: 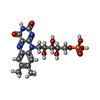 ChemComp-FMN: 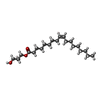 ChemComp-OLC: 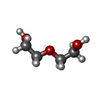 ChemComp-PEG: 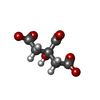 ChemComp-FLC:  ChemComp-HOH:  ChemComp-PGE:  ChemComp-ZN: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / Human GPR52 receptor / Class A / orphan GPCR / agonist c17 / flavodoxin / LCP / apo form / rubredoxin / G-protein coupled receptor / self-activation / cryo-EM |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers





 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)
 desulfovibrio vulgaris str. hildenborough (bacteria)
desulfovibrio vulgaris str. hildenborough (bacteria)