+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Reducing effects of particle adsorption to the air-water interface in cryo-EM. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Methods, Vol. 15, Issue 10, Page 793-795, Year 2018 |
| Publish date | Sep 24, 2018 |
 Authors Authors | Alex J Noble / Hui Wei / Venkata P Dandey / Zhening Zhang / Yong Zi Tan / Clinton S Potter / Bridget Carragher /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Most protein particles prepared in vitreous ice for single-particle cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) are adsorbed to air-water or substrate-water interfaces, which can cause the particles to adopt ...Most protein particles prepared in vitreous ice for single-particle cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) are adsorbed to air-water or substrate-water interfaces, which can cause the particles to adopt preferred orientations. By using a rapid plunge-freezing robot and nanowire grids, we were able to reduce some of the deleterious effects of the air-water interface by decreasing the dwell time of particles in thin liquid films. We demonstrated this by using single-particle cryo-EM and cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET) to examine hemagglutinin, insulin receptor complex, and apoferritin. |
 External links External links |  Nat Methods / Nat Methods /  PubMed:30250056 / PubMed:30250056 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (tomography) / EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.77 - 6.09 Å |
| Structure data |  EMDB-7623:  EMDB-7624:  EMDB-7625:  EMDB-7627:  EMDB-7628:  EMDB-7629:  EMDB-7630: 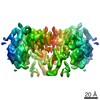 EMDB-7788: 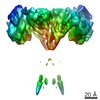 EMDB-7791: 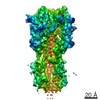 EMDB-7792: |
| Source |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers



 Tabanus atratus (black horsefly)
Tabanus atratus (black horsefly) Homo sapiens (human)
Homo sapiens (human) Influenza A virus (A/Hong Kong/26/1983(H3N2))
Influenza A virus (A/Hong Kong/26/1983(H3N2))