+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Molecular mechanism of the arrestin-biased agonism of neurotensin receptor 1 by an intracellular allosteric modulator. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Cell Res, Vol. 35, Issue 4, Page 284-295, Year 2025 |
| Publish date | Mar 21, 2025 |
 Authors Authors | Demeng Sun / Xiang Li / Qingning Yuan / Yuanxia Wang / Pan Shi / Huanhuan Zhang / Tao Wang / Wenjing Sun / Shenglong Ling / Yuanchun Liu / Jinglin Lai / Wenqin Xie / Wanchao Yin / Lei Liu / H Eric Xu / Changlin Tian /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Biased allosteric modulators (BAMs) of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) have been at the forefront of drug discovery owing to their potential to selectively stimulate therapeutically relevant ...Biased allosteric modulators (BAMs) of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) have been at the forefront of drug discovery owing to their potential to selectively stimulate therapeutically relevant signaling and avoid on-target side effects. Although structures of GPCRs in complex with G protein or GRK in a BAM-bound state have recently been resolved, revealing that BAM can induce biased signaling by directly modulating interactions between GPCRs and these two transducers, no BAM-bound GPCR-arrestin complex structure has yet been determined, limiting our understanding of the full pharmacological profile of BAMs. Herein, we developed a chemical protein synthesis strategy to generate neurotensin receptor 1 (NTSR1) with defined hexa-phosphorylation at its C-terminus and resolved high-resolution cryo-EM structures (2.65-2.88 Å) of NTSR1 in complex with both β-arrestin1 and the BAM SBI-553. These structures revealed a unique "loop engagement" configuration of β-arrestin1 coupling to NTSR1 in the presence of SBI-553, markedly different from the typical "core engagement" configuration observed in the absence of BAMs. This configuration is characterized by the engagement of the intracellular loop 3 of NTSR1 with a cavity in the central crest of β-arrestin1, representing a previously unobserved, arrestin-selective conformation of GPCR. Our findings fill the critical knowledge gap regarding the regulation of GPCR-arrestin interactions and biased signaling by BAMs, which would advance the development of safer and more efficacious GPCR-targeted therapeutics. |
 External links External links |  Cell Res / Cell Res /  PubMed:40118988 / PubMed:40118988 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.65 - 3.41 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-60578, PDB-8zyt: EMDB-60579, PDB-8zyu: EMDB-60583, PDB-8zyy: EMDB-63543, PDB-9m0d: |
| Chemicals | 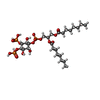 ChemComp-PIO:  ChemComp-SRW: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / neurotensin receptor / beta-arrestin1 / phosphorylation / intracellular agonist / SBI-553 / GPCR / Neurotensin receptore 1 / Complex / beta-arrestin 1 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers







 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)
