+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Structure and mechanism of the plastid/parasite ATP/ADP translocator. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Nature, Vol. 641, Issue 8063, Page 797-804, Year 2025 |
| 掲載日 | 2025年3月12日 |
 著者 著者 | Huajian Lin / Jian Huang / Tianming Li / Wenjuan Li / Yutong Wu / Tianjiao Yang / Yuwei Nian / Xiang Lin / Jiangqin Wang / Ruiying Wang / Xiaohui Zhao / Nannan Su / Jinru Zhang / Xudong Wu / Minrui Fan /  |
| PubMed 要旨 | Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the principal energy currency of all living cells. Metabolically impaired obligate intracellular parasites, such as the human pathogens Chlamydia trachomatis and ...Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the principal energy currency of all living cells. Metabolically impaired obligate intracellular parasites, such as the human pathogens Chlamydia trachomatis and Rickettsia prowazekii, can acquire ATP from their host cells through a unique ATP/adenosine diphosphate (ADP) translocator, which mediates the import of ATP into and the export of ADP and phosphate out of the parasite cells, thus allowing the exploitation of the energy reserves of host cells (also known as energy parasitism). This type of ATP/ADP translocator also exists in the obligate intracellular endosymbionts of protists and the plastids of plants and algae and has been implicated to play an important role in endosymbiosis. The plastid/parasite type of ATP/ADP translocator is phylogenetically and functionally distinct from the mitochondrial ATP/ADP translocator, and its structure and transport mechanism are still unknown. Here we report the cryo-electron microscopy structures of two plastid/parasite types of ATP/ADP translocators in the apo and substrate-bound states. The ATP/ADP-binding pocket is located at the interface between the N and C domains of the translocator, and a conserved asparagine residue within the pocket is critical for substrate specificity. The translocator operates through a rocker-switch alternating access mechanism involving the relative rotation of the two domains as rigid bodies. Our results provide critical insights for understanding ATP translocation across membranes in energy parasitism and endosymbiosis and offer a structural basis for developing drugs against obligate intracellular parasites. |
 リンク リンク |  Nature / Nature /  PubMed:40074904 PubMed:40074904 |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 2.72 - 2.9 Å |
| 構造データ | EMDB-61117, PDB-9j3j: EMDB-61118, PDB-9j3l: EMDB-61119, PDB-9j3m: EMDB-61120, PDB-9j3n: EMDB-61121, PDB-9j3o: |
| 化合物 |  ChemComp-ATP:  ChemComp-ADP:  ChemComp-PO4: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / ATP/ADP translocator;non-mitochondrial;antiporter |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について




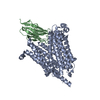

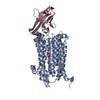
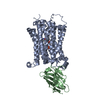

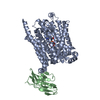

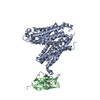


 chlamydia pneumoniae (肺炎クラミジア)
chlamydia pneumoniae (肺炎クラミジア)