+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Zinc transporter 1 functions in copper uptake and cuproptosis. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Cell Metab, Vol. 36, Issue 9, Page 2118-22129.e6, Year 2024 |
| Publish date | Sep 3, 2024 |
 Authors Authors | Yehua Li / Jiahao Ma / Rui Wang / Yuanhanyu Luo / Sanduo Zheng / Xiaodong Wang /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Copper (Cu) is a co-factor for several essential metabolic enzymes. Disruption of Cu homeostasis results in genetic diseases such as Wilson's disease. Here, we show that the zinc transporter 1 (ZnT1) ...Copper (Cu) is a co-factor for several essential metabolic enzymes. Disruption of Cu homeostasis results in genetic diseases such as Wilson's disease. Here, we show that the zinc transporter 1 (ZnT1), known to export zinc (Zn) out of the cell, also mediates Cu entry into cells and is required for Cu-induced cell death, cuproptosis. Structural analysis and functional characterization indicate that Cu and Zn share the same primary binding site, allowing Zn to compete for Cu uptake. Among ZnT members, ZnT1 harbors a unique inter-subunit disulfide bond that stabilizes the outward-open conformations of both protomers to facilitate efficient Cu transport. Specific knockout of the ZnT1 gene in the intestinal epithelium caused the loss of Lgr5+ stem cells due to Cu deficiency. ZnT1, therefore, functions as a dual Zn and Cu transporter and potentially serves as a target for using Zn in the treatment of Wilson's disease caused by Cu overload. |
 External links External links |  Cell Metab / Cell Metab /  PubMed:39111308 PubMed:39111308 |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.26 - 3.59 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-60410, PDB-8zsb: EMDB-60435, PDB-8zsz: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-ZN: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSPORT PROTEIN / Copper uptake / Cuproptosis / ZnT family / zinc transport |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers




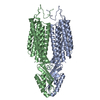

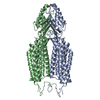
 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)