+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the brine shrimp mitochondrial ATP synthase suggests an inactivation mechanism for the ATP synthase leak channel. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Cell Death Differ, Vol. 32, Issue 8, Page 1518-1535, Year 2025 |
| Publish date | Mar 19, 2025 |
 Authors Authors | Amrendra Kumar / Juliana da Fonseca Rezende E Mello / Yangyu Wu / Daniel Morris / Ikram Mezghani / Erin Smith / Stephane Rombauts / Peter Bossier / Juno Krahn / Fred J Sigworth / Nelli Mnatsakanyan /   |
| PubMed Abstract | Mammalian mitochondria undergo Ca-induced and cyclosporinA (CsA)-regulated permeability transition (mPT) by activating the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) situated in mitochondrial ...Mammalian mitochondria undergo Ca-induced and cyclosporinA (CsA)-regulated permeability transition (mPT) by activating the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) situated in mitochondrial inner membranes. Ca-induced prolonged openings of mPTP under certain pathological conditions result in mitochondrial swelling and rupture of the outer membrane, leading to mitochondrial dysfunction and cell death. While the exact molecular composition and structure of mPTP remain unknown, mammalian ATP synthase was reported to form voltage and Ca-activated leak channels involved in mPT. Unlike in mammals, mitochondria of the crustacean Artemia franciscana have the ability to accumulate large amounts of Ca without undergoing the mPT. Here, we performed structural and functional analysis of A. franciscana ATP synthase to study the molecular mechanism of mPTP inhibition in this organism. We found that the channel formed by the A. franciscana ATP synthase dwells predominantly in its inactive state and is insensitive to Ca, in contrast to porcine heart ATP synthase. Single-particle cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) analysis revealed distinct structural features in A. franciscana ATP synthase compared with mammals. The stronger density of the e-subunit C-terminal region and its enhanced interaction with the c-ring were found in A. franciscana ATP synthase. These data suggest an inactivation mechanism of the ATP synthase leak channel and its possible contribution to the lack of mPT in this organism. |
 External links External links |  Cell Death Differ / Cell Death Differ /  PubMed:40108410 / PubMed:40108410 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.5 - 4.0 Å |
| Structure data | 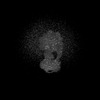 EMDB-43079: Artemia franciscana ATP synthase state 3a, pH 8 EMDB-44061, PDB-9b0x: 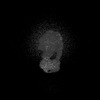 EMDB-44087: Artemia franciscana ATP synthase state 1, pH 7.0 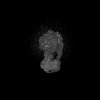 EMDB-44094: Artemia franciscana ATP synthase state 3a, pH 7.0  EMDB-44096: Artemia franciscana ATP synthase F1 domain, state 3a, pH 7.0 EMDB-44142, PDB-9b3j:  EMDB-44162: Artemia franciscana ATP synthase FO domain, state 2, pH 7.0  EMDB-44165: Artemia franciscana ATP synthase F1 domain, state 2, pH 7.0  EMDB-44169: Artemia franciscana ATP synthase FO domain, state 2, pH 8.0  EMDB-44170: Artemia franciscana ATP synthase F1 domain, state 2, pH 8.0  EMDB-44172: Artemia franciscana ATP synthase peripheral stalk, state 2, pH 8.0  EMDB-44173: Artemia franciscana ATP synthase, state 1, pH 8.0  EMDB-44177: Artemia franciscana ATP synthase, state 2, FOF1 with weak density of the peripheral stalk, pH 8.0 EMDB-44776, PDB-9bpg:  EMDB-49579: Artemia franciscana ATP synthase, state 2, pH 8.0, consensus map  EMDB-49580: Artemia franciscana ATP synthase, state 2, pH 7.0, consensus map |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-ATP:  ChemComp-MG:  ChemComp-ADP: 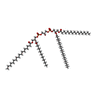 ChemComp-CDL: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / ATP synthesis / Complex V / mitochondria / oxidative-phosphorylation |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers






 artemia franciscana (crustacean)
artemia franciscana (crustacean)