+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Single-Molecule Insight Into α-Synuclein Fibril Structure and Mechanics Modulated by Chemical Compounds. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Adv Sci (Weinh), Vol. 12, Issue 14, Page e2416721, Year 2025 |
| Publish date | Feb 14, 2025 |
 Authors Authors | Xiang Li / Lulu Bi / Shenqing Zhang / Qianhui Xu / Wencheng Xia / Youqi Tao / Shaojuan Wu / Yanan Li / Weidong Le / Wenyan Kang / Dan Li / Bo Sun / Cong Liu /  |
| PubMed Abstract | α-Syn fibrils, a key pathological hallmark of Parkinson's disease, is closely associated with disease initiation and progression. Several small molecules are found to bind or dissolve α-syn ...α-Syn fibrils, a key pathological hallmark of Parkinson's disease, is closely associated with disease initiation and progression. Several small molecules are found to bind or dissolve α-syn fibrils, offering potential therapeutic applications. Here, an innovative optical tweezers-based, fluorescence-combined approach is developed to probe the mechanical characteristics of α-syn fibrils at the single-molecule level. When subjected to axial stretching, local deformation within α-syn fibrils appeared at forces above 50 pN. These structural alternations occurred stepwise and are irreversible, suggesting unfolding of individual α-syn molecules or subdomains. Additionally, α-syn fibrils exhibits high heterogeneity in lateral disruption, with rupture force ranging from 50 to 500 pN. The impact of different compounds on the structure and mechanical features of α-syn fibrils is further examined. Notably, epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) generally attenuates the rupture force of fibrils by wedging into the N-terminal polar groove and induces fibril dissociation. Conversely, copper chlorophyllin A (CCA) attaches to four different sites wrapping around the fibril core, reinforcing the stability of the fibril against rupture forces. The work offers an effective method for characterizing single-fibril properties and bridges compound-induced structural alternations with mechanical response. These insights are valuable for understanding amyloid fibril mechanics and their regulation by small molecules. |
 External links External links |  Adv Sci (Weinh) / Adv Sci (Weinh) /  PubMed:39951335 / PubMed:39951335 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (helical sym.) |
| Resolution | 3.1 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-38733, PDB-8xwd: |
| Chemicals | 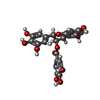 ChemComp-KDH: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | PROTEIN FIBRIL / amyloid |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers





 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)