+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Filament structures unveil the dynamic organization of human acetyl-CoA carboxylase. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Sci Adv, Vol. 10, Issue 41, Page eado4880, Year 2024 |
| Publish date | Oct 11, 2024 |
 Authors Authors | Fayang Zhou / Yuanyuan Zhang / Yuyao Zhu / Qiang Zhou / Yigong Shi / Qi Hu /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Human acetyl-coenzyme A (CoA) carboxylases (ACCs) catalyze the carboxylation of acetyl-CoA, which is the rate-limiting step in fatty acid synthesis. The molecular mechanism underlying the dynamic ...Human acetyl-coenzyme A (CoA) carboxylases (ACCs) catalyze the carboxylation of acetyl-CoA, which is the rate-limiting step in fatty acid synthesis. The molecular mechanism underlying the dynamic organization of ACCs is largely unknown. Here, we determined the cryo-electron microscopy (EM) structure of human ACC1 in its inactive state, which forms a unique filament structure and is in complex with acetyl-CoA. We also determined the cryo-EM structure of human ACC1 activated by dephosphorylation and citrate treatment, at a resolution of 2.55 Å. Notably, the covalently linked biotin binds to a site that is distant from the acetyl-CoA binding site when acetyl-CoA is absent, suggesting a potential coordination between biotin binding and acetyl-CoA binding. These findings provide insights into the structural dynamics and regulatory mechanisms of human ACCs. |
 External links External links |  Sci Adv / Sci Adv /  PubMed:39383219 / PubMed:39383219 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.55 - 4.14 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-38432, PDB-8xkz: EMDB-38433, PDB-8xl0: EMDB-38434, PDB-8xl1: EMDB-38435, PDB-8xl2: |
| Chemicals | 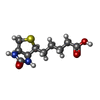 ChemComp-BTN: 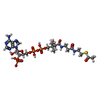 ChemComp-ACO: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | LIGASE / Biotin-dependent carboxylase |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers








 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)