[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
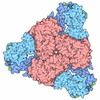
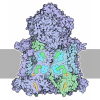
Yorodumi- PDB-8xl0: Citrate-induced filament of human acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase 1... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8xl0 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Citrate-induced filament of human acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase 1 (ACC1-citrate) | ||||||
 Components Components | Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | LIGASE / Biotin-dependent carboxylase | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationacetyl-CoA carboxylase / fatty-acyl-CoA biosynthetic process / Defective HLCS causes multiple carboxylase deficiency / Biotin transport and metabolism / malonyl-CoA biosynthetic process / Fatty acyl-CoA biosynthesis / ChREBP activates metabolic gene expression / acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity / acetyl-CoA metabolic process / tissue homeostasis ...acetyl-CoA carboxylase / fatty-acyl-CoA biosynthetic process / Defective HLCS causes multiple carboxylase deficiency / Biotin transport and metabolism / malonyl-CoA biosynthetic process / Fatty acyl-CoA biosynthesis / ChREBP activates metabolic gene expression / acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity / acetyl-CoA metabolic process / tissue homeostasis / Carnitine shuttle / lipid homeostasis / Activation of gene expression by SREBF (SREBP) / fibrillar center / fatty acid biosynthetic process / cellular response to prostaglandin E stimulus / actin cytoskeleton / protein homotetramerization / mitochondrion / ATP binding / metal ion binding / identical protein binding / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.14 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhou, F.Y. / Zhang, Y.Y. / Zhou, Q. / Hu, Q. | ||||||
| Funding support | 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2024 Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2024Title: Filament structures unveil the dynamic organization of human acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Authors: Fayang Zhou / Yuanyuan Zhang / Yuyao Zhu / Qiang Zhou / Yigong Shi / Qi Hu /  Abstract: Human acetyl-coenzyme A (CoA) carboxylases (ACCs) catalyze the carboxylation of acetyl-CoA, which is the rate-limiting step in fatty acid synthesis. The molecular mechanism underlying the dynamic ...Human acetyl-coenzyme A (CoA) carboxylases (ACCs) catalyze the carboxylation of acetyl-CoA, which is the rate-limiting step in fatty acid synthesis. The molecular mechanism underlying the dynamic organization of ACCs is largely unknown. Here, we determined the cryo-electron microscopy (EM) structure of human ACC1 in its inactive state, which forms a unique filament structure and is in complex with acetyl-CoA. We also determined the cryo-EM structure of human ACC1 activated by dephosphorylation and citrate treatment, at a resolution of 2.55 Å. Notably, the covalently linked biotin binds to a site that is distant from the acetyl-CoA binding site when acetyl-CoA is absent, suggesting a potential coordination between biotin binding and acetyl-CoA binding. These findings provide insights into the structural dynamics and regulatory mechanisms of human ACCs. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8xl0.cif.gz 8xl0.cif.gz | 2 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8xl0.ent.gz pdb8xl0.ent.gz | 1.6 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8xl0.json.gz 8xl0.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xl/8xl0 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xl/8xl0 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xl/8xl0 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xl/8xl0 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  38433MC  8xkzC  8xl1C 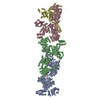 8xl2C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
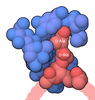
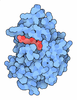
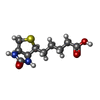
| #1: Protein | Mass: 265869.375 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q13085, acetyl-CoA carboxylase Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q13085, acetyl-CoA carboxylase#2: Chemical | ChemComp-BTN / Has ligand of interest | Y | Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Citrate-induced filament of human acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase 1 (ACC1-citrate) Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2200 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.14 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 36041 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj