+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Molecular basis for ATPase-powered substrate translocation by the Lon AAA+ protease. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | J Biol Chem, Vol. 297, Issue 4, Page 101239, Year 2021 |
| Publish date | Sep 24, 2021 |
 Authors Authors | Shanshan Li / Kan-Yen Hsieh / Shih-Chieh Su / Grigore D Pintilie / Kaiming Zhang / Chung-I Chang /    |
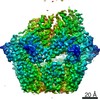
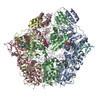
| PubMed Abstract | The Lon AAA+ (adenosine triphosphatases associated with diverse cellular activities) protease (LonA) converts ATP-fuelled conformational changes into sufficient mechanical force to drive ...The Lon AAA+ (adenosine triphosphatases associated with diverse cellular activities) protease (LonA) converts ATP-fuelled conformational changes into sufficient mechanical force to drive translocation of a substrate into a hexameric proteolytic chamber. To understand the structural basis for the substrate translocation process, we determined the cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of Meiothermus taiwanensis LonA (MtaLonA) in a substrate-engaged state at 3.6 Å resolution. Our data indicate that substrate interactions are mediated by the dual pore loops of the ATPase domains, organized in spiral staircase arrangement from four consecutive protomers in different ATP-binding and hydrolysis states. However, a closed AAA+ ring is maintained by two disengaged ADP-bound protomers transiting between the lowest and highest position. This structure reveals a processive rotary translocation mechanism mediated by LonA-specific nucleotide-dependent allosteric coordination among the ATPase domains, which is induced by substrate binding. |
 External links External links |  J Biol Chem / J Biol Chem /  PubMed:34563541 / PubMed:34563541 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.6 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-21870, PDB-6wqh: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-AGS: 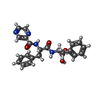 ChemComp-4KZ:  ChemComp-ADP: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | MOTOR PROTEIN / Lon AAA+ / protease / cryo-EM / dual pore-loops |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers



 meiothermus taiwanensis (bacteria)
meiothermus taiwanensis (bacteria)
