+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Influence of lipid bilayer on the structure of the muscle-type nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, Vol. 121, Issue 19, Page e2319913121, Year 2024 |
| Publish date | May 7, 2024 |
 Authors Authors | Nigel Unwin /  |
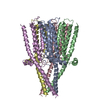
| PubMed Abstract | The muscle-type nicotinic acetylcholine receptor is a transmitter-gated ion channel residing in the plasma membrane of electrocytes and striated muscle cells. It is present predominantly at synaptic ...The muscle-type nicotinic acetylcholine receptor is a transmitter-gated ion channel residing in the plasma membrane of electrocytes and striated muscle cells. It is present predominantly at synaptic junctions, where it effects rapid depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane in response to acetylcholine released into the synaptic cleft. Previously, cryo-EM of intact membrane from revealed that the lipid bilayer surrounding the junctional receptor has a uniquely asymmetric and ordered structure, due to a high concentration of cholesterol. It is now shown that this special lipid environment influences the transmembrane (TM) folding of the protein. All five submembrane MX helices of the membrane-intact junctional receptor align parallel to the surface of the cholesterol-ordered lipids in the inner leaflet of the bilayer; also, the TM helices in the outer leaflet are splayed apart. However in the structure obtained from the same protein after extraction and incorporation in nanodiscs, the MX helices do not align to a planar surface, and the TM helices arrange compactly in the outer leaflet. Realignment of the MX helices of the nanodisc-solved structure to a planar surface converts their adjoining TM helices into an obligatory splayed configuration, characteristic of the junctional receptor. Thus, the form of the receptor sustained by the special lipid environment of the synaptic junction is the one that mediates fast synaptic transmission; whereas, the nanodisc-embedded protein may be like the extrajunctional form, existing in a disordered lipid environment. |
 External links External links |  Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A /  PubMed:38683987 / PubMed:38683987 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) / EM (helical sym.) |
| Resolution | 4.7 - 9.4 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-18596, PDB-8qqm:  EMDB-18785: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor  EMDB-18802: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor 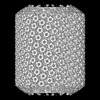 EMDB-18804: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor 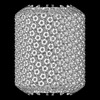 EMDB-18805: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor  EMDB-18816: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine recptor  EMDB-18817: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor  EMDB-18823: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor  EMDB-18824: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor  EMDB-18831: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor  EMDB-18832: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor  EMDB-18835: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor  EMDB-18836: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor  EMDB-18837: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor  EMDB-18838: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor  EMDB-18840: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor  EMDB-18843: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor  EMDB-18844: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor  EMDB-18845: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor  EMDB-18846: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor  EMDB-18847: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor  EMDB-18849: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor  EMDB-18850: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor  EMDB-18853: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor  EMDB-18854: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor  EMDB-18855: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor  EMDB-18856: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor  EMDB-18857: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor  EMDB-18858: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor  EMDB-18862: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor  EMDB-18863: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor  EMDB-18865: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor  EMDB-18867: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor  EMDB-18869: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor  EMDB-18870: Influence of lipid bilayer on structure of acetylcholine receptor |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / Ion channel |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers