+Search query
-Structure paper
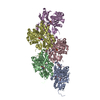
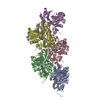
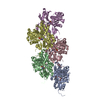
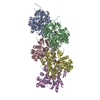
| Title | Structural basis of actin filament assembly and aging. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nature, Vol. 611, Issue 7935, Page 374-379, Year 2022 |
| Publish date | Oct 26, 2022 |
 Authors Authors | Wout Oosterheert / Björn U Klink / Alexander Belyy / Sabrina Pospich / Stefan Raunser /  |
| PubMed Abstract | The dynamic turnover of actin filaments (F-actin) controls cellular motility in eukaryotes and is coupled to changes in the F-actin nucleotide state. It remains unclear how F-actin hydrolyses ATP and ...The dynamic turnover of actin filaments (F-actin) controls cellular motility in eukaryotes and is coupled to changes in the F-actin nucleotide state. It remains unclear how F-actin hydrolyses ATP and subsequently undergoes subtle conformational rearrangements that ultimately lead to filament depolymerization by actin-binding proteins. Here we present cryo-electron microscopy structures of F-actin in all nucleotide states, polymerized in the presence of Mg or Ca at approximately 2.2 Å resolution. The structures show that actin polymerization induces the relocation of water molecules in the nucleotide-binding pocket, activating one of them for the nucleophilic attack of ATP. Unexpectedly, the back door for the subsequent release of inorganic phosphate (P) is closed in all structures, indicating that P release occurs transiently. The small changes in the nucleotide-binding pocket after ATP hydrolysis and P release are sensed by a key amino acid, amplified and transmitted to the filament periphery. Furthermore, differences in the positions of water molecules in the nucleotide-binding pocket explain why Ca-actin shows slower polymerization rates than Mg-actin. Our work elucidates the solvent-driven rearrangements that govern actin filament assembly and aging and lays the foundation for the rational design of drugs and small molecules for imaging and therapeutic applications. |
 External links External links |  Nature / Nature /  PubMed:36289337 / PubMed:36289337 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.15 - 2.24 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-15104, PDB-8a2r: EMDB-15105, PDB-8a2s: EMDB-15106, PDB-8a2t: EMDB-15107, PDB-8a2u: EMDB-15108, PDB-8a2y: EMDB-15109, PDB-8a2z: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-ADP:  ChemComp-MG:  ChemComp-BEF:  ChemComp-HOH:  ChemComp-PO4:  ChemComp-CA: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / actin / cytoskeleton / filament / nucleotide state |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers