[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-15108: Cryo-EM structure of F-actin in the Ca2+-ADP-Pi nucleotide state. -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of F-actin in the Ca2+-ADP-Pi nucleotide state. | |||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Sharpened, local-resolution filtered cryo-EM density map of F-actin in the Ca2 -ADP-Pi nucleotide state. | |||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcytoskeletal motor activator activity / myosin heavy chain binding / tropomyosin binding / actin filament bundle / troponin I binding / filamentous actin / mesenchyme migration / skeletal muscle myofibril / actin filament bundle assembly / striated muscle thin filament ...cytoskeletal motor activator activity / myosin heavy chain binding / tropomyosin binding / actin filament bundle / troponin I binding / filamentous actin / mesenchyme migration / skeletal muscle myofibril / actin filament bundle assembly / striated muscle thin filament / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly / actin monomer binding / skeletal muscle fiber development / stress fiber / titin binding / actin filament polymerization / actin filament / filopodium / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / calcium-dependent protein binding / lamellipodium / cell body / protein domain specific binding / hydrolase activity / calcium ion binding / positive regulation of gene expression / magnesium ion binding / ATP binding / identical protein binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   | |||||||||||||||
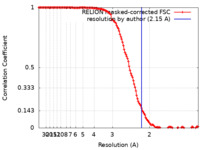
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.15 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Oosterheert W / Klink BU / Belyy A / Pospich S / Raunser S | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support | European Union,  Germany, 4 items Germany, 4 items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2022 Journal: Nature / Year: 2022Title: Structural basis of actin filament assembly and aging. Authors: Wout Oosterheert / Björn U Klink / Alexander Belyy / Sabrina Pospich / Stefan Raunser /  Abstract: The dynamic turnover of actin filaments (F-actin) controls cellular motility in eukaryotes and is coupled to changes in the F-actin nucleotide state. It remains unclear how F-actin hydrolyses ATP and ...The dynamic turnover of actin filaments (F-actin) controls cellular motility in eukaryotes and is coupled to changes in the F-actin nucleotide state. It remains unclear how F-actin hydrolyses ATP and subsequently undergoes subtle conformational rearrangements that ultimately lead to filament depolymerization by actin-binding proteins. Here we present cryo-electron microscopy structures of F-actin in all nucleotide states, polymerized in the presence of Mg or Ca at approximately 2.2 Å resolution. The structures show that actin polymerization induces the relocation of water molecules in the nucleotide-binding pocket, activating one of them for the nucleophilic attack of ATP. Unexpectedly, the back door for the subsequent release of inorganic phosphate (P) is closed in all structures, indicating that P release occurs transiently. The small changes in the nucleotide-binding pocket after ATP hydrolysis and P release are sensed by a key amino acid, amplified and transmitted to the filament periphery. Furthermore, differences in the positions of water molecules in the nucleotide-binding pocket explain why Ca-actin shows slower polymerization rates than Mg-actin. Our work elucidates the solvent-driven rearrangements that govern actin filament assembly and aging and lays the foundation for the rational design of drugs and small molecules for imaging and therapeutic applications. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_15108.map.gz emd_15108.map.gz | 129.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-15108-v30.xml emd-15108-v30.xml emd-15108.xml emd-15108.xml | 26.1 KB 26.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_15108_fsc.xml emd_15108_fsc.xml | 13.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_15108.png emd_15108.png | 91.8 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_15108_msk_1.map emd_15108_msk_1.map | 216 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Others |  emd_15108_additional_1.map.gz emd_15108_additional_1.map.gz emd_15108_half_map_1.map.gz emd_15108_half_map_1.map.gz emd_15108_half_map_2.map.gz emd_15108_half_map_2.map.gz | 168.9 MB 170.7 MB 170.7 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-15108 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-15108 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-15108 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-15108 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8a2yMC  8a2rC  8a2sC  8a2tC  8a2uC  8a2zC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_15108.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_15108.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Sharpened, local-resolution filtered cryo-EM density map of F-actin in the Ca2 -ADP-Pi nucleotide state. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
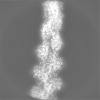
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.695 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_15108_msk_1.map emd_15108_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
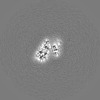
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
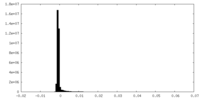
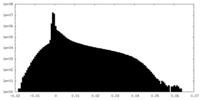
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: 3D-refined, unsharpened cryo-EM density map of F-actin in...
| File | emd_15108_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | 3D-refined, unsharpened cryo-EM density map of F-actin in the Ca2 -ADP-Pi nucleotide state. | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
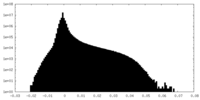
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Unfiltered half map 1 of F-actin in the Ca2 -ADP-Pi nucleotide state.
| File | emd_15108_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Unfiltered half map 1 of F-actin in the Ca2 -ADP-Pi nucleotide state. | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Unfiltered half map 2 of F-actin in the Ca2 -ADP-Pi nucleotide state.
| File | emd_15108_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Unfiltered half map 2 of F-actin in the Ca2 -ADP-Pi nucleotide state. | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : rabbit skeletal alpha-actin in the filamentous state.
| Entire | Name: rabbit skeletal alpha-actin in the filamentous state. |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: rabbit skeletal alpha-actin in the filamentous state.
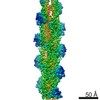
| Supramolecule | Name: rabbit skeletal alpha-actin in the filamentous state. / type: complex / Chimera: Yes / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 Details: The helical rise of F-actin is 27.5 Angstrom, with a helical twist of ~166.5 degrees. |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 15.2 kDa/nm |
-Macromolecule #1: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle
| Macromolecule | Name: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 5 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 41.875633 KDa |
| Sequence | String: DEDETTALVC DNGSGLVKAG FAGDDAPRAV FPSIVGRPRH QGVMVGMGQK DSYVGDEAQS KRGILTLKYP IE(HIC)GII TNW DDMEKIWHHT FYNELRVAPE EHPTLLTEAP LNPKANREKM TQIMFETFNV PAMYVAIQAV LSLYASGRTT GIVLDSG DG VTHNVPIYEG ...String: DEDETTALVC DNGSGLVKAG FAGDDAPRAV FPSIVGRPRH QGVMVGMGQK DSYVGDEAQS KRGILTLKYP IE(HIC)GII TNW DDMEKIWHHT FYNELRVAPE EHPTLLTEAP LNPKANREKM TQIMFETFNV PAMYVAIQAV LSLYASGRTT GIVLDSG DG VTHNVPIYEG YALPHAIMRL DLAGRDLTDY LMKILTERGY SFVTTAEREI VRDIKEKLCY VALDFENEMA TAASSSSL E KSYELPDGQV ITIGNERFRC PETLFQPSFI GMESAGIHET TYNSIMKCDI DIRKDLYANN VMSGGTTMYP GIADRMQKE ITALAPSTMK IKIIAPPERK YSVWIGGSIL ASLSTFQQMW ITKQEYDEAG PSIVHRKCF |
-Macromolecule #2: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 5 / Formula: ADP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 427.201 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ADP: |
-Macromolecule #3: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 5 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Macromolecule #4: PHOSPHATE ION
| Macromolecule | Name: PHOSPHATE ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 5 / Formula: PO4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 94.971 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-PO4: |
-Macromolecule #5: water
| Macromolecule | Name: water / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 528 / Formula: HOH |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.015 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-HOH: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.67 mg/mL | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
Details: F-phosphate buffer: 5 mM Tris, 100 mM KCl, 2 mM CaCl2, 2 mM NaN3, 1 mM DTT, 50 mM potassium phosphate pH 7.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/1 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 286 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV Details: The Vitrobot was operated at 13 degrees celsius and the samples were blotted for 9 seconds with a blot force of -25.. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Slit width: 15 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 5760 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 4092 pixel / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 10156 / Average exposure time: 3.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 88.8 e/Å2 / Details: Images were collected in supperresolution mode. |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.7000000000000001 µm / Nominal magnification: 130000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | PDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Details | The structures were then refined through a similar protocol of iterative cycles in Coot and phenix real-space refine. All solvent molecules (ions, waters) were placed manually in Coot in the central actin subunit, and were then placed in the other subunits using NCS. Because the local resolution of each F-actin reconstruction is highest in the center and lower at the periphery of the map, we inspected all waters in each structure manually before the final phenix refinement; water molecular with poor corresponding cryo-EM density were removed. |
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT |
| Output model |  PDB-8a2y: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)