+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Pathogen-sugar interactions revealed by universal saturation transfer analysis. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Science, Vol. 377, Issue 6604, Page eabm3125, Year 2022 |
| Publish date | Jul 22, 2022 |
 Authors Authors | Charles J Buchanan / Ben Gaunt / Peter J Harrison / Yun Yang / Jiwei Liu / Aziz Khan / Andrew M Giltrap / Audrey Le Bas / Philip N Ward / Kapil Gupta / Maud Dumoux / Tiong Kit Tan / Lisa Schimaski / Sergio Daga / Nicola Picchiotti / Margherita Baldassarri / Elisa Benetti / Chiara Fallerini / Francesca Fava / Annarita Giliberti / Panagiotis I Koukos / Matthew J Davy / Abirami Lakshminarayanan / Xiaochao Xue / Georgios Papadakis / Lachlan P Deimel / Virgínia Casablancas-Antràs / Timothy D W Claridge / Alexandre M J J Bonvin / Quentin J Sattentau / Simone Furini / Marco Gori / Jiandong Huo / Raymond J Owens / Christiane Schaffitzel / Imre Berger / Alessandra Renieri / / James H Naismith / Andrew J Baldwin / Benjamin G Davis /     |
| PubMed Abstract | Many pathogens exploit host cell-surface glycans. However, precise analyses of glycan ligands binding with heavily modified pathogen proteins can be confounded by overlapping sugar signals and/or ...Many pathogens exploit host cell-surface glycans. However, precise analyses of glycan ligands binding with heavily modified pathogen proteins can be confounded by overlapping sugar signals and/or compounded with known experimental constraints. Universal saturation transfer analysis (uSTA) builds on existing nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy to provide an automated workflow for quantitating protein-ligand interactions. uSTA reveals that early-pandemic, B-origin-lineage severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike trimer binds sialoside sugars in an "end-on" manner. uSTA-guided modeling and a high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structure implicate the spike N-terminal domain (NTD) and confirm end-on binding. This finding rationalizes the effect of NTD mutations that abolish sugar binding in SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Together with genetic variance analyses in early pandemic patient cohorts, this binding implicates a sialylated polylactosamine motif found on tetraantennary N-linked glycoproteins deep in the human lung as potentially relevant to virulence and/or zoonosis. |
 External links External links |  Science / Science /  PubMed:35737812 PubMed:35737812 |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.27 - 2.49 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-14152, PDB-7qur: EMDB-14153, PDB-7qus:  EMDB-14154: SARS-CoV-2 Spike with ethylbenzamide-tri-iodo Siallyllactose, C1 symmetry  EMDB-14155: SARS-CoV-2 Spike, C1 symmetry |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-NAG: 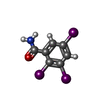 ChemComp-GE9: 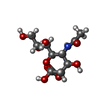 ChemComp-SIA:  ChemComp-EIC:  ChemComp-HOH: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | VIRAL PROTEIN / SARS-CoV-2 Spike |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers








