+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the dimeric Rhodobacter sphaeroides RC-LH1 core complex at 2.9 Å: the structural basis for dimerisation. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Biochem J, Vol. 478, Issue 21, Page 3923-3937, Year 2021 |
| Publish date | Nov 12, 2021 |
 Authors Authors | Pu Qian / Tristan I Croll / Andrew Hitchcock / Philip J Jackson / Jack H Salisbury / Pablo Castro-Hartmann / Kasim Sader / David J K Swainsbury / C Neil Hunter /   |
| PubMed Abstract | The dimeric reaction centre light-harvesting 1 (RC-LH1) core complex of Rhodobacter sphaeroides converts absorbed light energy to a charge separation, and then it reduces a quinone electron and ...The dimeric reaction centre light-harvesting 1 (RC-LH1) core complex of Rhodobacter sphaeroides converts absorbed light energy to a charge separation, and then it reduces a quinone electron and proton acceptor to a quinol. The angle between the two monomers imposes a bent configuration on the dimer complex, which exerts a major influence on the curvature of the membrane vesicles, known as chromatophores, where the light-driven photosynthetic reactions take place. To investigate the dimerisation interface between two RC-LH1 monomers, we determined the cryogenic electron microscopy structure of the dimeric complex at 2.9 Å resolution. The structure shows that each monomer consists of a central RC partly enclosed by a 14-subunit LH1 ring held in an open state by PufX and protein-Y polypeptides, thus enabling quinones to enter and leave the complex. Two monomers are brought together through N-terminal interactions between PufX polypeptides on the cytoplasmic side of the complex, augmented by two novel transmembrane polypeptides, designated protein-Z, that bind to the outer faces of the two central LH1 β polypeptides. The precise fit at the dimer interface, enabled by PufX and protein-Z, by C-terminal interactions between opposing LH1 αβ subunits, and by a series of interactions with a bound sulfoquinovosyl diacylglycerol lipid, bring together each monomer creating an S-shaped array of 28 bacteriochlorophylls. The seamless join between the two sets of LH1 bacteriochlorophylls provides a path for excitation energy absorbed by one half of the complex to migrate across the dimer interface to the other half. |
 External links External links |  Biochem J / Biochem J /  PubMed:34622934 / PubMed:34622934 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.9 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-13590, PDB-7pqd: |
| Chemicals | 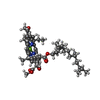 ChemComp-BCL: 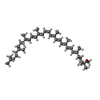 ChemComp-SP2:  ChemComp-3PE:  ChemComp-CD4: 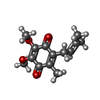 ChemComp-UQ1: 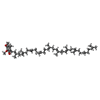 ChemComp-U10:  ChemComp-BPH:  ChemComp-SQD:  ChemComp-LMT:  ChemComp-FE:  ChemComp-HOH: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | PHOTOSYNTHESIS / light harvesting complex / Cryo-EM / purple bacteria / RC-LH1 / RC-LH1-PufXYZ / dimer / dimeric core complex |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers




 cereibacter sphaeroides 2.4.1 (bacteria)
cereibacter sphaeroides 2.4.1 (bacteria)