+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Molecular organization of the E. coli cellulose synthase macrocomplex. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Nat Struct Mol Biol, Vol. 28, Issue 3, Page 310-318, Year 2021 |
| 掲載日 | 2021年3月11日 |
 著者 著者 | Justin F Acheson / Ruoya Ho / Nicolette F Goularte / Lynette Cegelski / Jochen Zimmer /  |
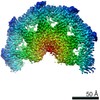
| PubMed 要旨 | Cellulose is frequently found in communities of sessile bacteria called biofilms. Escherichia coli and other enterobacteriaceae modify cellulose with phosphoethanolamine (pEtN) to promote host tissue ...Cellulose is frequently found in communities of sessile bacteria called biofilms. Escherichia coli and other enterobacteriaceae modify cellulose with phosphoethanolamine (pEtN) to promote host tissue adhesion. The E. coli pEtN cellulose biosynthesis machinery contains the catalytic BcsA-B complex that synthesizes and secretes cellulose, in addition to five other subunits. The membrane-anchored periplasmic BcsG subunit catalyzes pEtN modification. Here we present the structure of the roughly 1 MDa E. coli Bcs complex, consisting of one BcsA enzyme associated with six copies of BcsB, determined by single-particle cryo-electron microscopy. BcsB homo-oligomerizes primarily through interactions between its carbohydrate-binding domains as well as intermolecular beta-sheet formation. The BcsB hexamer creates a half spiral whose open side accommodates two BcsG subunits, directly adjacent to BcsA's periplasmic channel exit. The cytosolic BcsE and BcsQ subunits associate with BcsA's regulatory PilZ domain. The macrocomplex is a fascinating example of cellulose synthase specification. |
 リンク リンク |  Nat Struct Mol Biol / Nat Struct Mol Biol /  PubMed:33712813 / PubMed:33712813 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 3.4 - 4.2 Å |
| 構造データ | EMDB-23146, PDB-7l2z: EMDB-23267, PDB-7lby: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | BIOSYNTHETIC PROTEIN / bacterial cellulose / periplasmic / structural subunit / TRANSFERASE / synthase |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について