+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Large domain movements through the lipid bilayer mediate substrate release and inhibition of glutamate transporters. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Elife, Vol. 9, Year 2020 |
| 掲載日 | 2020年11月6日 |
 著者 著者 | Xiaoyu Wang / Olga Boudker /  |
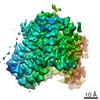
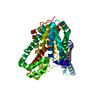
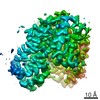
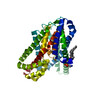
| PubMed 要旨 | Glutamate transporters are essential players in glutamatergic neurotransmission in the brain, where they maintain extracellular glutamate below cytotoxic levels and allow for rounds of transmission. ...Glutamate transporters are essential players in glutamatergic neurotransmission in the brain, where they maintain extracellular glutamate below cytotoxic levels and allow for rounds of transmission. The structural bases of their function are well established, particularly within a model archaeal homolog, sodium, and aspartate symporter Glt. However, the mechanism of gating on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane remains ambiguous. We report Cryo-EM structures of Glt reconstituted into nanodiscs, including those structurally constrained in the cytoplasm-facing state and either apo, bound to sodium ions only, substrate, or blockers. The structures show that both substrate translocation and release involve movements of the bulky transport domain through the lipid bilayer. They further reveal a novel mode of inhibitor binding and show how solutes release is coupled to protein conformational changes. Finally, we describe how domain movements are associated with the displacement of bound lipids and significant membrane deformations, highlighting the potential regulatory role of the bilayer. |
 リンク リンク |  Elife / Elife /  PubMed:33155546 / PubMed:33155546 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 3.05 - 3.71 Å |
| 構造データ | EMDB-21986, PDB-6x12: EMDB-21987, PDB-6x13: EMDB-21988, PDB-6x14: EMDB-21989, PDB-6x15: EMDB-21990, PDB-6x16: EMDB-21991, PDB-6x17: |
| 化合物 | 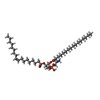 ChemComp-6OU: 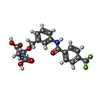 ChemComp-7O9:  ChemComp-NA: 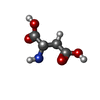 ChemComp-ASP:  ChemComp-HG:  ChemComp-HOH:  ChemComp-TB1: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | TRANSPORT PROTEIN / sodium-coupled L-aspartate transporter |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について









 pyrococcus horikoshii (古細菌)
pyrococcus horikoshii (古細菌)