+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Structural principles of SNARE complex recognition by the AAA+ protein NSF. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Elife, Vol. 7, Year 2018 |
| 掲載日 | 2018年9月10日 |
 著者 著者 | K Ian White / Minglei Zhao / Ucheor B Choi / Richard A Pfuetzner / Axel T Brunger /  |
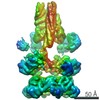
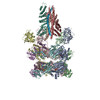
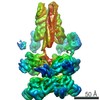
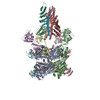
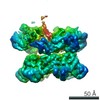
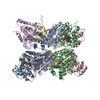
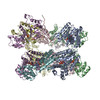
| PubMed 要旨 | The recycling of SNARE proteins following complex formation and membrane fusion is an essential process in eukaryotic trafficking. A highly conserved AAA+ protein, NSF (-ethylmaleimide sensitive ...The recycling of SNARE proteins following complex formation and membrane fusion is an essential process in eukaryotic trafficking. A highly conserved AAA+ protein, NSF (-ethylmaleimide sensitive factor) and an adaptor protein, SNAP (soluble NSF attachment protein), disassemble the SNARE complex. We report electron-cryomicroscopy structures of the complex of NSF, αSNAP, and the full-length soluble neuronal SNARE complex (composed of syntaxin-1A, synaptobrevin-2, SNAP-25A) in the presence of ATP under non-hydrolyzing conditions at ~3.9 Å resolution. These structures reveal electrostatic interactions by which two αSNAP molecules interface with a specific surface of the SNARE complex. This interaction positions the SNAREs such that the 15 N-terminal residues of SNAP-25A are loaded into the D1 ring pore of NSF via a spiral pattern of interactions between a conserved tyrosine NSF residue and SNAP-25A backbone atoms. This loading process likely precedes ATP hydrolysis. Subsequent ATP hydrolysis then drives complete disassembly. |
 リンク リンク |  Elife / Elife /  PubMed:30198481 / PubMed:30198481 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 3.8 - 4.4 Å |
| 構造データ | EMDB-9100, PDB-6mdm: EMDB-9101, PDB-6mdn: |
| 化合物 |  ChemComp-ATP:  ChemComp-ADP: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | HYDROLASE / SNARE / NSF / SNAP / ATPase / AAA / disassembly / synapse / membrane fusion / exocytosis |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について