+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Cryo-EM structures of human SPCA1a reveal the mechanism of Ca/Mn transport into the Golgi apparatus. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Sci Adv, Vol. 9, Issue 9, Page eadd9742, Year 2023 |
| 掲載日 | 2023年3月3日 |
 著者 著者 | Zhenghao Chen / Satoshi Watanabe / Hironori Hashida / Michio Inoue / Yasukazu Daigaku / Masahide Kikkawa / Kenji Inaba /  |
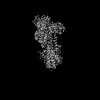
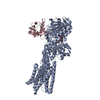
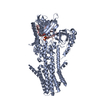
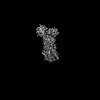
| PubMed 要旨 | Secretory pathway Ca/Mn ATPase 1 (SPCA1) actively transports cytosolic Ca and Mn into the Golgi lumen, playing a crucial role in cellular calcium and manganese homeostasis. Detrimental mutations of ...Secretory pathway Ca/Mn ATPase 1 (SPCA1) actively transports cytosolic Ca and Mn into the Golgi lumen, playing a crucial role in cellular calcium and manganese homeostasis. Detrimental mutations of the gene encoding SPCA1 cause Hailey-Hailey disease. Here, using nanobody/megabody technologies, we determined cryo-electron microscopy structures of human SPCA1a in the ATP and Ca/Mn-bound (E1-ATP) state and the metal-free phosphorylated (E2P) state at 3.1- to 3.3-Å resolutions. The structures revealed that Ca and Mn share the same metal ion-binding pocket with similar but notably different coordination geometries in the transmembrane domain, corresponding to the second Ca-binding site in sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase (SERCA). In the E1-ATP to E2P transition, SPCA1a undergoes similar domain rearrangements to those of SERCA. Meanwhile, SPCA1a shows larger conformational and positional flexibility of the second and sixth transmembrane helices, possibly explaining its wider metal ion specificity. These structural findings illuminate the unique mechanisms of SPCA1a-mediated Ca/Mn transport. |
 リンク リンク |  Sci Adv / Sci Adv /  PubMed:36867705 / PubMed:36867705 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 3.1 - 3.3 Å |
| 構造データ | EMDB-33711, PDB-7yag: EMDB-33712, PDB-7yah: EMDB-33713, PDB-7yai: EMDB-33714, PDB-7yaj: EMDB-33717, PDB-7yam: |
| 化合物 | 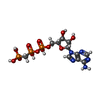 ChemComp-ACP:  ChemComp-CA: 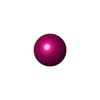 ChemComp-MN:  ChemComp-BEF:  ChemComp-MG: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | TRANSPORT PROTEIN / Golgi Ca2+/Mn2+ transporter |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について







 homo sapiens (ヒト)
homo sapiens (ヒト)
