+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | First exposure to the pandemic H1N1 virus induced broadly neutralizing antibodies targeting hemagglutinin head epitopes. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Sci Transl Med, Vol. 13, Issue 596, Year 2021 |
| 掲載日 | 2021年6月2日 |
 著者 著者 | Jenna J Guthmiller / Julianna Han / Lei Li / Alec W Freyn / Sean T H Liu / Olivia Stovicek / Christopher T Stamper / Haley L Dugan / Micah E Tepora / Henry A Utset / Dalia J Bitar / Natalie J Hamel / Siriruk Changrob / Nai-Ying Zheng / Min Huang / Florian Krammer / Raffael Nachbagauer / Peter Palese / Andrew B Ward / Patrick C Wilson /  |
| PubMed 要旨 | Broadly neutralizing antibodies are critical for protection against both drifted and shifted influenza viruses. Here, we reveal that first exposure to the 2009 pandemic H1N1 influenza virus recalls ...Broadly neutralizing antibodies are critical for protection against both drifted and shifted influenza viruses. Here, we reveal that first exposure to the 2009 pandemic H1N1 influenza virus recalls memory B cells that are specific to the conserved receptor-binding site (RBS) or lateral patch epitopes of the hemagglutinin (HA) head domain. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) generated against these epitopes are broadly neutralizing against H1N1 viruses spanning 40 years of viral evolution and provide potent protection in vivo. Lateral patch-targeting antibodies demonstrated near universal binding to H1 viruses, and RBS-binding antibodies commonly cross-reacted with H3N2 viruses and influenza B viruses. Lateral patch-targeting mAbs were restricted to expressing the variable heavy-chain gene VH3-23 with or without the variable kappa-chain gene VK1-33 and often had a Y-x-R motif within the heavy-chain complementarity determining region 3 to make key contacts with HA. Moreover, lateral patch antibodies that used both VH3-23 and VK1-33 maintained neutralizing capability with recent pH1N1 strains that acquired mutations near the lateral patch. RBS-binding mAbs used a diverse repertoire but targeted the RBS epitope similarly and made extensive contacts with the major antigenic site Sb. Together, our data indicate that RBS- and lateral patch-targeting clones are abundant within the human memory B cell pool, and universal vaccine strategies should aim to drive antibodies against both conserved head and stalk epitopes. |
 リンク リンク |  Sci Transl Med / Sci Transl Med /  PubMed:34078743 / PubMed:34078743 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 3.2 - 25.0 Å |
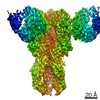
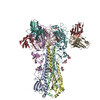
| 構造データ | EMDB-23792, PDB-7mem: 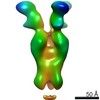 EMDB-23793:  EMDB-23794: 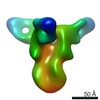 EMDB-23795: 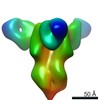 EMDB-23796:  EMDB-23797: 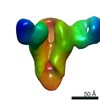 EMDB-23798: |
| 化合物 |  ChemComp-NAG: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード |  Viral protein/IMMUNE SYSTEM (ウイルス性) / Viral protein/IMMUNE SYSTEM (ウイルス性) /  Hemagglutinin (ヘマグルチニン) / Hemagglutinin (ヘマグルチニン) /  monoclonal antibody (モノクローナル抗体) / monoclonal antibody (モノクローナル抗体) /  influenza virus (オルトミクソウイルス科) / influenza virus (オルトミクソウイルス科) /  IMMUNE SYSTEM (免疫系) / IMMUNE SYSTEM (免疫系) /  Viral protein-IMMUNE SYSTEM complex (ウイルス性) Viral protein-IMMUNE SYSTEM complex (ウイルス性) |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について